Fixed Cost: Explanation, Formula, Calculation, and Examples
Fixed Cost Definition
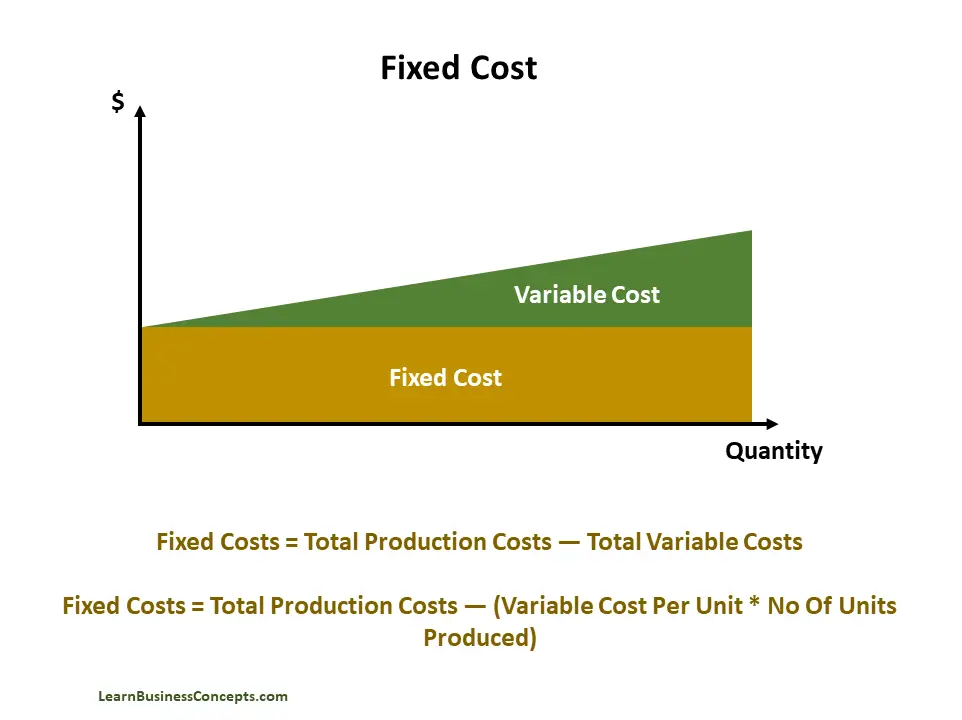
Fixed cost is a type of cost that does not change with an increase or reduction in production quantity. The company has to pay the fixed cost despite the number of units produced. These costs remain same over a specific period, regardless of the company’s activity level.
Despite the business performance, production quantity, work in progress, or other factors, a fixed cost will always remain constant.
Table of Content:
- Understanding Fixed Cost
- How to Calculate Fixed Cost? Calculation Steps & Formula
- Fixed Cost Per Unit Calculation Formula
- Fixed Cost Examples
- Fixed Cost vs. Variable Cost: What is the Difference?
- Short-Term vs Long-Term Fixed Costs
- How to Calculate Break Even Point
- How Do Fixed Costs Impacts the Break Even Point (BEP)?
- How Do Fixed Costs Impact Operating Leverage?
- How Does Fixed Costs Impact Economies of Scale?
- How Does Fixed Costs Affects Budgeting and Planning?
- How do Companies Reduce Fixed Costs – with Real World Examples
- How to Account Fixed Cost in Balance Sheet (Statement of Financial Position)?
- How to Account Fixed Cost in Income Statement (Statement of Profit and Loss)?
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Understanding Fixed Cost
Fixed costs can be understood as the types of expenses the company must pay, which are not dependent on any specific business activities. Fixed costs are generally considered as indirect costs since it is not applied to a company’s production level of any goods or services. These costs are constant over a specified time and the amount does not change with production output levels.
Fixed costs are usually established by contract agreements or schedules. As an example, for rent payment, there is a specific agreement that specifies the duration and the fixed amount which the company should pay. Fixed costs usually do not change throughout the agreement.
Total Fixed Cost (TFC)
Total Fixed Cost (TFC) is the sum of all fixed expenses a business incurs over a specific period. These costs remain constant regardless of the level of production or sales. Examples of fixed costs include rent, salaries, insurance premium, loan interest, and equipment depreciation. For instance, if a business pays $20,000 per month for office rent, $10,000 for salaries, $3,000 for insurance, and $2,000 for loan interest, the TFC would be the sum of all costs, which is $35,000 per month.
Total Fixed Cost does not change with production levels changes. It means TFC remains the same whether the company produces nothing or thousands of units. It is a constant value.
TFC helps businesses to understand following,
- Identify the baseline costs the company should to cover even with no revenue or no production.
- Plan for scenarios involving low production or revenue.
- Make strategic decisions about scaling or maintaining operations.
Average Fixed Cost
Average Fixed Cost (AFC) is the fixed cost allocated per unit of output. It is calculated by dividing the Total Fixed Cost by the quantity of output produced. Since fixed costs remain constant regardless of production levels, AFC decreases as the quantity of output increases, demonstrating the benefits of economies of scale.
For example, if a business incurs $30,000 in fixed costs per month and produces 2,000 units, the AFC is $15 per unit ($30,000 / 2,000). If production increases to 3,000 units, the AFC drops to $10 per unit, and at 5,000 units, it falls further to $6 per unit. The AFC never reaches zero but consistently decreases as fixed costs are spread over a larger number of units.
AFC helps businesses to understand following,
- Understanding AFC helps in pricing decisions to ensure the business covers all costs.
- A declining AFC with higher production indicates efficient use of resources.
- AFC contributes to total cost calculations, which are vital for determining break-even points.
How to Calculate Fixed Cost? Calculation Steps & Formula
Option 1 – Using Total Cost and Variable Cost
- Identify Total Cost (TC) – Determine the overall cost incurred, including both fixed and variable costs.
- Identify Variable Cost (VC) – Calculate or estimate the costs that change with production, such as raw materials or direct labor.
- Determine Total Fixed Cost (TFC) – Subtract the variable cost from the total cost.
Total Fixed Cost = Total Cost - Variable Cost
Option 2 – Using Average Fixed Cost
- Identify Average Fixed Cost (AFC) – Determine the fixed cost per unit.
- Find Quantity of Output (Q) – Identify the total number of units produced.
- Calculate Total Fixed Cost (TFC) – Multiply the AFC by the quantity of output.
Total Fixed Cost = Average Fixed Cost x Quantity
Option 3 – Using Break-Even Analysis
- Identify Break-Even Sales Revenue – Determine the revenue at the break-even point (where profit is zero).
- Calculate Variable Costs at Break-Even – Use the variable cost per unit to find the total variable costs at this level.
- Subtract Total Variable Costs from Break-Even Revenue – The remainder is your total fixed cost.
Total Fixed Cost = Break Even Revenue - Total Variable Cost at Break Even
Fixed Cost Per Unit Calculation Formula
Following data points are needed to calculate the fixed cost per unit,
- Total Fixed Cost (TFC) – The total of all fixed expenses incurred by the business, such as rent, salaries, or insurance.
- Quantity of Output (Q) – The total number of units produced.
The formula is following,
Fixed Cost Per Unit = Total Fixed Cost (TFC) / Output Quantity (Q)
As an example, if a company has a Total Fixed Cost (TFC) of $50,000 and produces 10,000 units, the Fixed Cost Per Unit is $5 per unit ($50,000 / 10,000).
Fixed Cost Examples
Following are some examples of Fixed Costs,
- Rent and Lease Payments – Regular payments for office, factory, or retail space that remain constant regardless of production levels.
- Salaries & Wages – Fixed compensation for employees such as managers or administrative staff.
- Insurance Premiums – Monthly or annual payments for business insurance, such as property, liability, or equipment coverage.
- Depreciation – The gradual reduction in the value of fixed assets, such as machinery or buildings, calculated over time.
- Property Taxes – Taxes paid on owned property that remain unchanged over a financial period.
- Utility Base Charges – The fixed portion of utility bills, such as electricity or water, which is not influenced by usage.
- Loan Repayments (Interest Component) – Fixed interest payments on loans or mortgages, as per agreement terms.
- Marketing Expenses (Fixed Campaigns) – Costs for long-term or pre-paid advertising and sponsorships that don’t vary with production.
- Software Subscriptions or Licenses – Monthly or annual fees for business-critical software tools, like accounting or project management software.
- Equipment Leasing Costs – Regular payments for leasing machinery or office equipment, irrespective of usage.
Fixed Cost vs. Variable Cost: What is the Difference?
Fixed costs are expenses that remain constant over a specific period, regardless of production or sales levels, while variable costs fluctuate directly with the level of production or sales. Fixed costs, such as rent or salaries, do not change whether a business produces 1 unit or 10,000 units. In contrast, variable costs, like raw materials and direct labor, increase as more units are produced.
- Dependency on Production
Fixed costs are independent of production, meaning they do not vary with output. For instance, the rent for a factory remains the same regardless of how much is produced inside it.
On the other hand, variable costs depend on production levels. For example, the cost of materials will rise if more units are manufactured because each unit requires additional resources.
- Behavior Over Time
Fixed costs stay the same in the short term but can change in the long term due to factors like contract renewals or inflation. For example, a business’s rent may remain unchanged for a year but could increase upon lease renewal.
Variable costs, however, change immediately with production levels. Variable costs like electricity for machinery or shipping costs will stop if production stops.
- Cost Per Unit
Fixed costs per unit decrease as production increases because the total cost is spread over more units. For example, if a factory incurs $60,000 in fixed costs and produces 1,000 units, the fixed cost per unit is $60, but this drops to $5 per unit if production doubles.
On other hand variable costs per unit remain constant. The cost of producing one additional unit stays the same regardless of how many are already produced.
- Impact on Financial Planning
Fixed costs provide stability and predictability in budgeting, making it easier to forecast expenses. However, they require careful management during periods of low production, as they still need to be paid. High fixed costs result in a higher break-even point.
Variable costs are flexible and scale with production, making them easier to adjust during changing business conditions. But they can make financial planning challenging due to their variability.
Examples of fixed costs include rent, insurance, and depreciation, which remain stable over time. Variable costs include raw materials, packaging, and direct labor, which increase as more units are produced or sold.
Short-Term vs Long-Term Fixed Costs
Short-Term Fixed Costs are expenses that remain constant over a relatively less period, typically within a year or less. These costs do not change in the immediate future (within upcoming 1 year), regardless of the level of production or sales. Examples of short-term fixed costs include rent, insurance premiums, and salaried employee wages. These expenses are predictable and fixed with a agreement. These short tern fixed costs are generally easy to budget for as it will not change frequently. Businesses rely on short-term fixed costs to plan their day-to-day operations and maintain steady financial management.
Long-Term Fixed Costs are expenses that remain stable in a longer period. These costs are typically associated with long-term commitments, such as lease agreements extending beyond a year. Also capital investments like machinery or buildings, and costs related to expanding operations are some other examples. Unlike short-term fixed costs, long-term fixed costs involve strategic decisions and significant investments that impact a company’s financial position for years. They require careful planning, as these commitments can have long-lasting effects on cash flow and overall profitability.
How to Calculate Break Even Point
The Break-Even Point (BEP) is the point at which total revenues equal total costs. This means the business is not making a profit, but it is not incurring a loss either. It helps businesses determine the level of sales needed to cover all fixed and variable costs.
Break-Even Point (BEP) = Total Fixed Costs (TFC) / [ Selling Price per Unit (SP) - Variable Cost per Unit (VC) ]
- Step 01 – Identify Total Fixed Costs (TFC): These are the costs that do not change regardless of production, such as rent, salaries, and insurance.
- Step 02 – Determine Selling Price per Unit (SP): This is the price at which you sell each product.
- Step 03 – Identify Variable Cost per Unit (VC): These are the costs that vary with the production level, such as raw materials, direct labor, or shipping costs.
- Step 04 Apply the Formula: Substitute the values of TFC, SP, and VC into the formula to calculate the Break-Even Point in units.
As example, assume Total Fixed Costs (TFC) is $100,000, Selling Price per Unit (SP) is $50, and Variable Cost per Unit (VC) is $30.
Break-Even Point (BEP) = 100,000 / (50 – 30) = 100,000 / 20 = 5,000 Units
This means the business needs to sell 5,000 units to cover all fixed and variable costs.
How Do Fixed Costs Impacts the Break Even Point (BEP)?
Fixed costs have a direct impact on the break-even point, because BEP represent the baseline expenses that must be covered before a business can begin to make a profit. The higher the fixed costs, the higher the break-even point will be. This is because fixed costs do not change regardless of the number of units sold. Hence, a business needs to generate enough revenue from sales to cover these costs. As a result, when fixed costs increase such as due to higher rent, salaries, or insurance, the business must sell more units or generate more revenue to break even.
Lower fixed costs lead to a lower break-even point. This makes it easier for a business to reach profitability. This is important for new or smaller businesses, as reducing fixed costs allows them to achieve profitability with fewer sales. A business can decrease the number of units it needs to sell to cover its expenses by carefully managing and reducing fixed costs, resulting reaching its break-even point faster.
How Do Fixed Costs Impact Operating Leverage?
Fixed costs have a high impact on operating leverage. Operating leverage refers to the degree to which a company can increase their profits by increasing sales. A company has higher operating leverage when a business has high fixed costs. This means that once the break-even point is reached, additional sales generate a larger proportion of profit. This is because fixed costs remain constant regardless of production levels, so every additional sale contributes directly to covering variable costs and then to profit.
On other hand, businesses with low fixed costs have lower operating leverage. In this case, greater proportion of sales must go towards covering variable costs before contributing to profit.
High operating leverage can be beneficial in growing markets because it allows for larger profit margins as sales increase, but it also introduces greater risk. A higher degree of operating leverage creates more sensitivity to changes in revenue. If sales decline, businesses with high fixed costs may experience a more significant drop in profitability. Therefore, managing the balance between fixed and variable costs is crucial for maintaining healthy operating leverage.
How Does Fixed Costs Impact Economies of Scale?
Economies of scale are the cost advantages that a business can achieve as it increases production. As production volume rises, fixed costs like as rent, salaries, and equipment depreciation spreads over a larger number of units. This reduces the fixed cost per unit. This reduction in per-unit fixed costs allows the company to produce goods more efficiently and at a lower cost per unit.
As a summary, fixed costs remain constant regardless of production levels. When a business scales up production, it benefits from spreading these costs over more units and this leads to cost savings and improved profitability. The more a company produces, the more it can leverage its fixed costs to gain a competitive advantage.
As an example, a factory with high fixed costs like expensive machinery will have the cost per unit decline as production volume increases. This is why large scale producers often have a cost advantage over smaller companies. However, while economies of scale can lead to lower per-unit costs, businesses must also manage variable costs carefully. The combination of reducing fixed costs per unit and controlling variable costs is key to maximizing economies of scale and achieving long-term profitability.
How Does Fixed Costs Affects Budgeting and Planning?
Fixed costs have a significant impact on budgeting and planning. Fixed cost represent expenses that remain constant regardless of changes in production or sales levels. Since fixed costs must be paid regardless of business performance, they create a baseline for financial planning. Businesses must factor in these costs when developing budgets to ensure that they have enough revenue to cover them. Failure to properly account for fixed costs can lead to cash flow problems. This is because these expenses do not fluctuate with demand or sales, and must be paid consistently even during periods of low sales.
When considering budgeting, fixed costs require careful monitoring to ensure that they do not outpace revenue or growth. High fixed costs can strain a business’s finances, especially if sales are inconsistent or lower than expected. This makes it crucial for businesses to plan for how they will cover these costs during downturns.
Effective budget planning involves analyzing fixed costs and integrating them into pricing strategies, break-even analysis, and long-term financial goals. Businesses can make informed decisions about cost management, pricing, and scaling operations by understanding the role of fixed costs in budgeting. This ensures companies remain financially stable even during challenging periods.
How do Companies Reduce Fixed Costs – with Real World Examples
Companies reduce fixed costs through various strategies like increasing efficiency, lowering overhead, and minimizing unnecessary expenses. Here are several common approaches which successful companies used to reduce the fixed costs,
1. Outsourcing Non-Core Activities
Companies often reduce fixed costs by outsourcing functions that do not directly contribute to their core business. For example, many companies outsource their IT, customer service, or human resources functions to third-party providers. This reduces the need for in-house staff, office space, and associated expenses.
Real-World Example – IBM reduced its fixed costs significantly by outsourcing IT services and administrative functions to external vendors, allowing it to focus on higher-value activities and innovation.
2. Renegotiating Lease Agreements
Businesses can lower fixed costs by renegotiating leases or moving to more affordable spaces. Companies that need physical office space might relocate to smaller, less expensive buildings or opt for shared office spaces with rising real estate prices.
Real-World Example – In 2020, during the pandemic, many businesses like Twitter and Facebook reduced their fixed costs by allowing employees to work remotely, reducing the need for large office spaces.
3. Automating Processes
Automation can help businesses reduce labor costs, which are often a significant portion of fixed costs. Businesses can lower the need for full-time employees and reduce the associated overhead by implementing technology such as robots or software for routine tasks.
Real-World Example – Ford has invested in robotics and automation at its manufacturing plants, which has helped to reduce the number of employees required on the factory floor, thereby lowering its fixed costs related to labor.
4. Switching to Variable Costs
Companies can convert fixed costs into variable costs, providing more flexibility in the long run. For example, businesses may choose subscription-based services for software or equipment leasing rather than buying them outright, allowing costs to scale with usage.
Real-World Example – Instead of investing in expensive in-house data centers, many companies like Dropbox and Netflix have migrated to cloud computing platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS), which operate on a pay-per-use model, reducing the need for large upfront investments.
5. Cutting Unnecessary Overhead
Companies often review and trim down expenses that contribute to fixed costs but do not add significant value. This can include reducing energy consumption, limiting waste, and streamlining operational processes.
Real-World Example: Starbucks took steps to reduce fixed costs by closing underperforming stores and optimizing its supply chain to reduce waste and inefficiency, helping the company become more cost-effective.
6. Outsourcing Manufacturing
Instead of maintaining expensive in-house production facilities, many companies opt to outsource manufacturing to lower-cost regions or third-party manufacturers. This allows them to avoid the high fixed costs associated with factory operations.
Real-World Example: Apple significantly reduces its fixed costs by outsourcing manufacturing to companies like Foxconn in China, which manages production facilities on Apple’s behalf, saving on infrastructure and labor costs.
By utilizing strategies such as outsourcing, renegotiating leases, automating processes, and leveraging flexible business models, companies can effectively reduce fixed costs, improve profitability, and increase operational efficiency.
How to Account Fixed Cost in Balance Sheet (Statement of Financial Position)?
Fixed costs are usually not directly listed on the Balance Sheet (Statement of Financial Position). The balance sheet primarily reflects a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a given point in time. However, certain fixed costs, such as long-term liabilities (e.g. loans or leases) and depreciation, are indirectly represented. For example, fixed assets like property, plant, and equipment are listed as assets on the balance sheet, and these assets are subject to depreciation, which is an accounting method for spreading the cost of a fixed asset over its useful life. Depreciation reduces the book value of these assets, impacting both the total value of assets and equity.
Long-term liabilities related to fixed costs such as a lease or a loan for capital equipment recorded under non-current liabilities on the balance sheet. These obligations represent fixed costs the company must pay over a period of time. The ongoing portion of fixed costs that relate to current expenses, such as rent or insurance, are typically reflected in the income statement (profit and loss statement) as expenses. Therefore, while fixed costs themselves don’t directly appear on the balance sheet, their impact is seen through the depreciation of assets and the recording of related liabilities.
How to Account Fixed Cost in Income Statement (Statement of Profit and Loss)?
Fixed costs are accounted for in the income statement (Statement of Profit and Loss) as part of operating expenses. These costs are incurred regardless of the level of production or sales and are listed under headings such as administrative expenses, selling expenses, or general expenses. Fixed costs include items like rent, salaries, insurance, and depreciation, which are critical to running the business. Unlike variable costs, fixed costs do not fluctuate with sales or production levels and remain consistent over the reporting period.
Following are list of common fixed costs and where they appear in the Statement of Profit and Loss (Income Statement),
- Rent Expense – Operating Expenses or SG&A
- Salaries (Fixed) – Operating Expenses or Personnel Costs
- Insurance Premium – Operating Expenses or General Expenses
- Depreciation – Depreciation and Amortization or Operating Expenses
- Utilities (Fixed Portion) – Operating Expenses
- Amortization of Intangible Assets – Depreciation and Amortization or Operating Expenses
- Equipment Leasing Costs – Operating Expenses or Rent and Lease Expenses
In the income statement, fixed costs are subtracted from gross profit to determine the operating profit (or EBIT – Earnings Before Interest and Taxes). For example, after accounting for revenue and the cost of goods sold (COGS), which include variable costs, fixed costs are listed as operating expenses. This breakdown provides insight into how much of the company’s revenue is consumed by fixed obligations and helps assess its profitability. Properly categorizing and accounting for fixed costs in the income statement ensures accurate financial reporting and aids in evaluating the business’s operational efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1 – What are Examples of Fixed Costs?
Common examples include rent, equipment leases, depreciation, insurance premiums, and salaried employee wages.
Q2 – Why Are Fixed Costs Important?
Fixed costs are critical for budgeting and financial planning as they represent baseline expenses that must be covered for the business to operate.
Q3 – How Do Fixed Costs Affect the Break-Even Point?
Higher fixed costs result in a higher break-even point, requiring more sales to cover expenses.
Q4 – Can Fixed Costs Change Over Time?
Yes, fixed costs can change due to factors like lease renegotiations, inflation, or decisions to scale operations.
Q5 – How Can a Business Reduce Fixed Costs?
Businesses can reduce fixed costs by outsourcing, automating processes, renegotiating leases, or switching to variable cost models.
Q6 – Are Fixed Costs Always Non-Controllable?
While many fixed costs are non-controllable in the short term, some, like lease agreements, can be adjusted in the long term.
Q7 – What is the Impact of Fixed Costs on Operating Leverage?
High fixed costs increase operating leverage, meaning profitability rises significantly with increased sales but also adds risk during downturns.
Q8 – Are Fixed Costs Always Necessary?
Fixed costs are often unavoidable in operating a business, but companies can strategically evaluate whether some fixed costs can be converted into variable costs.
Q9 – What Industries Have High Fixed Costs?
Industries like manufacturing, airlines, and telecommunications typically have high fixed costs due to significant investments in infrastructure and equipment.
Q10 – What are Semi-Fixed Costs?
Semi-fixed costs are expenses that remain constant within a certain range but can change once a production threshold is crossed, such as utility costs with high usage.
Q11 – How Do Fixed Costs Affect Pricing Decisions?
Fixed costs play a key role in pricing strategy, as businesses need to set prices that cover both fixed and variable costs to ensure profitability.
Q12 – Does Fixed Costs Impact Cash Flow?
Yes, fixed costs create consistent cash outflows that must be managed carefully, especially during periods of low revenue.
Q13 – What Happens to Fixed Costs in the Long Term?
Over time, fixed costs may become more variable as companies restructure or negotiate new terms for rent, salaries, or other long-term expenses.
Q14 – How Do Fixed Costs Affect Margins?
High fixed costs can squeeze profit margins if sales volume is low, but they can improve margins significantly when sales volumes are high.
Q15 – Can Fixed Costs Be Eliminated?
While some fixed costs are essential, others can be reduced or eliminated through strategic decisions, such as shifting to remote work to avoid office rent.
Q16 – How Are Fixed Costs Relevant in a Shutdown Decision?
Fixed costs are critical when deciding whether to shut down operations temporarily, as they must be paid even if production halts.
Q17 – What is the Relationship Between Fixed Costs and Capacity Utilization?
High fixed costs encourage businesses to maximize capacity utilization to spread costs over more units and achieve profitability.
Read More:
- Variable Cost – Explanation, Formula, Calculation, Examples
- Marginal Cost – Explanation, Formula, Curve, Examples
- Incremental Cost – Explanation, Examples, Formula
- Sunk Cost – Definition, Explanation, with Examples