Value Chain: Explanation, Guide, Importance & Real Examples
Table of Contents:
- Overview of Value Chain
- Understanding Value Chain Activities
- Step By Step Guide to Analyze the Value Chain
- Real World Examples of Value Chain
- Importance
- Background and History
- Explanation of Value Chain Map
- Explanation of Value Chain Node
- What is Value Chain Analysis
- Potential Future Trends in Value Chain Management
- Pros / Benefits of Porter’s Value Chain
- Cons / Drawbacks of Porter’s Value Chain
- Difference Between Value Chain and Supply Chain
- Other Business Concepts related to Porter’s Value Chain
- What is Value Stream Management (VSM)
- How to Derive the Profit Margin using Value Chain Analysis
- FAQs of Porter’s Value Chain
Overview of Porter’s Value Chain
The value chain analysis is a business concept that describes all activities essential to deliver products or services from start to end. It consists of a series of interconnected activities that contribute to the production, marketing, delivery, and support of a product or service. The value chain concept also describes various supporting activities that essential throughout these activities, such as strategic planning, quality management, finance, recruitment, technology, and procurement.
As an overview, the value chain divided into primary activities (such as inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and service) and support activities (including procurement, technology development, human resource management, and infrastructure). The value chain illustrates how each activity adds value to the final product.
Businesses can pinpoint areas of strength and weakness, optimize processes, reduce costs, and differentiate themselves from competitors by dissecting the value chain. Moreover, the value chain framework enables organizations to understand the entire scope of their operations, from raw material sourcing to customer service, allowing for strategic decision-making and resource allocation.
Understanding Value Chain Activities
Value chain analysis is a value-based internal assessment to obtain a competitive advantage. The goal is to determine the internal links of the activities in the company and improve efficiency in each activity. Customer satisfaction retains based on the value of the products or services. Successful companies produce products or services which have greater value for their customers than what it cost for production.
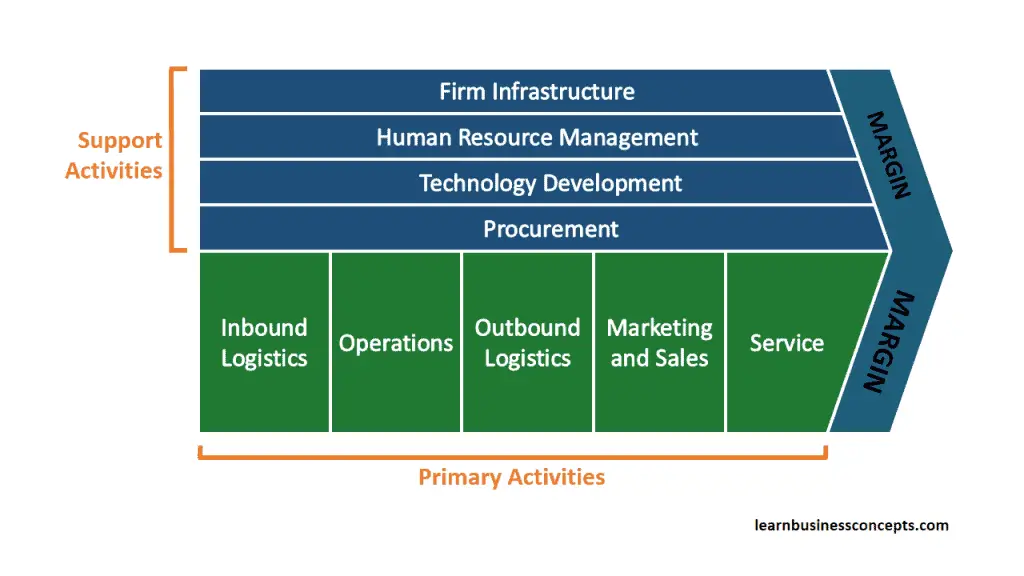
Primary Activities

1. Inbound Logistics
Inbound logistics involves the management of incoming materials, their storage, and their distribution within the company’s operations. This activity includes tasks such as sourcing raw materials, inventory management, and transportation logistics. Typical examples are: raw material input, storage, control inventory, distribution, and return damaged goods to suppliers.
Efficient inbound logistics are crucial as they impact production costs, quality control, and overall operational efficiency. For instance, a manufacturing company receiving raw materials from suppliers must ensure timely delivery and proper storage to prevent disruptions in the production process.
2. Operations
Operations refer to the core activities where raw materials are transformed into finished products or services. This includes manufacturing, assembly, packaging, and any other processes involved in creating the final output. Various streams of value are added to the product at this stage as it moves through the production line.
The importance of efficient operations cannot be overstated, as they directly affect product quality, production speed, and cost-effectiveness. For example, a car manufacturer must optimize its assembly line to minimize production time and maximize output while maintaining quality standards.
Examples: production belts, production process, packaging, machinery maintenance, quality assurance, defects testing, printing, and all operations of the factory.
3. Outbound Logistics
Outbound logistics activity is the management of finished products, including their storage, handling, and distribution to customers. This encompasses activities such as order fulfillment, warehousing, transportation, and delivery.
For a manufacturing company, their immediate customer would be the wholesaler. The end customer may receive the product through the distribution channels of wholesalers and retailers. Distribution of the finished good from the company to their immediate customer is treated as the outbound logistics.
Effective outbound logistics are crucial for ensuring timely delivery, reducing transit costs, and optimizing inventory levels. For instance, a retail company must efficiently manage its distribution network to deliver products to stores or directly to customers’ doorsteps.
Examples: finished goods distribution, vehicle schedule handling, delivery order handling, sales order processing, and process the sales returns.
4. Marketing and Sales
Every product has a target market of potential consumers which known as the “target market”. Marketing and sales activities are focused on promoting, selling, and distributing products or services to target markets. This includes market research, advertising, branding, sales promotions, and pricing strategies. The significance of marketing and sales lies in creating awareness, generating demand, and driving revenue growth. Simply this activity focus on how well the company presented and sold the product to the potential target market.
Duty of the sales professionals in the company to make sure the product awareness is there on the target audience. A mix of marketing strategies can be used to fulfill this activity.
Examples: brand building, marketing, promotion, salesforce, tenders, quotations, target market selection, customer relationships, and product pricing.
5. Services
After-sales support is crucial for the long term survival of the business. Service activities encompass post-sale support and customer assistance, aiming to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. This includes services such as installation, maintenance, repairs, and customer support. Providing excellent service is essential for building long-term relationships with customers and fostering brand loyalty. For example, a software company offers regular updates, technical support, and training to help users maximize the value of its products.
Comments from the unsatisfied customers can easily damage the reputation of the product. The company should focus on the right processes to take care of the customer inquiries which raise after the sales. Solid after-sales services are essential to enhance or maintain the value of the product after it has been sold and delivered.
Examples: repair, periodic scheduled maintenance services, warranty, guarantee, training, and after-sale services.
Support Activities of the Value Chain
1. Procurement
Procurement refers to the process of acquiring goods and services necessary for the operation of the business. This is not only the purchasing inputs or not only related to the raw materials. Procurement activity covers sourcing suppliers, negotiating contracts, and managing vendor relationships. Effective procurement practices are crucial for obtaining high-quality inputs at the best possible prices, thereby impacting the cost structure and competitiveness of the company.
For example, a manufacturing company procuring raw materials from reliable suppliers at competitive rates ensures a steady supply chain and cost-effective production processes.
Further examples are: Tendering processes, advertising, procurement criteria definition, offer the contract/purchase order, and budget management.
2. Technology Development
This activity is related to research and development (R&D), innovation, and technological infrastructure development. Technology helps to streamline the entire value chain. Investing in technology development is essential for staying competitive, improving product quality, and creating new market opportunities.
This will lead to an increase in the efficiency in activities, which leads to a competitive advantage. These activities related to the effort that the company is making to improve the products and the processes. For instance, a software company investing in R&D to develop cutting-edge software solutions gains a competitive edge in the market and satisfies evolving customer needs.
Examples: enterprise resource planning (ERP) solutions, product research for enhancements, research for new products, and improving the technology used in existing activities/processes.
3. Human Resource Management
The company cannot survive in the market without having talented, skilled employees in the organization structure. This activity is related to the recruitment, training, development, and retention of employees within the organization. Further this also includes programs, and implementing performance management systems. Effective human resource management is vital for building a skilled and motivated workforce, fostering innovation, and achieving organizational goals.
Staff satisfaction should be measured in a periodical manner to reduce turnover. Also, staff should be motivated based on fringe benefits and other facilities. The company finds and retains the highest level of talent at the firm. Technological and consulting companies depend heavily on their talented employees.
Examples: recruitment, on-boarding, development, training, retention programs, and off-boarding.
4. Firm Infrastructure
Firm infrastructure encompasses activities that support the entire organization, including strategic planning, finance, accounting, and legal functions. This includes organizational structure, internal control systems, governance, compliance, and the culture of the company. This also related to activities such as accounting, finance, legal, control, audit, quality management, and general (strategic) management. For example, a multinational corporation maintaining robust financial and legal departments ensures transparency, accountability, and compliance with regulatory requirements across its global operations.
This is the place where business decisions made. The effectiveness of these decisions is based on the capacity of the activities of firm infrastructure. These are the most powerful source of competitive advantage for the company.
Examples: strategic management, finance, legal, customer relationship, public relations, and quality control.
Step By Step Guide to Analyze the Value Chain
1. Understand the Concept
Familiarize yourself with the basic concept of Porter’s Value Chain and its components, including primary activities and secondary activities.
2. Identify Your Organization’s Value Chain
Map out the activities involved in your organization’s value chain, from sourcing raw materials to delivering the final product or service to customers.
3. Break Down Primary Activities
In this step, the each primary activity should be analyzed in detail,
- Inbound Logistics: Assess how efficiently raw materials are sourced, transported, and stored.
- Operations: Evaluate the effectiveness of manufacturing or service delivery processes.
- Outbound Logistics: Examine the efficiency of product distribution and delivery to customers.
- Marketing and Sales: Review strategies for promoting products or services and generating sales.
- Service: Assess the quality and effectiveness of post-sale customer support and service.
4. Evaluate Secondary Activities
Analyze each secondary activity. You should have a good understand how they support primary activities,
- Procurement: Evaluate supplier relationships, cost-effectiveness of procurement processes, and supply chain resilience.
- Technology Development: Assess investments in research, development, and technology to improve product quality and operational efficiency.
- Human Resource Management: Evaluate workforce capabilities, training programs, and employee satisfaction levels.
- Firm Infrastructure: Examine organizational structure, leadership, and support functions such as finance, legal, and IT.
5. Identify Strengths and Weaknesses
Identify areas where your organization excels (strengths) and areas that need improvement (weaknesses) within each activity of the value chain.
6. Benchmark Against Competitors
Compare your organization’s value chain activities and performance against competitors to identify areas where you lag behind or outperform.
7. Prioritize Opportunities for Improvement
Prioritize areas for improvement based on their potential impact on value creation, cost reduction, or competitive advantage.
8. Develop Strategies
Develop strategies to address weaknesses and capitalize on strengths identified through the analysis. Make sure to consider ways to optimize processes, improve resource allocation, enhance employee skills, or leverage technology. Also you have to align strategies with overarching business objectives and market dynamics.
9. Implement Changes
Implement changes and improvements identified through the analysis, ensuring buy-in from relevant stakeholders and allocating necessary resources.
10. Monitor and Review
Continuously monitor and review value chain performance, tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) and adjusting strategies as needed to adapt to changing market conditions or internal dynamics.
Real World Examples of Porter’s Value Chain
Porter’s value chain is a framework that helps businesses analyze specific activities within their organization to identify sources of competitive advantage. Here are some practical real-world examples of Porter’s value chain in action:
Manufacturing Industry
- Toyota Production System (TPS): Toyota revolutionized the automotive industry with its lean manufacturing principles, which are a key aspect of its value chain. By continuously improving processes, minimizing waste, and empowering employees to contribute ideas for efficiency gains, Toyota has achieved high levels of productivity and quality while reducing costs.
- Primary Activities
- Inbound Logistics – An automobile manufacturer procuring steel, rubber, plastic, and electronic components from various suppliers worldwide to assemble vehicles.
- Operations – A textile factory weaving cotton fibers into fabric, dyeing it, and then cutting and sewing it into garments.
- Outbound Logistics – A consumer electronics company packaging smartphones after manufacturing and then distributing them through retail stores and online channels.
- Marketing and Sales – A furniture manufacturer conducting market research to identify trends, then branding and advertising their products through digital and print media, and selling them through both their own website and retail partners.
- Service – An industrial equipment manufacturer providing installation services, maintenance contracts, and technical support for their machinery after sale.
- Secondary Activities
- Procurement – An aircraft manufacturer sourcing specialized materials such as titanium alloys and carbon fiber composites from global suppliers for constructing airplane components.
- Technology Development – A pharmaceutical company investing in R&D to develop new drug formulations and manufacturing processes to improve efficacy and reduce production costs.
- Human Resource Management – An electronics manufacturer hiring skilled engineers, technicians, and assembly line workers, and providing them with training programs to enhance their skills and productivity.
- Infrastructure – An energy company building and maintaining a state-of-the-art refinery for processing crude oil into various petroleum products like gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel.
- Firm Infrastructure – An agricultural machinery manufacturer developing strategic plans to expand into emerging markets, managing finances to invest in new production facilities, and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
Retail Industry
- Walmart: Walmart is known for its efficient supply chain management, which is a critical component of its value chain. Through technologies like RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) and a sophisticated inventory management system, Walmart optimizes its inventory levels, reduces stockouts, and minimizes holding costs. Additionally, its strong vendor relationships enable it to negotiate favorable terms and maintain low prices for customers.
- Primary Activities
- Inbound Logistics – A clothing retailer receiving shipments of apparel from manufacturers and distributors at its distribution center.
- Operations – A grocery store stocking shelves, organizing displays, and managing checkout processes to ensure smooth operations and efficient customer service.
- Outbound Logistics – An online retailer packaging customer orders and arranging for shipping through various carriers to deliver products to customers’ doorsteps.
- Marketing and Sales – A department store running advertising campaigns, offering promotions, and hosting sales events to attract customers and drive sales both in-store and online.
- Service – A electronics retailer providing warranty support, technical assistance, and repair services for products purchased by customers.
- Secondary Activities
- Procurement – A home goods retailer sourcing products from manufacturers and wholesalers domestically and internationally to replenish inventory.
- Technology Development – An e-commerce platform investing in website development, mobile apps, and digital marketing tools to enhance the online shopping experience for customers.
- Human Resource Management – A chain of supermarkets hiring and training staff for various roles such as cashiers, stock clerks, and customer service representatives to meet operational needs.
- Infrastructure – A chain of convenience stores investing in building and maintaining physical store locations, including facilities, equipment, and IT systems for inventory management and point-of-sale operations.
- Firm Infrastructure – A luxury retailer developing strategic partnerships with high-end brands, managing financial resources to invest in store renovations and expansions, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements in each location.
Technology Industry
- Apple Inc.: Apple’s value chain is characterized by its tight control over design, manufacturing, and distribution. By vertically integrating key aspects of its supply chain, such as chip design, hardware assembly, and software development, Apple maintains a high level of quality and innovation while differentiating its products in the competitive tech market. Additionally, its retail stores and online presence contribute to a seamless customer experience.
- Primary Activities
- Inbound Logistics – A hardware manufacturer receiving shipments of electronic components such as processors, memory chips, and displays from suppliers to use in assembling computers.
- Operations – A software development company coding, testing, and deploying software applications, such as a new mobile app or enterprise software solution.
- Outbound Logistics – A consumer electronics company packaging smartphones after manufacturing and then distributing them through retail stores and online channels.
- Marketing and Sales – A tech startup running digital marketing campaigns, attending industry conferences, and conducting product demonstrations to attract customers and drive sales of its innovative software product.
- Service – A cloud computing provider offering technical support, system maintenance, and software updates to clients using its platform for hosting applications and data storage.
- Secondary Activities
- Procurement – A semiconductor company sourcing raw materials such as silicon wafers and chemicals for chip fabrication processes from suppliers worldwide.
- Technology Development – A biotechnology firm investing in research and development to discover new drugs, develop advanced medical devices, or improve existing healthcare technologies.
- Human Resource Management – A cybersecurity company hiring skilled engineers, data analysts, and ethical hackers, and providing them with ongoing training to enhance their expertise in cybersecurity solutions and services.
- Infrastructure – A telecommunications company building and maintaining a network infrastructure of towers, cables, and data centers to provide high-speed internet and telecommunications services to customers.
- Firm Infrastructure – A multinational technology corporation developing strategic plans to expand into emerging markets, managing finances to invest in research and development projects, and ensuring compliance with intellectual property laws and regulations.
Service Industry
- McDonald’s: McDonald’s excels in its service delivery through efficient operations management, a crucial aspect of its value chain. From standardized processes in food preparation to streamlined order fulfillment and customer service, McDonald’s focuses on speed, consistency, and customer satisfaction across its global network of restaurants.
- Primary Activities
- Inbound Logistics – A hotel chain receiving deliveries of linens, toiletries, and food supplies from suppliers to ensure smooth operations and guest satisfaction.
- Operations – A healthcare provider offering medical services such as consultations, diagnostic tests, and treatments to patients at its clinics and hospitals.
- Outbound Logistics – A courier service packaging and delivering parcels and documents to customers’ homes and businesses on time.
- Marketing and Sales – A digital marketing agency promoting its services through online advertising, social media campaigns, and content marketing to attract clients and generate leads.
- Service – An IT support company providing technical assistance, troubleshooting, and system maintenance to businesses that subscribe to its managed services.
- Secondary Activities
- Procurement – A catering company sourcing ingredients, kitchen equipment, and packaging materials from suppliers to prepare and deliver meals for corporate events and private functions.
- Technology Development – A software-as-a-service (SaaS) provider investing in research and development to enhance its cloud-based platform for project management and collaboration.
- Human Resource Management – A consulting firm recruiting and training consultants with expertise in various industries and domains to deliver high-quality advisory services to clients.
- Infrastructure – A telecommunications company building and maintaining a network infrastructure of towers, cables, and data centers to provide reliable phone and internet services to residential and business customers.
- Firm Infrastructure – A financial services firm developing strategic plans to expand into new markets, managing finances to invest in technology upgrades and regulatory compliance, and ensuring adherence to industry standards and best practices.
Healthcare Industry
- Mayo Clinic: Mayo Clinic’s value chain is centered around patient-centric care and clinical excellence. By integrating medical services, research, and education, Mayo Clinic delivers high-quality healthcare outcomes while maintaining operational efficiency. Its collaborative approach among physicians, researchers, and administrators ensures a seamless patient experience and continuous improvement in healthcare delivery.
- Primary Activities
- Inbound Logistics – A hospital receiving medical supplies such as medications, surgical equipment, and disposable supplies from pharmaceutical companies and distributors.
- Operations – A medical clinic providing patient care services including consultations, diagnostic tests (like blood tests or X-rays), treatments, and surgeries.
- Outbound Logistics – A pharmacy dispensing prescription medications to patients and managing the delivery of medications to home-bound or elderly patients.
- Marketing and Sales – A healthcare network promoting its services through advertising campaigns, community outreach programs, and physician referrals to attract patients seeking specialized care.
- Service – A home healthcare agency offering skilled nursing care, physical therapy, and personal care services to patients recovering from surgery or managing chronic illnesses in their own homes.
- Secondary Activities
- Procurement – A medical equipment manufacturer sourcing raw materials and components to produce medical devices such as MRI machines, ultrasound equipment, and prosthetic limbs.
- Technology Development – A pharmaceutical company investing in research and development to discover new drugs, vaccines, and treatments for various diseases and medical conditions.
- Human Resource Management – A healthcare staffing agency recruiting and training healthcare professionals such as doctors, nurses, and allied health workers to fill temporary or permanent positions in hospitals and clinics.
- Infrastructure – A healthcare system investing in building and maintaining hospital facilities, medical equipment, and information technology systems to support patient care delivery and administrative functions.
- Firm Infrastructure – A health insurance company developing strategic plans to expand its network of healthcare providers, managing financial resources to cover medical claims and administrative costs, and ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations and standards.
Importance of Porter’s Value Chain
Porter’s Value Chain framework holds significant importance for businesses in several key ways as following,
1. Identifying Value Creation Opportunities – By breaking down the entire business operation into primary and secondary activities, the Value Chain model helps organizations identify specific areas where value is created. This enables businesses to focus their resources and efforts on activities that directly contribute to creating value for customers, thereby enhancing competitiveness and profitability.
2. Cost Analysis and Cost Reduction – The Value Chain model allows businesses to conduct a detailed analysis of costs associated with each activity. By understanding the cost structure of their operations, companies can identify opportunities for cost reduction and efficiency improvements. This could involve streamlining processes, optimizing resource allocation, or outsourcing non-core activities to reduce costs and improve overall profitability.
3. Enhancing Competitive Advantage – Through a thorough analysis of primary and support activities, businesses can identify sources of competitive advantage. By optimizing key activities and differentiating themselves from competitors, organizations can create unique value propositions that resonate with customers. This could involve offering superior product quality, faster delivery times, or better customer service, all of which contribute to building a sustainable competitive advantage.
4. Improving Operational Efficiency – The Value Chain model provides a structured framework for evaluating and improving operational efficiency. By identifying bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement within the value chain, businesses can implement strategies to streamline processes, reduce waste, and enhance productivity. This leads to improved resource utilization, faster cycle times, and ultimately, better overall performance.
5. Supporting Strategic Decision-Making – Understanding the value chain allows businesses to make more informed strategic decisions. By evaluating the impact of different strategies on each activity within the value chain, organizations can assess their potential to create value and drive competitive advantage. This facilitates strategic planning, resource allocation, and investment decisions that are aligned with the organization’s goals and objectives.
Background and History of Value Chain
Porter’s Value Chain was developed by Michael E. Porter, a renowned economist and professor at Harvard Business School. Porter introduced the concept in his 1985 book titled “Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance.” The Value Chain framework is a strategic management tool that helps businesses analyze their internal activities in order to identify areas where they can create value and gain competitive advantage. Porter’s Value Chain has now become a cornerstone in business strategy and operations management, guiding companies in optimizing their processes and enhancing their competitive position in the market.
Explanation of Value Chain Map
A value chain map is a graphical representation or visualization of the various activities involved in the production of goods or services within an organization or across an industry. It illustrates the sequence of activities required to deliver a product or service to the end customer, from raw material sourcing to distribution and after-sales service.
Value chain maps typically consist of a series of interconnected nodes or steps, each representing a specific activity or process in the value chain. These activities can include procurement, manufacturing, marketing, sales, logistics, and customer service.
Value chain mapping helps organizations understand the flow of value creation, identify inefficiencies, pinpoint areas for improvement, and assess competitive positioning relative to other players in the industry.
Explanation of Value Chain Node
A value chain node refers to each discrete activity or process depicted in a value chain map. Each node represents a stage or step in the value creation process, where value is added to the product or service.
Analyzing value chain nodes involves assessing their efficiency, cost-effectiveness, quality, and contribution to overall value creation. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each node, organizations can develop strategies to optimize their value chains, reduce costs, and enhance competitiveness.
Examples of value chain nodes include raw material sourcing, manufacturing, assembly, packaging, distribution, marketing, sales, customer support, and product maintenance.
As a conclusion: a value chain map provides a visual representation of the entire value creation process, while value chain nodes represent the individual activities or stages within that process. Together, they form a framework for analyzing and improving the efficiency and effectiveness of an organization’s value chain.
What is Value Chain Analysis
Value chain analysis is a strategic management tool used to evaluate the sequence of activities within a company’s operations, from raw material sourcing to final product delivery. This analysis has the aim of identifying opportunities to enhance value creation and competitive advantage. Businesses can analyze each step to understand where costs are incurred and where value is added by breaking down the value chain into discrete activities. This analysis enables organizations to optimize their processes, reduce costs, improve efficiency, and ultimately deliver greater value to customers.
Potential Future Trends in Value Chain Management
Value chain management is constantly evolving due to technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, globalization, and sustainability concerns. Here are some potential future trends in value chain management,
1. Digitalization and Automation: Increasing adoption of digital technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain for streamlining processes, enhancing visibility, and improving decision-making across the value chain.
2. Data Analytics for Insights: Utilizing big data analytics to gain actionable insights into customer behavior, market trends, supply chain risks, and operational efficiencies. Predictive analytics can help in demand forecasting and inventory optimization.
3. Supply Chain Transparency and Traceability: Growing emphasis on transparency and traceability throughout the value chain to meet regulatory requirements, ensure product quality, and address consumer concerns regarding sustainability, ethical sourcing, and social responsibility.
4. Circular Economy Practices: Embracing circular economy principles to minimize waste, maximize resource efficiency, and promote product reuse, recycling, and remanufacturing. Companies may implement strategies like product-as-a-service, closed-loop supply chains, and eco-design.
5. Resilience and Risk Management: Building resilient supply chains capable of adapting to disruptions such as natural disasters, geopolitical conflicts, pandemics, and trade disputes. This involves diversifying sourcing, enhancing supplier collaboration, and implementing contingency plans.
6. Sustainable and Ethical Sourcing: Increasing focus on sustainable procurement practices, including sourcing raw materials from environmentally responsible suppliers, reducing carbon footprint, and ensuring fair labor practices throughout the supply chain.
7. Collaborative Networks and Ecosystems: Formation of collaborative ecosystems involving suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, logistics providers, and customers to drive innovation, reduce costs, and create shared value through mutual cooperation.
8. Customer-Centric Supply Chains: Shifting towards customer-centric supply chains that prioritize personalized products, faster delivery options, seamless omnichannel experiences, and enhanced after-sales support to meet evolving customer expectations.
9. Reshoring and Nearshoring: Reassessing global sourcing strategies and considering reshoring or nearshoring manufacturing operations to mitigate geopolitical risks, reduce transportation costs, and improve supply chain agility.
10. Dynamic Supply Chain Orchestration: Implementing agile and responsive supply chain orchestration capabilities enabled by real-time data, advanced analytics, and automation to dynamically adjust production, inventory, and distribution in response to changing market conditions and customer demands.
These trends are likely to shape the future landscape of value chain management, driving innovation, efficiency, sustainability, and resilience across industries.
Pros / Benefits of Porter’s Value Chain
Porter’s Value Chain offers a comprehensive framework for understanding and optimizing a company’s internal operations, driving improvements in efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and competitiveness. This has many benefits which are highlighted as below,
1. Enhanced Efficiency
Understanding the value chain helps companies to streamline their processes and eliminate inefficiencies. Company management can direct the company strategy to improve operational efficiency and productivity by optimizing workflows and resource allocation.
2. Structured Analysis
Porter’s Value Chain provides a structured framework for analyzing a company’s internal operations. Companies can systematically examine each step of their production and delivery processes by breaking down the value chain into distinct activities.
3. Cost Reduction Opportunities
Companies can identify areas where costs are incurred and look for opportunities to streamline operations and reduce expenses by using this tool. This can lead to significant cost savings, improving overall profitability.
4. Strategic Decision Making
Porter’s Value Chain serves as a valuable tool for strategic decision-making. By providing insights into the internal workings of a company, value chain analysis helps management make informed decisions about resource allocation, investment priorities, and overall business strategy.
5. Competitive Advantage Identification
Porter’s Value Chain enables companies to identify activities that directly contribute to creating value for customers. Companies can develop a competitive advantage by offering products or services that meet customer needs more effectively than their competitors by focusing on these value-adding activities.
6. Differentiation Opportunities
Value chain analysis allows businesses to identify opportunities for differentiation. Senior management of the companies can develop distinctive products or services that set them apart in the market and create value for customers by understanding their unique strengths and capabilities.
7. Innovation Stimulus
Companies can uncover opportunities for innovation and improvement by analyzing the value chain. This can lead to the development of new processes, technologies, or products that enhance value for customers and drive business growth.
Cons / Drawbacks of Porter’s Value Chain
Porter’s Value Chain offers valuable insights into a company’s internal operations and value creation processes. It is good to recognize its limitations and complement it with other strategic approaches to develop a more holistic understanding of a company’s competitive position and strategic options. Following are some drawbacks or cons of Porter’s Value Chain,
1. Limited Scope
The value chain framework tends to be more applicable to traditional manufacturing industries with tangible products and linear production processes. Service-oriented businesses or those operating in knowledge-based industries may find it challenging to apply the value chain model effectively. This may not adequately capture the complexity of their value creation processes.
2. Focus on Internal Processes
Porter’s Value Chain primarily focuses on internal activities within a company. This provides valuable insights into a firm’s operations, but it may overlook external factors such as market dynamics, customer preferences, and competitive pressures. These will also significantly impact a company’s performance and competitive advantage.
3. Complexity Management
Value chain analysis can become overly complex, especially for large, diversified organizations with multiple business units or operating across various geographic regions. Managing and analyzing the interconnected activities within such complex value chains may pose challenges in terms of data collection, integration, and interpretation, potentially limiting the effectiveness of the analysis.
4. Static Analysis
Value chain analysis provides a snapshot of a company’s operations at a specific point in time. However, businesses operate in dynamic environments characterized by constant change and evolving market conditions. As such, relying solely on a static value chain analysis may limit a company’s ability to adapt to emerging trends, technological advancements, or shifts in consumer behavior.
5. Cost vs. Value Focus
Value chain analysis helps identify cost reduction opportunities, but it may inadvertently lead to a cost-focused mindset that prioritizes efficiency over innovation and value creation. Overemphasis on cost reduction can hinder investments in research and development, customer experience enhancement, or strategic partnerships, which are critical for long-term competitiveness and growth.
6. Lack of Integration with External Factors
Porter’s Value Chain primarily focuses on internal activities, often neglecting external factors that influence a company’s performance. To address this limitation, businesses should complement value chain analysis with other strategic tools such as SWOT analysis, PESTEL analysis, or competitor analysis to gain a more comprehensive understanding of their competitive landscape and market environment.
Difference Between Value Chain and Supply Chain
The primary difference between the value chain and the supply chain lies in their scope and focus. The value chain refers to the entire sequence of activities involved in the creation and delivery of a product or service, from raw material acquisition to the final consumption by the end customer. It encompasses both primary activities, such as inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and service, as well as support activities like procurement, technology development, human resource management, and firm infrastructure.
On the other hand, the supply chain specifically focuses on the flow of materials, information, and resources from suppliers to manufacturers, then to distributors, and finally to customers. While the value chain is broader and includes all activities that contribute to value creation, the supply chain is a subset of the value chain, concentrating on the logistical and operational aspects of sourcing, producing, and delivering goods and services.
Other Business Concepts related to Porter’s Value Chain
1. Balanced Scorecard
The Balanced Scorecard is a strategic performance management tool that measures organizational performance across four perspectives like financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and growth.
The Balanced Scorecard provides a broader framework for evaluating overall organizational performance from multiple perspectives. On other hand, Porter’s Value Chain focuses on analyzing and optimizing specific activities within the value chain
Porter’s Value Chain is more operational and focused on internal processes, while the Balanced Scorecard is strategic and considers both internal and external factors affecting performance.
2. Lean Management
Lean Management is a methodology aimed at reducing waste and improving efficiency in business operations.
Lean Management provides specific tools and techniques for streamlining processes and eliminating non-value-added activities. In contrast, Porter’s Value Chain identifies value-creating activities and opportunities for optimization.
Both concepts share the goal of enhancing efficiency, but Lean Management offers more detailed methodologies for achieving efficiency gains within the value chain.
3. Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology focused on reducing defects and variation in processes to improve quality and performance.
Six Sigma provides a systematic approach to quality improvement within specific processes. On other hand, Porter’s Value Chain considers activities across the entire value chain.
What is Value Stream Management (VSM)
Value Stream Management (VSM) is a strategic approach to optimize and streamline the end-to-end process of delivering value to customers. It involves analyzing, visualizing, and improving the flow of work across all stages of product development and delivery, from concept to deployment. VSM focuses on identifying and eliminating waste, improving efficiency, and maximizing value creation by aligning people, processes, and technology towards delivering high-quality products or services that meet customer needs effectively.
How to Derive the Profit Margin using Value Chain Analysis
The firm’s margin or profit depends on its “effectiveness” in performing above primary and support activities efficiently. The difference between the “amount” that the customer willing to pay for the products and the cost of the activities in the value chain is the profit margin of the company. Hence, the profit margin can be increased by the following ways,
1. Reduce the cost of the activities (streamline the primary and support activities)
2. Increase the value of the product through technology development
It would be easy for a company to eventually achieve economies of scale by optimizing the entire value chain.
FAQs of Porter’s Value Chain
Q1: What is Porter’s Value Chain framework?
Answer: Porter’s Value Chain is a framework that helps businesses analyze their internal activities to understand how they create value for customers and gain a competitive advantage.
Q2: What are the primary activities in Porter’s Value Chain?
Answer: The primary activities in Porter’s Value Chain include inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and service.
Q3: What are the secondary activities in Porter’s Value Chain?
Answer: The secondary activities in Porter’s Value Chain comprise procurement, technology development, human resource management, and firm infrastructure.
Q4: How does Porter’s Value Chain help businesses gain a competitive advantage?
Answer: Porter’s Value Chain helps businesses gain a competitive advantage by enabling them to identify areas for efficiency improvement, cost reduction, and differentiation within their operations.
Q5: What are some examples of value chain analysis in real-world business scenarios?
Answer: Examples of value chain analysis include identifying cost-saving opportunities in logistics, improving product quality through operations optimization, and enhancing customer service through service activities.
Q6: How can businesses apply Porter’s Value Chain framework to their operations?
Answer: Businesses can apply Porter’s Value Chain framework by systematically evaluating each activity in their value chain to identify opportunities for improvement and strategic alignment.
Q7: What role does technology play in Porter’s Value Chain framework?
Answer: Technology plays a critical role in Porter’s Value Chain framework by enabling automation, data analytics, and process optimization across various activities.
Q8: How does Porter’s Value Chain relate to other strategic management concepts?
Answer: Porter’s Value Chain complements other strategic management concepts such as SWOT analysis, Porter’s Five Forces, and the Resource-Based View by providing insights into internal operational dynamics.
Q9: What are some common challenges companies face when implementing Porter’s Value Chain framework?
Answer: Common challenges include data availability and accuracy, organizational resistance to change, and the need for cross-functional collaboration.
Q10: How can businesses continuously monitor and evaluate their value chain performance?
Answer: Businesses can continuously monitor and evaluate their value chain performance through key performance indicators (KPIs), regular performance reviews, and benchmarking against industry standards.
Read More About Porter’s Five Forces,
- Porter’s Five Forces: Explanation with Industry Examples
- Porter’s Five Forces: Advantages and Disadvantages
- How to Apply Porter’s Five Forces to Industry / Business: Step-By-Step Simple Detail Guide with Examples
- Porter’s Five Forces Model: Applied To Airline Industry with Real World Examples
- Porter’s Five Forces: Applied To Fast Food Restaurants Industry with Real World Examples
- Porter’s Five Forces: Applied To Starbucks with Examples
- Porter’s Five Forces: Applied To Banking Industry with Real World Examples
- Porter’s Five Forces: Applied To Clothing / Fashion Industry with Real World Examples