Porter’s Five Forces: Explanation with Industry Examples
Table of Content:
- Understanding the Porter’s Five Forces
- Step-by-Step Guide on Analysis using Porter’s Five Forces Framework
- Usage of Porter’s Five Forces
- Pros of Porter’s Five Forces
- Cons of Porter’s Five Forces
- How does New Technological Advancements like Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Digital Advancements Effect Porter’s Five Forces?
- How to Measure the Competition from Porter’s Five Forces
- Competition of Key Industries in the World
- Criticisms of Porter’s Five Forces Model
- Substitute for Porter’s Five Forces
- Relationship between Porter’s Five Forces and Generic Strategies
- Difference of Porter’s Five Forces and SWOT Analysis
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Understanding the Porter’s Five Forces
Porter’s Five Forces is a competitive position analysis tool. This is a simple framework to analyze the competitive strength and competitive position of a company. Company strengths and weaknesses are measured compared to the competitive forces.
Simply, porter’s five forces analysis business concept demonstrates how industry-related forces affect your company’s performance. If the competitive forces are strong then it is unlikely for an industry to be profitable.
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis will help to answer the below questions.
- Why companies in various industries able to sustain a different level of profitability?
- How can a company increase its competitive advantage?
- What are external powers affect the business?
- Understanding the strength of the company in the current competitive position?
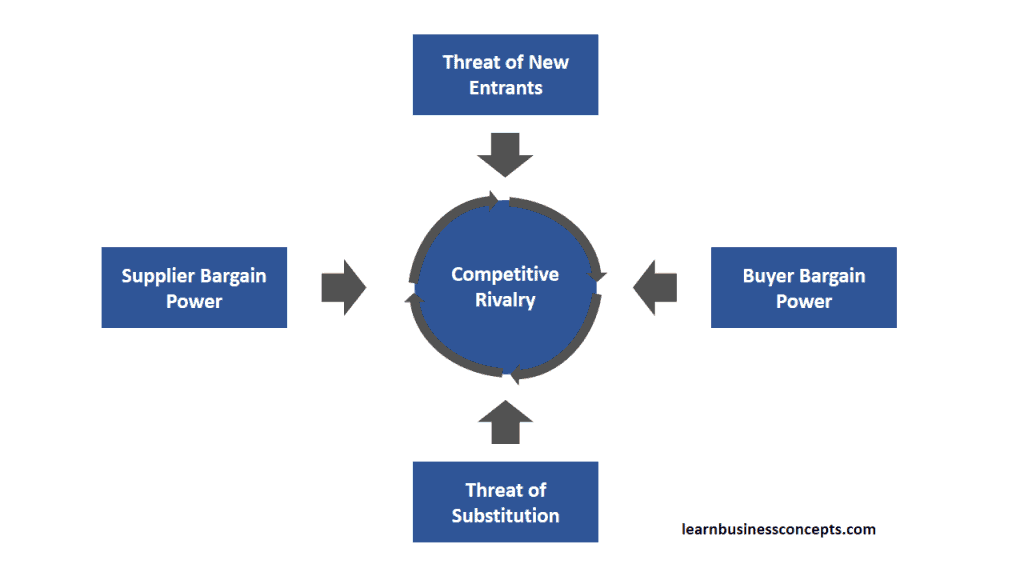
Michael E. Porter identified five forces of the competitive environment. Those are,
- Threat of New Entrants
- Buyer Bargain Power
- Threat of Substitution
- Supplier Bargain Power
- Competitive Rivalries
1. Threat of New Entrants
This force determines the relative easiness to enter a particular industry. The company’s risk of market share dilution depends on this force. The power of this force depends on the difficulty of a new company to offer the same product and enter the industry. This is also called as barriers of entering into the industry,
There are six types of barriers to entry,
- Economies of Scale – When the company grows bigger it will experience cost decreases along with the increase in its level of output.
- Required Capital – Initial investment required to start a company in the industry.
- Regulation Policy – Complexity and level of regulation of the industry.
- Specialized Skill/Patents Required – Some industries required specialized skills and patents to enter into the market.
- Product Differentiation – the level of variants available on the products in the market.
- Access to Distribution Channels – the level of easiness to a partnership with the distribution channels of the industry.
Industry Examples:
- Airline Industry: The airline industry has a high barrier to entry due to the substantial capital investment required for airplanes and airport infrastructure. Also, it is essential to obtain operating licenses from regulatory authorities to open an airline and this is a difficult time consuming activity. – Read More about Porter’s Five Forces Model Applied To Airline Industry with Real World Examples.
- Oil and Gas Industry: It is difficult for a new company to enter into the oil and gas industry because it is hard to achieve economies of scale, require a high level of capital, and complex regulations policy.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: It is difficult for a new company to enter into the Pharmaceutical Industry because of initial capital, patent/specialized skill requirements, and product differentiation.
2. Buyer Bargain Power
This force evaluates the influence customers have on prices, product choices, and terms of sale. Buyers can demand lower prices or higher quality products when buyers have substantial power. Also buyer bargain power depends on easiness for the buyer (customer) to drive the prices down. There are four drives of this power,
- Cost of Switching Suppliers – Customer’s power of bargain will be more if switching cost is less.
- Number of Sellers versus Number of Customers – Customer’s power of bargain will be more if the relative number of customers is less than the suppliers.
- Product Differentiation – Customer’s power of bargain will be more if products are less differentiated.
- The Threat of Forward Integration – Customer’s power of bargain will be more there is less threat of forwarding value chain integration.
Industry Examples:
- Clothing/Fashion Industry: In the clothing industry, suppliers include textile manufacturers, fabric suppliers, and garment factories. The bargaining power of suppliers can vary depending on factors such as the availability of raw materials, manufacturing capacity, and uniqueness of fabrics – Read more about Porter’s Five Forces: Applied To Clothing / Fashion Industry with Real World Examples.
- FMG (Fast Moving Goods) Industry: Customer’s bargain power is high because of the high number of customers, less product differentiation, and less switching cost.
- Aircraft Manufacturing Industry: Customer’s bargain power is low because of less number of suppliers, high product differentiation, less threat of forwarding integration, and high switching cost.
3. Threat of Substitution
Substitutes are alternative products or services that fulfill similar needs. This force determines the likelihood of the product being replaced. Simply, this depends on how much is it easy for the customer to find a similar product in the market. When this thread is high then it will reduce the supplier power and attractiveness of the industry. There are three drivers of this power,
- Cost of switching between products/service – higher the switching cost is better for existing veteran suppliers.
- The uniqueness of the product/service compare to the other similar products – it is harder to replace when the product/service is much unique.
- The number of identical substitutes in the market – supplier power will reduce drastically when this is there are many similar substitutes.
Industry Examples:
- Coffee Industry (Starbucks): Buyer power in the coffee industry varies depending on the location and customer segment. Starbucks caters to a diverse customer base ranging from individual consumers to businesses. However, consumers have a range of alternatives, including other coffeehouses, cafes, convenience stores, and at-home brewing options. Read more about How Porter’s Five Forces Applied To Starbucks with Examples.
- Mobile Device Manufacturing Industry: the threat of substitution is high because the cost of switching is low, the uniqueness of each model becoming low and the number of identical substitutes is high.
- Cruise Ship Manufacturing Industry: the threat of substitution is low because each ship has it’s own uniqueness, identical suppliers being low and the cost of switching is higher.
4. Supplier Bargain Power
Bargain power of suppliers related to how much influence the supplier has to demand the price, quality, and delivery timelines. When suppliers have significant leverage, they can dictate terms to industry players. This directly hit the profit of the buyer because of the high prices on supplies.
As an example if you own a bakery and if there is only one supplier sells flour. In this case, you don’t have any alternative but purchase with the supplier high price. There are four drivers of this power,
- Cost of Switching Suppliers – The demand for the suppliers will become high when the switching cost is high.
- Number of Suppliers versus Number of Customers – Price and the demand will become low when there are more suppliers.
- The threat of Forward Integration – Supplier power will be increase when it is easy to integrate on forwarding value chain integration.
- Size of the main suppliers in the industry – If there are big suppliers in the market then the supplier power will increase.
Industry Examples:
- Banking Industry: In the banking industry, suppliers primarily mean the providers of funds, such as depositors and institutional investors. Individual depositors have limited power as a supply of funds. But institutional investors have a greater influence when banks require significant capital or funding. Read more about How Porter’s Five Forces Applied To Banking Industry with Real World Examples.
- Defense Products Manufacturing Industry: Supplier bargain power is high because there is less number of suppliers who are qualified in this industry. Those suppliers are big companies, comparatively lesser than customers, and have high switching costs.
- FMG (Fast Moving Goods) Industry: Supplier bargain power is very low because there are many customers compared with suppliers. The cost of switching suppliers is very low and very easy.
5. Competitive Rivalries
The competitive rivalry of Porter’s Five Forces Analysis is related to how intense the competition of the industry as a whole. This force depends on all four previous forces. Market attractiveness reduces when competitors offer undifferentiated products/services. The company should be aware of its competitors to ensure its market share.
High competition results in higher operational and administrative expenses, which results in the profitability of all companies in the industry low. All industries are not similar. Some industries have competition compared with others.
There are four drivers of this power,
- The number of Direct Competitors – Competitive rivalry increases when there is more direct competition.
- Entry Barriers – Competitive rivalry decreases when there is a higher level of entry barriers.
- Industry Growth Rate – Competitive rivalry increases when the industry growth rate is lower. In this case, all companies will try to get the market share from someone else.
- Customer Loyalty – Competitive rivalry decreases when customer loyalty is high.
Industry Examples:
- Fast Food Industry: The fast food industry is characterized by intense competition. There are numerous well-established global brands, regional chains, and independent local fast food restaurants. Competitive factors include pricing strategies, menu variety, brand recognition, customer service, and location. Read more about How Porter’s Five Forces: Applied To Fast Food Restaurants Industry with Real World Examples.
- Telecommunications Industry (Mobile Carriers): Rivalry among companies is comparatively low because of high entry barriers, high industry growth rate, and customer loyalty.
- Hotel Industry: Rivalry among companies is comparatively high because of low entry barriers, a high number of direct competitors, and fewer return customers.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Conduct Analysis using Porter’s Five Forces Framework
Step 01 – Identify the Industry
You have to define the industry or market you want to analyze. Clearly delineate the boundaries of the industry and understand its scope, including relevant products, services, and players.
Step 02 – Evaluate the Threat of New Entrants
Identify barriers to entry such as economies of scale, brand loyalty, capital requirements, and regulatory barriers. Then assess the likelihood of new competitors entering the market and the potential impact on industry profitability. You should consider factors that may deter or facilitate new entrants, such as proprietary technology, distribution channels, and government regulations.
Step 03 – Assess the Bargaining Power of Suppliers
Identify key suppliers within the industry and assess their bargaining power. Then evaluate factors such as supplier concentration, availability of substitutes, and switching costs. Also make sure to analyze the importance of suppliers’ inputs to the industry and the degree of differentiation among suppliers.
Step 04 – Analyze the Bargaining Power of Buyers
Identify key buyers or customers within the industry and assess their bargaining power. Do not forget to consider factors such as buyer concentration, volume of purchases, and availability of alternative suppliers. Also you need to evaluate the importance of the industry’s products or services to buyers and their ability to switch to alternatives.
Step 05 – Evaluate the Threat of Substitute Products or Services
Identify potential substitute products or services that fulfill similar needs or offer comparable benefits. Also assess factors such as price-performance trade-offs, switching costs, and brand loyalty. Make sure to analyze the availability and attractiveness of substitutes and their potential impact on industry profitability.
Step 06 – Assess Rivalry Among Existing Competitors
Identify key competitors within the industry and assess the intensity of rivalry. Also consider factors such as industry growth rate, concentration of competitors, and level of differentiation. Then evaluate competitive strategies, pricing dynamics, and barriers to exit.
Step 07 – Summarize Findings and Implications
Summarize the findings from each of the five forces to understand the overall competitive landscape of the industry. You have to identify key drivers of industry profitability and strategic implications for businesses operating within the industry. Make sure to consider potential opportunities and threats, as well as strategies for differentiation, competitive advantage, and sustainable profitability.
Usage of Porter’s Five Forces
Porter’s Five Forces framework offers valuable insights and serves various purposes for businesses across industries. Following are some main usages of Porter’s Five Forces.
1. Provides structured approach to analyze industry competitive dynamics
This method provides a structured approach to analyzing the competitive dynamics of an industry. This helps businesses understand the forces that shape competition and influence profitability. Businesses can gain a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape and identify strategic opportunities and threats by systematically evaluating the five forces. This analysis informs strategic decision-making processes, such as market entry strategies, pricing decisions, resource allocation, and competitive positioning.
2. Aids businesses in analyzing industry attractiveness and profitability
Porter’s Five Forces framework aids businesses in assessing industry attractiveness and profitability. Companies can determine the overall attractiveness of an industry in terms of potential profitability and growth prospects by examining the intensity of competitive forces. Industries with high barriers to entry, strong supplier and buyer bargaining power, low threat of substitutes, and moderate rivalry are generally more attractive in terms of profitability. Conversely, industries characterized by intense competition, low barriers to entry, and high bargaining power of buyers and suppliers may present challenges for profitability. This understanding helps businesses prioritize investments, allocate resources effectively, and identify industries with the greatest growth potential.
3. Facilitates competitive strategy development
Porter’s Five Forces analysis facilitates competitive strategy development by guiding businesses in identifying sources of competitive advantage and formulating strategies to achieve sustainable differentiation and superior performance. Businesses can develop strategies to strengthen their competitive position, mitigate threats, and capitalize on opportunities by understanding the underlying drivers of competitive forces. As an example, businesses may focus on building strong supplier relationships, enhancing product differentiation, investing in technology and innovation, or leveraging economies of scale to gain a competitive edge. This strategic alignment enables businesses to navigate industry dynamics effectively and create value for customers while achieving long-term profitability and success.
The usages of Porter’s Five Forces framework are manifold and encompass strategic analysis, industry assessment, and competitive strategy development. Companies can gain insights into industry dynamics, identify strategic opportunities and threats, and formulate effective strategies to achieve competitive advantage and sustainable growth in dynamic and competitive markets by systematically evaluating competitive forces.
Pros of Porter’s Five Forces
1. Helps to Estimate the Competition in the Industry
Porter’s five forces help to measure the threat of new entrants, the threat of substitution, supplier bargaining power, and buyer bargaining power. All of these will sum up to provide the competitive rivalry of the industry. This will support the company to understand the current competition of the industry to adjust the corporate strategy accordingly.
2. Showcase where the Strengths and Threats Exist
Porter’s five forces provide the output of understanding the supplier and buyer forces with risk of new entrants and substitute products. This will enable the senior management to find out where does the company’s strengths place in and where does the threat exist. Management will be able to take precautionary actions for the threats while enhancing the strengths more.
3. Identify which Entities Holding the Power
There are three entities to which Porter’s Five Forces are related. Those are suppliers, buyers (consumers), and competitors. This analysis will provide insights into which are entities hold more power and less power. This will enable the companies to make decisions on the best strategies to handle these entities.
4. Display Opportunities to Expand the Business
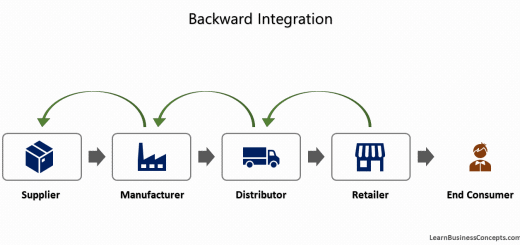
Porter’s five forces provide the power of suppliers and buyers in the industry. This will help the company to make decisions on whether to proceed with verticle integration to acquire suppliers and buyers to reduce their power and expand the business. Simply the business can conduct the forward integration to acquire their consumer side of the value chain, and/or backward integration to acquire their supplier side of the value chain, according to the information provided from the five forces.
5. Assist to Understand the Corporate Risk
Porter’s five forces will provide valuable insights into the power of suppliers, power of consumers, and power of competitors. All of this information will help the company to understand the corporate risk of the business, and make responses to those risks.
6. Helpful in Making Corporate Strategy and Vision
The corporate strategy helps the company to make strategic decisions by looking across all aspects of the business to determine how best possible to create the most value. Porter’s five forces will provide valuable information for this to make the corporate strategy more accurate by considering the impact of the external forces.
Cons of Porter’s Five Forces
1. Limitation on the Composition
Porter’s five forces only concentrate on the power of suppliers, power of consumers, substitution, and new competition. But other technological factors and business strategies that impact the company are not considered. As an example, technological evolvement is one of the biggest threats for all companies across all industries. Also, external forces such as government policies, taxation policies, cross-border business risk, environmental impact, etc are not considered. This can be a major aspect of the growth or else the downfall of the company.
2. Unavailability of Quantitative Dimensions
There is no built-in method to conduct the quantitative analysis of the external factors. This tool does not provide a quantitative idea of the depth and impact of the five forces described. Also, there is no quantitative idea of which forces out of the five are most important and least important.
3. Impractical to use on Large Companies
Practically it is difficult to use this analytical framework for a company that has a large product portfolio and operates in different market segments. This framework is meant to analyze a company in a single industry.
4. Can Be Used as Starting Point for the Analysis
Porter’s five forces is a simple tool that contains five external factors which can be beneficial or else drawback for a company. This can be used only as a tool for the starting point of a deep investigation. This framework provides the initial understanding of the company’s competitive position in an industry. This framework can not alone provide an in-detail investigation of the company.
5. Not Applicable for All Industries Universally
Porter’s five forces practically can not be used for some industries. As an example, not-for-profit companies can not use this method for the analysis. Also, companies conducting activities like R&D will not have much benefit from this.
6. Not Consider Business Risk Factors
External business risk factors like foreign exchange instabilities, natural catastrophes, methods of financing, legal constraints, fast technological evolutions, fluctuations in interest rates, etc not considered for this framework. These are major factors in determining the business risk of the company.
How does New Technological Advancements like Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Digital Advancements Effect Porter’s Five Forces?
New technological advancements such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Digital Advancements have a significant impact on Porter’s Five Forces framework, altering industry dynamics and reshaping competitive landscapes in many ways as following,
1. Threat of New Entrants:
Technological advancements can lower barriers to entry by reducing startup costs and enabling disruptive business models. For example, AI and ML algorithms allow startups to enter industries traditionally dominated by incumbents by offering innovative solutions and services without the need for extensive physical infrastructure or resources.
2. Bargaining Power of Suppliers:
Technology empowers suppliers with new capabilities and avenues to reach customers directly. This helps on potentially increasing their bargaining power. For instance, digital platforms enable suppliers to bypass traditional distribution channels and establish direct relationships with consumers, giving them more leverage in negotiations with industry players.
3. Bargaining Power of Buyers:
Digital advancements provide buyers with increased access to information, transparency, and choices, enhancing their bargaining power. AI-powered recommendation systems and price comparison tools enable consumers to make more informed purchasing decisions, putting pressure on businesses to offer competitive prices and value-added services to attract and retain customers.
4. Threat of Substitute Products or Services:
Technological innovations lead to the emergence of new substitute products or services that offer comparable or superior benefits. For example, advancements in digital healthcare technologies enable remote consultations, tele-medicine, and wearable health monitoring devices, posing a threat to traditional healthcare services and providers.
5. Rivalry Among Existing Competitors:
Technological advancements intensify competition among existing competitors by enabling them to innovate, differentiate, and deliver value to customers more effectively. As an example, AI and ML algorithms enhance data analysis, predictive modeling, and personalization capabilities, enabling companies to offer tailored products, services, and customer experiences that differentiate them from competitors.
How to Measure the Competition from Porter’s Five Forces
Porter’s Five Forces involves assessing the intensity of competitive forces within an industry. Companies uses the five forces to gauge the level of competition by evaluating factors such as the threat of new entrants, bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, threat of substitutes, and rivalry among existing competitors. This assessment allows businesses to identify areas of strength and weakness, understand the overall competitiveness of the industry, and develop strategies to enhance their competitive position. Also quantitative metrics such as market share, pricing dynamics, and profitability ratios can complement qualitative analysis to provide a more comprehensive understanding of competition within the industry.
Competition of Key Industries in the World
1. Pharmaceutical Industry
The pharmaceutical industry is characterized by intense competition among global pharmaceutical companies. Companies like Pfizer, Novartis, Roche, and Johnson & Johnson has intense competition in this industry. Competition of this industry is driven by factors such as research and development capabilities, patent protection, regulatory compliance, and market access. Companies compete to develop and commercialize innovative drugs, address unmet medical needs, and secure market share in therapeutic areas such as oncology, cardiovascular health, and immunology.
2. Technology Industry
The technology industry is highly competitive, driven by rapid innovation, technological advancements, and the constant introduction of new products and services. Major players such as Apple, Google, Microsoft, and Amazon compete fiercely across various segments, including hardware, software, cloud computing, and digital services. Competition is fueled by factors such as product differentiation, technological leadership, and market share dominance.
3. Fast Food Industry
The fast food industry is highly competitive, with global chains such as McDonald’s, Subway, KFC, Taco-Bell, Dominos, and Burger King competing for market share. Competition is driven by factors such as menu innovation, pricing, marketing campaigns, and customer experience. Companies also compete on factors like convenience, speed of service, and menu customization to attract and retain customers in a crowded market.
4. Automotive Industry
The automotive industry is characterized by intense competition among global manufacturers, including companies like Toyota, Volkswagen, General Motors, BYD, and Tesla. Competition is driven by factors such as product innovation, quality, pricing, and brand reputation. Companies compete for market share in various vehicle categories, including passenger cars, SUVs, electric vehicles, and autonomous vehicles. Also the companies investing heavily in research and development to stay ahead in emerging technologies like electric and self-driving cars.
5. Retail Industry
The retail industry is highly competitive, with both online and brick-and-mortar retailers vying for consumer spending. Examples include Walmart, Amazon, Alibaba, and Target. These companies strongly compete on factors such as pricing, product selection, customer service, and delivery speed. E-commerce giants like Amazon have disrupted traditional retail by offering convenience, competitive pricing, and a wide range of products, intensifying competition in the sector.
Read more about How Porter’s Five Forces Apply to Different Industries,
- Porter’s Five Forces Model: Applied To Airline Industry with Real World Examples
- Porter’s Five Forces: Applied To Fast Food Restaurants Industry with Real World Examples
- Porter’s Five Forces: Applied To Starbucks with Examples
- Porter’s Five Forces: Applied To Banking Industry with Real World Examples
- Porter’s Five Forces: Applied To Clothing / Fashion Industry with Real World Examples
Criticisms of Porter’s Five Forces Model
Porter’s Five Forces framework is much widely used and influential. But it has faced several criticisms over the years. Some of the key criticisms provided below,
1. Simplistic Analysis
Critics argue that Porter’s Five Forces provides a simplified view of industry dynamics and may overlook or oversimplify complex interactions and interdependencies within industries.
2. Static Analysis
The framework is criticized for its static nature, as it assesses industry dynamics at a specific point in time and may not adequately account for changes and dynamics over time, such as technological advancements, regulatory changes, or shifts in consumer preferences.
3. Limited Scope
Some critics argue that Porter’s Five Forces focuses primarily on traditional industry structures and may not be applicable or sufficient for analyzing emerging industries, digital markets, or industries characterized by rapid technological change and disruption.
4. Neglect of Complementary
The framework focuses primarily on competitive forces among existing players within an industry and may neglect the role of complementors (firms that provide complementary products or services that enhance the value of a company’s offerings).
5. Difficulty in Application
Critics contend that applying Porter’s Five Forces requires subjective judgment and may yield different results depending on the perspective of the analyst, leading to potential biases and inconsistencies in the analysis.
6. Inadequate Strategic Guidance
Some argue that Porter’s Five Forces may not provide sufficient strategic guidance or actionable insights for businesses, as it primarily focuses on diagnosing industry conditions rather than prescribing specific strategies for success.
Substitute for Porter’s Five Forces
Porter’s Five Forces is the widely used framework for industry analysis. But there are several alternative models and approaches that businesses can use to assess competitive dynamics and inform strategic decision-making. Here are some substitutes.
1. SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis evaluates a company’s Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. It provides a holistic view of both internal and external factors influencing a business, including market conditions, competitive landscape, and organizational capabilities.
2. PESTLE Analysis
PESTLE analysis examines Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting a business or industry. It helps businesses understand the broader external environment and anticipate changes or challenges that may affect their operations.
3. Value Chain Analysis
Value Chain analysis identifies the primary and support activities involved in creating value for customers. By examining each step in the value chain, businesses can identify opportunities for cost reduction, process improvement, and differentiation.
4. Blue Ocean Strategy
Blue Ocean Strategy focuses on creating uncontested market space by identifying and capitalizing on untapped market opportunities. It encourages businesses to innovate and differentiate their offerings to create new demand and escape from competition.
5. Resource-Based View (RBV)
RBV emphasizes the importance of a firm’s internal resources and capabilities in achieving sustainable competitive advantage. It examines the unique strengths and assets of a company and how they can be leveraged to create value and outperform competitors.
6. Competitor Analysis
Competitor analysis involves evaluating the strengths, weaknesses, strategies, and performance of competitors in the market. It helps businesses understand their competitive positioning and identify areas for differentiation and improvement.
7. Scenario Planning
Scenario Planning involves developing multiple plausible future scenarios based on different assumptions and trends. It helps businesses anticipate and prepare for various future outcomes, enabling more resilient and adaptive strategic decision-making.
8. Industry Life Cycle Analysis
Industry Life Cycle analysis examines the stages of development that industries typically go through, including introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. It helps businesses understand the dynamics of their industry and tailor strategies accordingly.
9. Game Theory
Game Theory analyzes strategic interactions among competing players in a given market or industry. It helps businesses anticipate competitors’ actions, make strategic decisions, and optimize outcomes in competitive situations.
10. Customer Segmentation and Analysis:
Customer Segmentation and Analysis involve identifying and understanding different customer segments within a market. It helps businesses tailor their products, services, and marketing efforts to meet the specific needs and preferences of different customer groups.
Each of these alternatives offers unique perspectives and insights into industry analysis and strategic planning, allowing businesses to adapt their approaches based on their specific needs and circumstances.
Relationship between Porter’s Five Forces and Generic Strategies
Porter’s Five Forces framework and generic strategies are closely related concepts that are both developed by Michael Porter and are widely used in strategic management Porter’s Five Forces framework analyzes the external competitive environment of an industry and generic strategies provide a framework for achieving competitive advantage within that industry.
The relationship between Porter’s Five Forces and generic strategies can be understood as follows:
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
Porter’s Five Forces framework examines the competitive dynamics of an industry by analyzing five key forces: threat of new entrants, bargaining power of suppliers, bargaining power of buyers, threat of substitute products or services, and rivalry among existing competitors. It helps businesses understand the competitive forces at play within their industry and identify strategic opportunities and threats.
Generic Strategies:
Porter proposed three generic strategies that businesses can use to achieve competitive advantage within their industry: cost leadership, differentiation, and focus. These strategies are based on the premise that a business must choose a clear path to competitive advantage and align its activities accordingly.
- Cost Leadership: Cost leadership involves becoming the lowest-cost producer in the industry while maintaining acceptable quality standards. By minimizing production and operational costs, businesses can offer products or services at lower prices than competitors, thereby attracting price-sensitive customers. Cost leadership requires a relentless focus on efficiency, economies of scale, process optimization, and tight cost control throughout the value chain.
- Differentiation: Differentiation strategy focuses on creating unique and distinct products or services that are valued by customers and difficult for competitors to replicate. Businesses using differentiation strategy seek to provide superior value through features, performance, quality, design, brand image, or customer service. Differentiation allows businesses to command premium prices, build customer loyalty, and reduce sensitivity to price competition.
- Focus (or Niche) Strategy: Focus strategy involves targeting a specific market segment or niche with unique needs and preferences. Instead of trying to serve the entire market, businesses using focus strategy concentrate their efforts on serving a narrow customer segment exceptionally well. Focus strategies can take two forms: cost focus, where the business aims to become the lowest-cost producer within its niche, or differentiation focus, where the business aims to differentiate its products or services within its niche.
Conclusion
The relationship between Porter’s Five Forces and generic strategies lies in the strategic insights provided by the Five Forces analysis, which inform the selection and implementation of generic strategies. For example a thorough analysis of Porter’s Five Forces may reveal high barriers to entry and limited supplier bargaining power, suggesting a favorable environment for cost leadership strategies.
Conversely, if there is high rivalry among existing competitors and significant threat of substitutes, a differentiation strategy may be more appropriate to create unique value for customers and differentiate from competitors. Focus strategies may be suitable when there are niche market segments with specific needs that are not well served by existing competitors, as identified through Porter’s Five Forces analysis.
Porter’s Five Forces analysis provides the foundation for understanding industry dynamics, while generic strategies offer a roadmap for achieving competitive advantage within that industry. Businesses can use insights from Porter’s Five Forces analysis to select and implement the most appropriate generic strategy that aligns with their strengths, market conditions, and strategic objectives.
Difference of Porter’s Five Forces and SWOT Analysis
Porter’s Five Forces and SWOT Analysis are both strategic frameworks used to assess business environments, but they focus on different aspects of analysis. Porter’s Five Forces examines the external competitive forces that shape an industry’s attractiveness and profitability, including the threat of new entrants, bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, threat of substitutes, and rivalry among existing competitors. In contrast, SWOT Analysis evaluates both internal strengths and weaknesses, such as organizational capabilities and resources, as well as external opportunities and threats, such as market trends and competitive pressures.
SWOT Analysis provides a more holistic view by considering both internal and external factors impacting a business’s strategic position while Porter’s Five Forces focuses solely on external factors influencing competition within an industry. Lastly, Porter’s Five Forces helps businesses understand industry dynamics and competitive forces, while SWOT Analysis helps identify strategic options and develop actionable strategies based on internal and external factors.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Who created the Porter’s Five Forces?
Porter’s Five Forces framework was developed by Michael E. Porter. He is a renowned economist and professor at Harvard Business School. Porter introduced the concept of Five Forces in his seminal 1979 Harvard Business Review article titled “How Competitive Forces Shape Strategy”. Since then, Porter’s Five Forces has become one of the most widely used and influential frameworks for analyzing industry competitiveness and shaping strategic decision-making in business.
2. What is the purpose of Porter’s Five Forces?
The purpose of Porter’s Five Forces framework is to analyze the competitive dynamics of an industry and understand its attractiveness for profitability. There are five key forces: threat of new entrants, bargaining power of suppliers, bargaining power of buyers, threat of substitute products or services, and rivalry among existing competitors. Businesses can gain insights into the underlying factors shaping industry profitability and competitive intensity. The framework helps businesses identify strategic opportunities, anticipate competitive threats, and formulate effective strategies to enhance their competitive advantage within the industry.
3. Is Porter’s Five Forces relates to Micro-Environment or Macro-Environment?
Porter’s Five Forces framework primarily relates to the micro-environment of a business. It focuses on analyzing the competitive dynamics within a specific industry or market and understanding the factors that directly impact the competitive position and profitability of individual businesses operating within that industry.
4. Is Competitive Advantage of Porter’s Five Forces still valid?
Yes, the concept of competitive advantage, as articulated by Michael Porter, remains valid and highly relevant in the current business contexts as well. Porter’s Five Forces framework is linked to the “competitive advantage”, as it helps businesses understand the sources of competitive pressure within their industries. Competitive advantage refers to the unique strengths and capabilities that enable a business to outperform its competitors and achieve superior performance in the marketplace.
Read More About Porter’s Five Forces,
- Porter’s Value Chain: Primary & Support/Secondary Activities
- Porter’s Five Forces: Advantages and Disadvantages
- How to Apply Porter’s Five Forces to Industry / Business: Step-By-Step Simple Detail Guide with Examples
- Porter’s Five Forces Model: Applied To Airline Industry with Real World Examples
- Porter’s Five Forces: Applied To Fast Food Restaurants Industry with Real World Examples
- Porter’s Five Forces: Applied To Starbucks with Examples
- Porter’s Five Forces: Applied To Banking Industry with Real World Examples
- Porter’s Five Forces: Applied To Clothing / Fashion Industry with Real World Examples