Porter’s Value Chain: Primary & Support/Secondary Activities Explanation
Table of Content
- What is Michael Porter’s Value Chain?
- Primary Activities of Porter’s Value Chain
- Support Activities of Porter’s Value Chain
- Step By Step Guide to Analyze Value Chain
- What is the Impact of Technology on the Value Chain
- Understanding How Value is Created with Porter’s Value Chain
- Explanation of Value Chain Map and Value Chain Node
- Real World Examples of Porter’s Value Chain
- Potential Future Trends in Value Chain Management
- Other Business Concepts related to Porter’s Value Chain
- How to Derive the Profit Margin using Value Chain Analysis
- FAQs of Porter’s Value Chain
What is Michael Porter’s Value Chain?
Value chain analysis is a business concept that describes all activities essential to deliver products or services from start to end. This concept encompasses steps from raw material sourcing, production to distribution, including sales and after-sales activities. In addition to these activities, the value chain concept also describes various supporting activities, including strategic planning, quality management, finances, recruitment, technology, and procurement.
This framework helps companies analyze their internal activities to understand how they can create value for customers and gain a competitive advantage. The concept was introduced by Michael Porter in his book “Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance”. Following are the Primary Activities and Secondary Activities of Porter’s Value Chain,
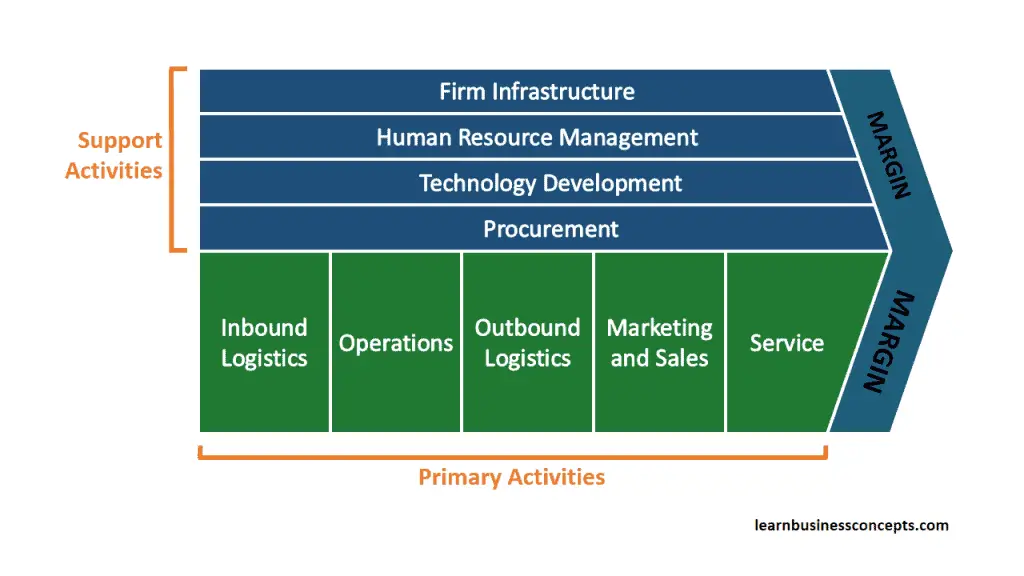
Primary Activities
- Inbound Logistics
- Operations
- Outbound Logistics
- Marketing and Sales
- Service
Secondary / Support Activities
- Procurement
- Technology Development
- Human Resource Management
- Firm Infrastructure
Primary Activities of Porter’s Value Chain

1. Inbound Logistics
This activity involves the processes of receiving, storing, and distributing inputs or raw materials required for the production process. Simply the resources required are obtained through inbound logistics. Production-oriented companies rely on inbound logistics to receive the raw materials.
The reception, storage, and distribution of raw materials are mainly included in this activity. Efficient inbound logistics is a critical activity for a business to help reduce costs, minimize inventory levels, and ensure timely availability of materials for production.
Examples: track raw material input, storage, control inventory, transport schedules, warehousing, and return damaged goods to suppliers.
2. Operations
This activity refers to the tasks involved in transforming inputs into finished products or services. This typically includes manufacturing processes, assembly, packaging, and quality control measures. There will be various streams of value are added to the product at this stage as it moves through the production line.
Efficiency and effectiveness in operations are crucial for maintaining product quality, reducing production costs, and meeting customer demands.
Examples: production belts, production process, packaging, machinery maintenance, quality assurance, defects testing, printing, and all operations of the factory.
3. Outbound Logistics
Outbound logistics is the process of storing and distributing finished products to customers. Typical tasks of outbound logistics are order processing, warehousing, transportation, and delivery to end-users.
For a manufacturing company, their immediate customer would be the wholesaler. The end customer may receive the product through the distribution channels of wholesalers and retailers. The distribution of finished goods from the manufacturer to their immediate customer is considered outbound logistics.
Effective outbound logistics ensure timely delivery, accurate order fulfillment, and customer satisfaction.
Examples: finished goods distribution, vehicle schedule handling, delivery order handling, sales order processing, and process the sales returns.
4. Marketing and Sales
Every product has a target market of potential consumers. Marketing and sales activities pretty much focused on promoting and selling products or services to customers. This is determined by how well the company presented and sold the product to the target market. The job of the sales professionals in the company is to ensure the target audience is aware of the product. A mix of marketing strategies can be used to fulfill this activity.
This activity usually includes market research, advertising, branding, pricing strategies, sales force management, and customer relationship management. The goal of marketing & sales is to attract customers, create demand, and generate sales revenue.
Examples: brand building, marketing, promotion, salesforce, tenders, quotations, target market selection, customer relationships, and product pricing.
5. Services
Service activities involve providing support and assistance to customers after the sale. This includes customer support, technical assistance, warranty services, maintenance, and repairs.
After-sales support is crucial for the long term survival of the business. Negative customer comments can easily damage the reputation of a product. The company should focus on the right processes to take care of the customer inquiries which raise after the sale. Solid after-sales services are essential to enhance or maintain the value of the product after it has been sold and delivered.
Examples: repair, periodic scheduled maintenance services, warranty, guarantee, training, and after-sale services.
Primary activities of value chain are interconnected and collectively contribute to the creation of value for customers. Companies can improve overall performance, reduce costs, enhance product quality, and gain a competitive advantage in the market by analyzing and optimizing each stage of the value chain,.
Support Activities of Porter’s Value Chain
1. Procurement
Procurement refers to the entire purchasing-related process of the company. Procurement covers the process of acquiring inputs such as raw materials, components, equipment, and services from suppliers. This also further covers raw materials, equipment for technology development, equipment related to periodic maintenance, administrative consumables, and fixed assets such as machinery and buildings. The objective of this activity is to find quality supplies that meet the criteria of procurement.
An efficient procurement practices will help companies to reduce costs, ensure the quality and reliability of inputs, and mitigate supply chain risks.
Examples: Tendering processes, advertising, procurement criteria definition, offer the contract/purchase order, and budget management.
2. Technology Development
This activity is related to the capacity for activities like research and development (R&D), design, engineering, prototyping, and testing of new technologies or products in the company. Technology helps to streamline the entire value chain. This will increase the efficiency of activities, which will lead to a competitive advantage. These activities are related to the effort that the company is making to improve its products and processes.
Investing in technology development can lead to product differentiation, improved efficiency, and competitive advantage.
Examples: enterprise resource planning (ERP) solutions, product research for enhancements, research for new products, and improving the technology used in existing activities/processes.
3. Human Resource Management
To survive in the market, the company needs talented and skillful employees. Recruitment, training, and development of the right people for the right job roles are part of this activity. This further includes workforce planning, talent acquisition, performance management, training and development programs, compensation, and employee relations.
Staff satisfaction should be measured regularly to reduce turnover. Also, staff should be motivated based on fringe benefits and other facilities. The company finds and retains the highest level of talent at the firm. Technological and consulting companies depend heavily on their talented employees.
Effective HRM practices contributes highly to the employee satisfaction, productivity, and organizational performance.
Examples: recruitment, onboarding, development, training, retention programs, and off-boarding.
4. Firm Infrastructure
Firm infrastructure refers to activities that support the entire value chain, including general management, finance, accounting, legal, and administrative functions. This further relates to the organizational structure, internal control systems, and culture of the company. This is also related to activities such as accounting, finance, legal, control, audit, quality management, and general (strategic) management.
This is the place where business decisions are made like strategic planning, financial management, budgeting, legal compliance, and organizational governance. The effectiveness of these decisions is based on the capacity of the activities of the firm infrastructure. These are the most powerful source of competitive advantage for the company.
A strong and efficient infrastructure provides the foundation for the effective operation of the value chain and overall business success.
Examples: strategic management, finance, legal, customer relationships, public relations, and quality control.
Step By Step Guide to Analyze Value Chain
1. Understand the Concept
Familiarize yourself with the basic concept of Porter’s Value Chain and its components, including primary activities and secondary activities.
2. Identify Your Organization’s Value Chain
Map out the activities involved in your organization’s value chain, from sourcing raw materials to delivering the final product or service to customers.
3. Break Down Primary Activities:
In this step, the each primary activity should be analyzed in detail,
- Inbound Logistics: Assess how efficiently raw materials are sourced, transported, and stored.
- Operations: Evaluate the effectiveness of manufacturing or service delivery processes.
- Outbound Logistics: Examine the efficiency of product distribution and delivery to customers.
- Marketing and Sales: Review strategies for promoting products or services and generating sales.
- Service: Assess the quality and effectiveness of post-sale customer support and service.
5. Evaluate Secondary Activities
Analyze each secondary activity. You should have a good understand how they support primary activities,
- Procurement: Evaluate supplier relationships, cost-effectiveness of procurement processes, and supply chain resilience.
- Technology Development: Assess investments in research, development, and technology to improve product quality and operational efficiency.
- Human Resource Management: Evaluate workforce capabilities, training programs, and employee satisfaction levels.
- Firm Infrastructure: Examine organizational structure, leadership, and support functions such as finance, legal, and IT.
6. Identify Strengths and Weaknesses
Identify areas where your organization excels (strengths) and areas that need improvement (weaknesses) within each activity of the value chain.
7. Benchmark Against Competitors
Compare your organization’s value chain activities and performance against competitors to identify areas where you lag behind or outperform.
8. Prioritize Opportunities for Improvement
Prioritize areas for improvement based on their potential impact on value creation, cost reduction, or competitive advantage.
9. Develop Strategies
Develop strategies to address weaknesses and capitalize on strengths identified through the analysis. Make sure to consider ways to optimize processes, improve resource allocation, enhance employee skills, or leverage technology. Also you have to align strategies with overarching business objectives and market dynamics.
10. Implement Changes
Implement changes and improvements identified through the analysis, ensuring buy-in from relevant stakeholders and allocating necessary resources.
11. Monitor and Review
Continuously monitor and review value chain performance, tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) and adjusting strategies as needed to adapt to changing market conditions or internal dynamics.
What is the Impact of Technology on the Value Chain
The impact of technology on the value chain has been transformative, revolutionizing the way businesses operate, create value, and compete in the marketplace. Here are some key ways in which technology has influenced the value chain,
1. Automation and Efficiency
Technology has enabled automation of repetitive tasks and processes across the value chain, leading to improved efficiency and reduced operational costs. Automated systems in areas such as manufacturing, logistics, and customer service streamline operations and minimize human error.
2. Data Analytics and Insights
Advanced analytics tools allow businesses to gather, analyze, and derive insights from vast amounts of data generated at various stages of the value chain. By harnessing data analytics, companies can optimize processes, identify trends, forecast demand, and make data-driven decisions to enhance performance and competitiveness.
3. Supply Chain Optimization
Technology facilitates real-time visibility and connectivity within supply chains, enabling companies to track inventory levels, monitor supplier performance, and manage logistics more effectively. Supply chain management software, IoT devices, and blockchain technology enhance transparency, traceability, and collaboration among supply chain partners.
4. Product Innovation and Customization
Technology accelerates the pace of innovation and enables companies to develop and introduce new products or services more rapidly. Digital design tools, simulation software, and 3D printing allow for rapid prototyping and customization, empowering businesses to meet diverse customer needs and preferences.
5. E-commerce and Digital Marketing
The rise of e-commerce platforms and digital marketing channels has transformed how companies reach and engage customers. Online storefronts, social media platforms, and targeted advertising enable businesses to connect with consumers directly, personalize marketing efforts, and expand market reach beyond traditional boundaries.
6. Enhanced Customer Experience
Technology has revolutionized the way companies interact with customers and deliver value-added services. Customer relationship management (CRM) systems, chatbots, and AI-powered assistants enable personalized communication, efficient problem-solving, and seamless customer experiences across multiple touchpoints.
7. Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Technology plays a crucial role in driving sustainability initiatives and reducing the environmental footprint of value chain activities. Renewable energy solutions, IoT sensors for resource monitoring, and eco-friendly materials enable companies to optimize resource utilization, minimize waste, and mitigate environmental risks.
8. Globalization and Market Expansion
Digital technologies facilitate global connectivity and enable businesses to expand their reach into new markets. E-commerce platforms, online marketplaces, and digital payment systems facilitate cross-border transactions, opening up opportunities for international trade and market expansion.
Technology has a major impacted the value chain by driving automation, data-driven decision-making, supply chain optimization, innovation, customer engagement, sustainability, and globalization. Leveraging technology effectively is essential for businesses to remain competitive and resilient in an increasingly digital and interconnected world.
Explanation of Value Chain Map and Value Chain Node
1. Value Chain Map
A value chain map is a graphical representation or visualization of the various activities involved in the production of goods or services within an organization or across an industry. It illustrates the sequence of activities required to deliver a product or service to the end customer, from raw material sourcing to distribution and after-sales service.
Value chain maps typically consist of a series of interconnected nodes or steps, each representing a specific activity or process in the value chain. These activities can include procurement, manufacturing, marketing, sales, logistics, and customer service.
Value chain mapping helps organizations understand the flow of value creation, identify inefficiencies, pinpoint areas for improvement, and assess competitive positioning relative to other players in the industry.
2. Value Chain Node
A value chain node refers to each discrete activity or process depicted in a value chain map. Each node represents a stage or step in the value creation process, where value is added to the product or service.
Analyzing value chain nodes involves assessing their efficiency, cost-effectiveness, quality, and contribution to overall value creation. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each node, organizations can develop strategies to optimize their value chains, reduce costs, and enhance competitiveness.
Examples of value chain nodes include raw material sourcing, manufacturing, assembly, packaging, distribution, marketing, sales, customer support, and product maintenance.
As a conclusion: a value chain map provides a visual representation of the entire value creation process, while value chain nodes represent the individual activities or stages within that process. Together, they form a framework for analyzing and improving the efficiency and effectiveness of an organization’s value chain.
Understanding How Value is Created with Porter’s Value Chain
A value chain analysis is an internal assessment aimed at gaining a competitive advantage. The idea is to determine the internal links between activities in the company and to increase efficiency in each activity. Customer satisfaction is determined based on the value of the products or services.
Real World Examples of Porter’s Value Chain
Porter’s value chain is a framework that helps businesses analyze specific activities within their organization to identify sources of competitive advantage. Here are some practical real-world examples of Porter’s value chain in action:
Manufacturing Industry
- Toyota Production System (TPS): Toyota revolutionized the automotive industry with its lean manufacturing principles, which are a key aspect of its value chain. By continuously improving processes, minimizing waste, and empowering employees to contribute ideas for efficiency gains, Toyota has achieved high levels of productivity and quality while reducing costs.
Retail Industry
- Walmart: Walmart is known for its efficient supply chain management, which is a critical component of its value chain. Through technologies like RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) and a sophisticated inventory management system, Walmart optimizes its inventory levels, reduces stockouts, and minimizes holding costs. Additionally, its strong vendor relationships enable it to negotiate favorable terms and maintain low prices for customers.
Technology Industry
- Apple Inc.: Apple’s value chain is characterized by its tight control over design, manufacturing, and distribution. By vertically integrating key aspects of its supply chain, such as chip design, hardware assembly, and software development, Apple maintains a high level of quality and innovation while differentiating its products in the competitive tech market. Additionally, its retail stores and online presence contribute to a seamless customer experience.
Service Industry
- McDonald’s: McDonald’s excels in its service delivery through efficient operations management, a crucial aspect of its value chain. From standardized processes in food preparation to streamlined order fulfillment and customer service, McDonald’s focuses on speed, consistency, and customer satisfaction across its global network of restaurants.
Healthcare Industry
- Mayo Clinic: Mayo Clinic’s value chain is centered around patient-centric care and clinical excellence. By integrating medical services, research, and education, Mayo Clinic delivers high-quality healthcare outcomes while maintaining operational efficiency. Its collaborative approach among physicians, researchers, and administrators ensures a seamless patient experience and continuous improvement in healthcare delivery.
Potential Future Trends in Value Chain Management
Value chain management is constantly evolving due to technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, globalization, and sustainability concerns. Here are some potential future trends in value chain management,
1. Digitalization and Automation: Increasing adoption of digital technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain for streamlining processes, enhancing visibility, and improving decision-making across the value chain.
2. Data Analytics for Insights: Utilizing big data analytics to gain actionable insights into customer behavior, market trends, supply chain risks, and operational efficiencies. Predictive analytics can help in demand forecasting and inventory optimization.
3. Supply Chain Transparency and Traceability: Growing emphasis on transparency and traceability throughout the value chain to meet regulatory requirements, ensure product quality, and address consumer concerns regarding sustainability, ethical sourcing, and social responsibility.
4. Circular Economy Practices: Embracing circular economy principles to minimize waste, maximize resource efficiency, and promote product reuse, recycling, and remanufacturing. Companies may implement strategies like product-as-a-service, closed-loop supply chains, and eco-design.
5. Resilience and Risk Management: Building resilient supply chains capable of adapting to disruptions such as natural disasters, geopolitical conflicts, pandemics, and trade disputes. This involves diversifying sourcing, enhancing supplier collaboration, and implementing contingency plans.
6. Sustainable and Ethical Sourcing: Increasing focus on sustainable procurement practices, including sourcing raw materials from environmentally responsible suppliers, reducing carbon footprint, and ensuring fair labor practices throughout the supply chain.
7. Collaborative Networks and Ecosystems: Formation of collaborative ecosystems involving suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, logistics providers, and customers to drive innovation, reduce costs, and create shared value through mutual cooperation.
8. Customer-Centric Supply Chains: Shifting towards customer-centric supply chains that prioritize personalized products, faster delivery options, seamless omnichannel experiences, and enhanced after-sales support to meet evolving customer expectations.
9. Reshoring and Nearshoring: Reassessing global sourcing strategies and considering reshoring or nearshoring manufacturing operations to mitigate geopolitical risks, reduce transportation costs, and improve supply chain agility.
10. Dynamic Supply Chain Orchestration: Implementing agile and responsive supply chain orchestration capabilities enabled by real-time data, advanced analytics, and automation to dynamically adjust production, inventory, and distribution in response to changing market conditions and customer demands.
These trends are likely to shape the future landscape of value chain management, driving innovation, efficiency, sustainability, and resilience across industries.
Other Business Concepts related to Porter’s Value Chain
1. Balanced Scorecard
The Balanced Scorecard is a strategic performance management tool that measures organizational performance across four perspectives like financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth.
The Balanced Scorecard provides a broader framework for evaluating overall organizational performance from multiple perspectives. On other hand, Porter’s Value Chain focuses on analyzing and optimizing specific activities within the value chain
Porter’s Value Chain is more operational and focused on internal processes, while the Balanced Scorecard is strategic and considers both internal and external factors affecting performance.
2. Lean Management
Lean Management is a methodology aimed at reducing waste and improving efficiency in business operations.
Lean Management provides specific tools and techniques for streamlining processes and eliminating non-value-added activities. In contrast, Porter’s Value Chain identifies value-creating activities and opportunities for optimization.
Both concepts share the goal of enhancing efficiency, but Lean Management offers more detailed methodologies for achieving efficiency gains within the value chain.
3. Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology focused on reducing defects and variation in processes to improve quality and performance.
Six Sigma provides a systematic approach to quality improvement within specific processes. On other hand, Porter’s Value Chain considers activities across the entire value chain.
How to Derive the Profit Margin using Value Chain Analysis
The margins or profit of a firm are determined by its “effectiveness” in performing the above primary and support activities. The difference between the price the customer is willing to pay for the products and the cost of the activities in the value chain is the profit margin of the company. Hence, the profit margin can be increased in the following ways,
- Reduce the cost of the activities (streamline the primary and support activities)
- Increase the value of the product through technology development
It would be easy for a company to eventually achieve economies of scale by optimizing the entire value chain.
FAQs of Porter’s Value Chain
Q1: What is Porter’s Value Chain framework?
Answer: Porter’s Value Chain is a framework that helps businesses analyze their internal activities to understand how they create value for customers and gain a competitive advantage.
Q2: What are the primary activities in Porter’s Value Chain?
Answer: The primary activities in Porter’s Value Chain include inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and service.
Q3: What are the secondary activities in Porter’s Value Chain?
Answer: The secondary activities in Porter’s Value Chain comprise procurement, technology development, human resource management, and firm infrastructure.
Q4: How does Porter’s Value Chain help businesses gain a competitive advantage?
Answer: Porter’s Value Chain helps businesses gain a competitive advantage by enabling them to identify areas for efficiency improvement, cost reduction, and differentiation within their operations.
Q5: What are some examples of value chain analysis in real-world business scenarios?
Answer: Examples of value chain analysis include identifying cost-saving opportunities in logistics, improving product quality through operations optimization, and enhancing customer service through service activities.
Q6: How can businesses apply Porter’s Value Chain framework to their operations?
Answer: Businesses can apply Porter’s Value Chain framework by systematically evaluating each activity in their value chain to identify opportunities for improvement and strategic alignment.
Q7: What role does technology play in Porter’s Value Chain framework?
Answer: Technology plays a critical role in Porter’s Value Chain framework by enabling automation, data analytics, and process optimization across various activities.
Q8: How does Porter’s Value Chain relate to other strategic management concepts?
Answer: Porter’s Value Chain complements other strategic management concepts such as SWOT analysis, Porter’s Five Forces, and the Resource-Based View by providing insights into internal operational dynamics.
Q9: What are some common challenges companies face when implementing Porter’s Value Chain framework?
Answer: Common challenges include data availability and accuracy, organizational resistance to change, and the need for cross-functional collaboration.
Q10: How can businesses continuously monitor and evaluate their value chain performance?
Answer: Businesses can continuously monitor and evaluate their value chain performance through key performance indicators (KPIs), regular performance reviews, and benchmarking against industry standards.
Read More About Porter’s Five Forces,
- Porter’s Five Forces: Explanation with Industry Examples
- Porter’s Five Forces: Advantages and Disadvantages
- How to Apply Porter’s Five Forces to Industry / Business: Step-By-Step Simple Detail Guide with Examples
- Porter’s Five Forces Model: Applied To Airline Industry with Real World Examples
- Porter’s Five Forces: Applied To Fast Food Restaurants Industry with Real World Examples
- Porter’s Five Forces: Applied To Starbucks with Examples
- Porter’s Five Forces: Applied To Banking Industry with Real World Examples
- Porter’s Five Forces: Applied To Clothing / Fashion Industry with Real World Examples