Perfect Competition: Advantages and Disadvantages
Perfect competition happens when there are many producers in the market, with very few entry barriers, and those producers produce identical products. Consumers have perfect information (with regards to the past, present, and future) about the product being sold and the prices charged by each corporation. Perfect competition is theoretically the opposite of a monopoly market.
Table of Content
- Definition of Perfect Competition
- Advantages of Perfect Competition
- Disadvantages of Perfect Competition
- Features of Perfect Competition
- Examples of Perfect Competition Market
- Long-Run Equilibrium in a Perfectly Competitive Market
- Demand and Supply in Perfect Competition
- Policy Implications of Perfect Competition
- Process of Entry and Exit in Perfect Competition
- Difference Between Perfect Competition and Monopoly
- FAQs About Perfect Competition
Definition of Perfect Competition
Perfect competition occurs when there are many sellers in the market, with very low entry barriers, and products are matched from one seller to another. In a perfect competition market, all companies sell identical products and any company cannot determine prices.
Perfect competition describes a market structure where competition is at the highest level. This market has a large number of producers, high competition, identical products, and less market power for a single firm. This is a hypothetical situation in which it is not practically available.
Following are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Perfect Competition.
Advantages (Pros / Positives / Benefits) of Perfect Competition
1. Very Low Barriers to Entry & Exit
Markets experiencing perfect competition have very low barriers to entry. The advantage is for both customers and the total industry. There will be new entrants in the market which brings healthy competition to the industry. Also, consumers will not be a risk when a few companies get together and increase their prices.
2. Chance Of Customer Exploitation Is Low
Any seller in the perfect competition market does not have monopoly pricing power. They can not influence the output and price as individuals or groups since barriers to entry are low. This is a positive factor for the consumers since their chance to be exploited is low.
3. Consumer Information Is High
Usually, there is a high level of information available to the customers in perfect competition firms. This provides a greater advantage for the consumers to make informative decisions. This will result “Customer Is King” level in the market.
4. Active Business Environment
Perfect competition results in an active business environment. There is a good level of competition, individuals or groups can not dominate in the market, and many firms have the market share distributed. These will result in many benefits for the industry.
5. Availability of High-Quality Products with Low Price
The level of competition is high in the perfect competition market. Firms have to lower their profit margin and provide consumers low price competitive products. The market share will be loosened otherwise. Also, firms have less chance to compromise the quality since consumers can move from one brand to another easily.
6. Decrease Room For Monopoly With A Large Number of Producer Availability
Since barriers to entry are low in perfect competition, there will be many producers who will join the market continuously. This is a very positive factor for the consumers and the industry as a whole.
7. Standardize Products Irrespective of Producers
Consumers will get standardized products in the perfect competition market irrespective of the seller. The consumer does not have to compare and think much since all products will serve the same purpose. Producers will also have to spend fewer advertisement expenses since all products are homogeneous.
8. Optimum Utilization Of Resources
Firms earn a fewer profit margin because producers have to compete with a lower price. Therefore producers try to increase efficiency and minimize wastage by utilizing resources properly which results to lower the cost of production. This will help the producers to increase their profit margin.
Disadvantages (Cons / Negatives / Drawbacks / Risks) of Perfect Competition
1. Identical (Non-Differentiated) Products and Services
Consumers will get the same kind of identical product in the perfect competition market. This is a disadvantage for the consumers since they are limited with choices and different experiences.
2. Heavy Competition Results More Producers Exit
Heavy competition is another disadvantage for producers due to low barriers to entry and exit. Producers may not continuously be in the market due to this. This will result in a negative impact on an industry whole.
3. Risk Of Predatory Pricing
If a company has a large investment capability, it can choose the option to set the prices very low to attempt to drive out competitors and create a monopoly. Competitors will not be able to sustain if a firm set the prices low for a consecutive duration. They can simply use the predatory pricing method.
4. Less Production Efficiency of Individual Firms
A perfect competition market allows many competitors in the market. This results in difficulty for the companies to achieve economies of scale. A company can not reach the optimum production efficiency capability due to the unavailability of economies of scale.
5. Less Research and Development
Producers have less potential to earn profit. This may result in fewer reserves for the producers to start more research to uplift the product portfolio.
6. Excess Resource Waste
Many firms compete in the market to produce similar products, using the same resources. But no firm can reach economies of scale. Any firm can not hit the optimum production optimization level. This will increase the resource waste in the industry as a whole.
7. Misleading Advertising
Firms may try to invest more and more in advertising with the non-differentiated products available. Some advertisements may be false and misleading. Firms may brag about the product quality more than what it is, which is unfavorable from a consumer’s point of view.
Features of Perfect Competition
Here are the key features of perfect competition:
- Many Buyers and Sellers: There are numerous buyers and sellers in a perfectly competitive market. None of those has a significant market share. No single buyer or seller can influence the market price.
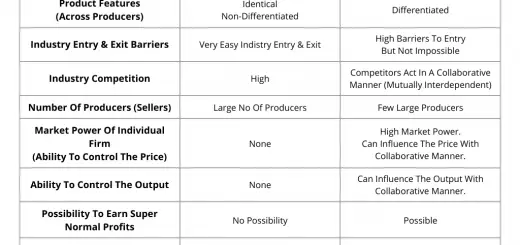
- Homogeneous Products: Firms in perfect competition produce identical or homogeneous products. Consumers perceive no difference between the products of one firm and those of another.
- Perfect Information: Buyers and sellers have perfect knowledge of market conditions, including prices, product quality, and production techniques. There are no information asymmetries.
- Free Entry and Exit: Firms can freely enter or exit the market without any barriers such as patents, licenses, or significant startup costs. This ensures that economic profits are driven to zero in the long run.
- Price Takers: Individual firms in perfect competition are price takers. This means they must accept the prevailing market price for their product. They have no influence over the market price and must adjust their output accordingly.
- Zero Economic Profits in the Long Run: Firms in perfect competition earn only normal profits in the long run due to free entry and exit. New firms will enter, increasing supply and driving prices down until profits are reduced to zero.if firms in the industry are making economic profits.
- Perfect Mobility of Factors of Production: Factors of production such as labor and capital can move freely between industries, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently.
- No Externalities: There are no external costs or benefits associated with production or consumption. Firms only consider private costs and benefits when making decisions.
Apart from the above, there are some other features of a perfect competition market like Market Power for Individual Firm, Number of Producers, Possibility of Super Economic Profits, Super Economic Profits, Substantial Market Share of Individual Firm, etc. Read the below article to find out the full list of the features of a perfect competition market.
Examples of Perfect Competition Market
1. Crops in the United States – Corn, wheat, soybeans, cotton, and hay are the major crops produced in the United States. These individual products are very similar. If we take wheat, it is a similar product produced by every American wheat farmer. As these products are non-differentiated, it is easy to buy land and start farming. This means low barriers to entry are there. But there is a high competition due to this. None of the farmers can be a price maker.
2. Pulp & Paper Manufacturing in Canada – The Paper Mills industry in Canada is a $6bn growing market. There are many companies in the industry including Cariboo, Kruger, Winpak, Supremex, and Hood Packaging. These manufacturers produce paper pulp and convert pulp into paper. These companies produce products like paper rolls and reams as the final output. Since there are many producers in the industry which produce identical products, any firm can not raise and control the prices on their own. The pulp and paper production industry is an example of perfect competition.
3. Foreign Exchange Market in World – People exchange money from one currency to another using a foreign exchange shop. The product is non-differentiated (homogeneous) due to the same currency types applicable on every exchange (US Dollar, Great British Pound, Euro, Australian Dollar, etc..). There are many sellers and buyers in the market. One shop can not manipulate the exchange rate and earn supernormal profits due to the competition.
Apart from the above, there are many real-world industry examples of perfect competition like Sugarcane Production in Australia, Dairy Products in America, Barley Harvest in Canada, etc. Read the below article to find out the full list of real-world examples of a perfect competition market.
Long-Run Equilibrium in a Perfectly Competitive Market
Long-run equilibrium in perfectly competitive markets results in two kinds of efficiencies. This happens when profit-maximizing firms in perfectly competitive markets combine with utility-maximizing consumers. These two efficiencies (conditions) depend on the resource allocation for their best alternative and the maximum satisfaction of the society.
1. Allocative Efficiency in Perfect Competition – Allocative efficiency means when it is chosen is a socially preferred condition. Price is equal to the marginal cost of production in a perfectly competitive market. When perfectly competitive firms follow the rule that profits are maximized by producing at the quantity where the price is equal to marginal cost, they are thus ensuring that the social benefits received from producing a good are in line with the social costs of production.
2. Productive Efficiency in Perfect Competition – Productive efficiency means producing without waste. In the long run in a perfectly competitive market, because of the process of entry and exit, the price in the market is equal to the minimum of the long-run average cost curve. In other words, goods are being produced and sold at the lowest possible average cost.
Demand and Supply in Perfect Competition
The interaction of demand and supply plays a fundamental role in determining the equilibrium price and quantity of goods or services exchanged n a perfectly competitive market. Both demand and supply are guided by the principles of perfect competition, where numerous buyers and sellers act independently, with no single entity having the power to influence market prices.
On the demand side, consumers are price takers, meaning they accept the prevailing market price as given. The demand curve in a perfectly competitive market reflects the willingness of consumers to purchase a particular quantity of a good or service at various price levels. This demand curve is relatively elastic, indicating that consumers are highly responsive to changes in price. As the market price decreases, the quantity demanded increases, and vice versa. However, individual consumers have no influence on the market price, as they are small relative to the overall market.
On the supply side, firms operate similarly as price takers. The supply curve in a perfectly competitive market reflects the willingness of firms to produce and sell a particular quantity of a good or service at various price levels. Firms in perfectly competitive markets aim to maximize profits by producing where marginal cost equals marginal revenue, which is equal to the market price. Since firms have perfect information about market conditions, they adjust their production levels in response to changes in market prices. In the long run, firms enter or exit the market depending on whether they can cover their costs at the prevailing market price.
The equilibrium price and quantity in a perfectly competitive market are determined at the point where demand equals supply. This equilibrium reflects the most efficient allocation of resources, as it maximizes consumer welfare while ensuring that firms cover their costs and earn normal profits. Any deviation from this equilibrium would result in either excess supply (a surplus) or excess demand (a shortage), prompting adjustments in production and consumption levels to restore equilibrium.
Policy Implications of Perfect Competition
- Consumer Protection Policies: Policies aimed at enhancing consumer protection, such as truth in advertising laws and product safety standards, can help maintain transparency and fairness in perfectly competitive markets. This ensures that consumers can make informed decisions and trust the products they purchase
- Antitrust Regulation: Governments may implement antitrust laws to prevent the formation of monopolies and cartels, ensuring that markets remain competitive. By fostering competition, these regulations aim to protect consumer welfare and promote economic efficiency.
- Support for Small Businesses: Governments may provide support and incentives for small businesses to enter and compete in markets dominated by larger firms. By reducing barriers to entry and promoting entrepreneurship, policymakers can enhance competition and innovation, leading to greater market efficiency.
- Market Monitoring and Enforcement: Effective enforcement of regulations and monitoring of market activities are essential to prevent anti-competitive behavior, such as collusion or predatory pricing. Robust regulatory bodies can help maintain a level playing field and uphold the principles of perfect competition.
- Public Goods Provision: In cases where perfect competition fails to provide public goods efficiently due to free-rider problems or externalities, governments may intervene to ensure their provision. Through taxation and public expenditure, policymakers can address market failures and promote social welfare.
- Trade Policies: International trade policies, such as tariffs and quotas, can impact the competitiveness of domestic firms in global markets. Policymakers must strike a balance between protecting domestic industries and promoting free trade to ensure the benefits of perfect competition extend beyond national borders.
- Intellectual Property Rights: The enforcement of intellectual property rights, such as patents and copyrights, can influence innovation and competition in markets characterized by perfect competition. Balancing incentives for innovation with the promotion of competition is crucial for fostering dynamic and efficient markets.
- Infrastructure Investment: Investments in infrastructure, such as transportation and communication networks, can facilitate market access and reduce barriers to entry for firms. By improving connectivity and reducing transaction costs, policymakers can enhance market competitiveness and promote economic growth.
Process of Entry and Exit in Perfect Competition
The process of entry and exit plays a crucial role in maintaining long-term equilibrium in a perfectly competitive market. Entry refers to the influx of new firms into the market, while exit involves the withdrawal of existing firms. The possibility of entry and exit is facilitated by the absence of barriers such as high startup costs, government regulations, or proprietary technology. When firms in a perfectly competitive market earn economic profits in the short run, it signals an opportunity for new firms to enter the market, attracted by the potential for profit.
Conversely, if firms incur losses, some may decide to exit the market, either by shutting down or reallocating resources to other industries. This movement of firms in and out of the market continues until economic profits are driven to zero in the long run, as firms enter in response to profits and exit in response to losses.
The process of entry and exit in perfect competition acts as a self-correcting mechanism that ensures resources are efficiently allocated over time. Entry increases market supply, exerting downward pressure on prices and reducing profits for existing firms. Conversely, exit decreases market supply, alleviating downward pressure on prices and allowing remaining firms to earn normal profits.
This dynamic process continues until firms in the market are operating at their minimum efficient scale, producing at the lowest possible average total cost. Overall, the fluidity of entry and exit in perfectly competitive markets fosters competition, innovation, and efficiency, benefiting both consumers and producers in the long run.
Difference Between Perfect Competition and Monopoly
The below provided is a comparison table outlining the key differences between Perfect Competition and Monopoly,
| Aspect | Perfect Competition | Monopoly |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Firms | Many small firms | Single dominant firm |
| Control Over Price | Price taker | Price maker |
| Product Differentiation | Homogeneous products | Unique products or significant differentiation |
| Barriers to Entry | No barriers, free entry and exit | High barriers, difficult entry |
| Market Power | No market power, firms are competitive | High market power, firm dominates market |
| Pricing Strategy | Prices are set by market forces | Prices are set by the monopolist |
| Efficiency | Maximizes both consumer and producer surplus | Usually results in lower output and higher prices, leading to deadweight loss |
| Allocative Efficiency | Achieved, resources allocated efficiently | May lead to misallocation of resources |
| Productive Efficiency | Achieved, firms produce at minimum efficient scale | May not produce at minimum efficient scale |
| Innovation and Investment | Lower incentives for innovation and investment | Higher incentives for innovation and investment |
| Government Regulation | Limited intervention, except for antitrust regulation | Often subject to regulation and antitrust measures |
| Examples | Agricultural markets, stock exchange (in theory) | Local utility companies, Microsoft (historically) |
FAQs About Perfect Competition
Q: Can perfect competition exist in real world?
A: Perfect competition rarely exists in the real world due to factors such as product differentiation, imperfect information, and barriers to entry, which deviate from the assumptions of the model.
Q: How does price determination occur in perfect competition?
A: Prices are determined by the intersection of demand and supply forces in the market, with individual firms acting as price takers.
Q: What is the main problem with perfect competition?
A: The main problem with perfect competition lies in its unrealistic assumptions, such as homogeneous products, perfect information, and free entry and exit, which rarely hold true in real-world markets, limiting its applicability as a descriptive model.
Q: What role do profits play in perfect competition?
A: In the short run, firms may earn economic profits or losses, but in the long run, profits are driven to zero as firms enter or exit the market until only normal profits are earned.
Q: What is the significance of homogeneous products in perfect competition?
A: Homogeneous products ensure that consumers perceive no differences between the offerings of different firms, allowing them to make choices based solely on price.
Q: How does perfect competition contribute to economic efficiency?
A: Perfect competition promotes allocative efficiency by maximizing consumer and producer surplus, as well as productive efficiency by ensuring firms produce at the minimum efficient scale.
Q: Why is perfect competition often considered an idealized model?
A: Perfect competition serves as a benchmark for analyzing market structures, but real-world markets often deviate due to factors like imperfect information, externalities, and barriers to entry.
Q: What are the implications of perfect competition for consumer welfare?
A: Perfect competition generally results in lower prices, greater choice, and higher quality products, leading to increased consumer welfare.
Q: Who benefits more from perfect competition?
A: Consumers benefit more from perfect competition as it leads to lower prices, higher quality products, and greater choice due to increased competition among firms.
Q: How does perfect competition differ from other market structures like monopoly or oligopoly?
A: Unlike perfect competition, monopoly and oligopoly involve fewer firms with market power, leading to higher prices, restricted output, and potential inefficiencies.
Read More:
Market Structures
Perfect Competition
- Overview, Definition, & Features of Perfect Competition
- Main Characteristics / Causes of Perfect Competition
- Real Examples of Perfect Competition (in USA, Canada, Australia, World)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Perfect Competition
Monopolistic Competition
- Overview, Definition, & Features of Monopolistic Competition
- Main Characteristics / Causes of Monopolistic Competition
- Real Examples of Monopolistic Competition (in USA, Canada, World)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Monopolistic Competition
Oligopoly Market
- Real Examples of Oligopoly Market (in the USA, Canada, World)
- Seven Important Characteristics of Oligopoly Market
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Oligopoly Market
Monopoly Market
- Definition, Examples, and Characteristics of Monopoly Market
- Real Examples of Monopoly Market (in the USA, Canada, Australia, World)
- Important Characteristics / Causes of Monopoly Market
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Monopoly Market