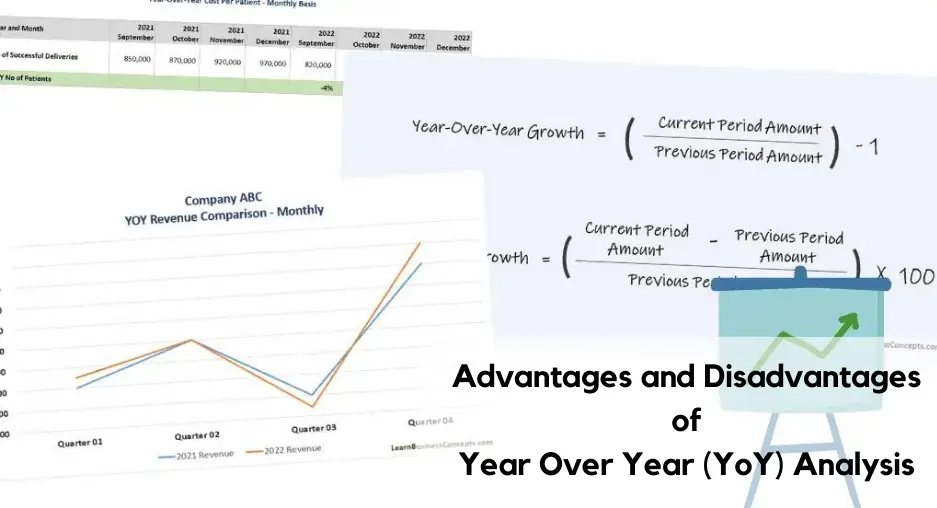
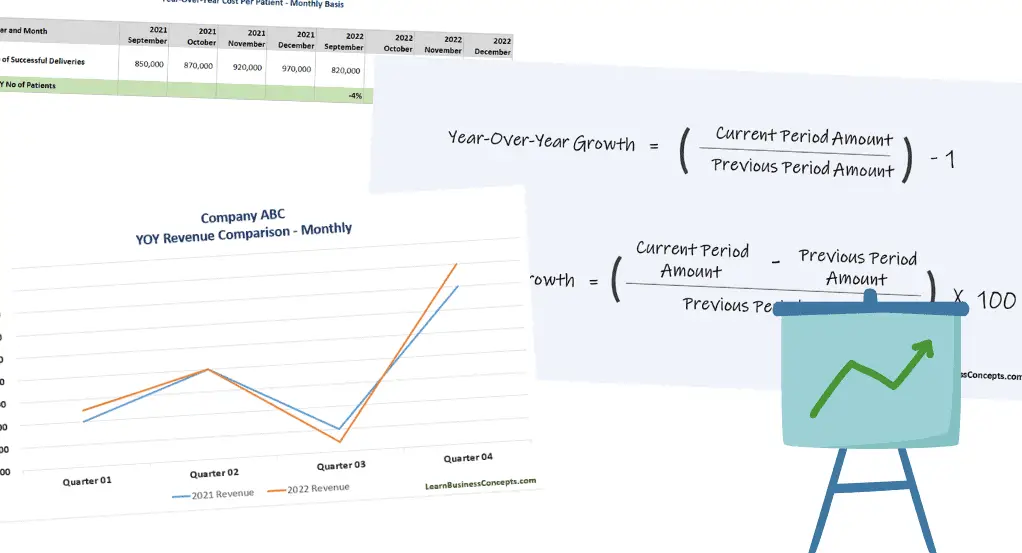
15 Proven Side Hustles for Ladies With Full-Time Jobs (Make Time & Money!)
Feeling stuck in your 9-to-5, yet craving more financial freedom or a creative outlet? You’re not alone. More and more women with full-time jobs are turning to side hustles to earn extra income, build...