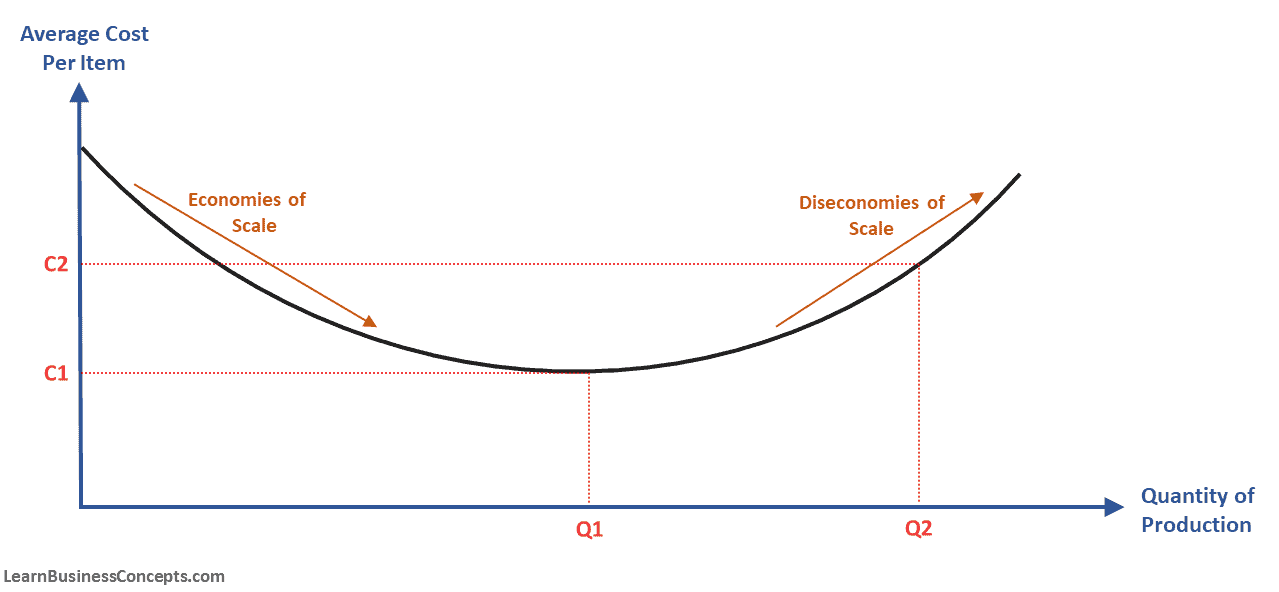
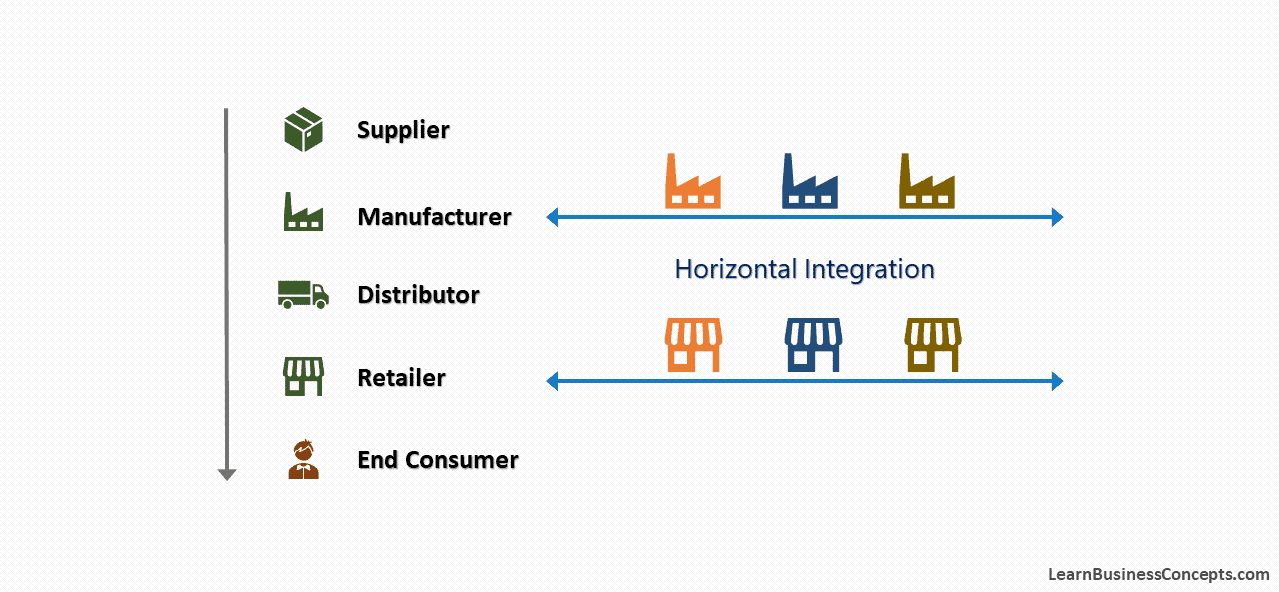
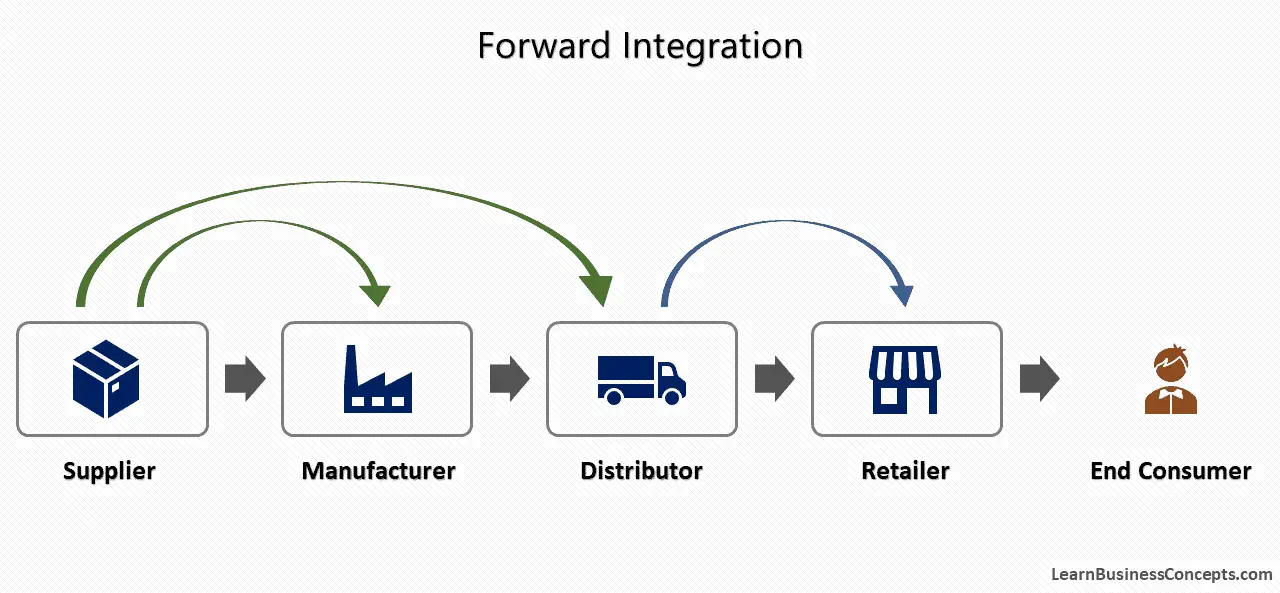
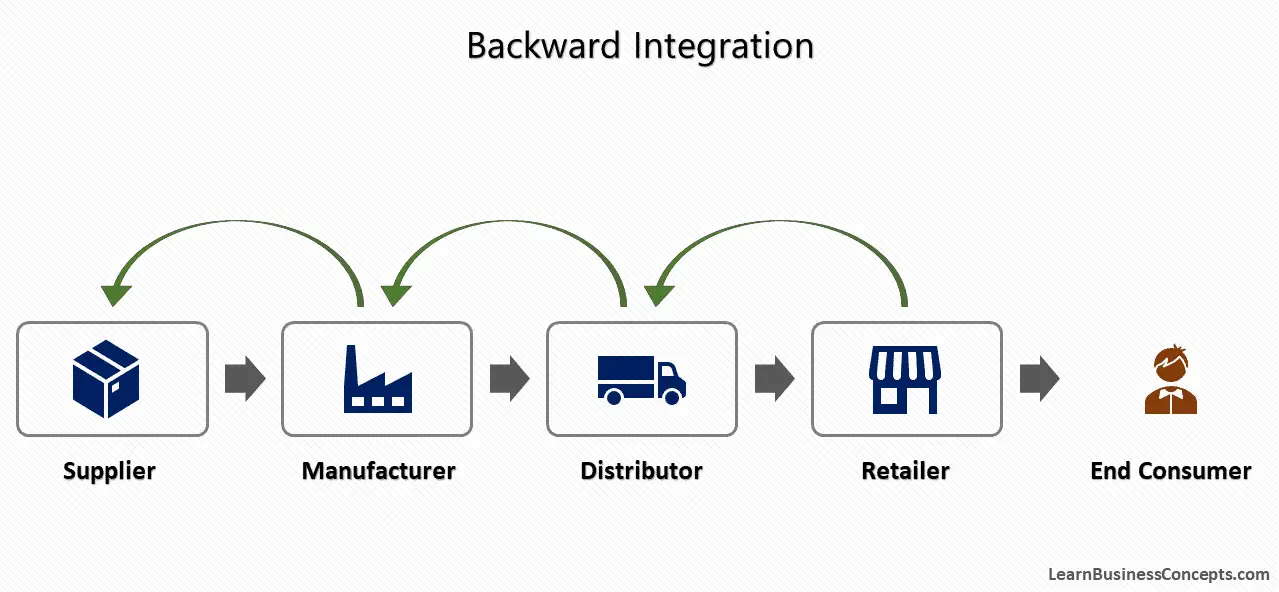
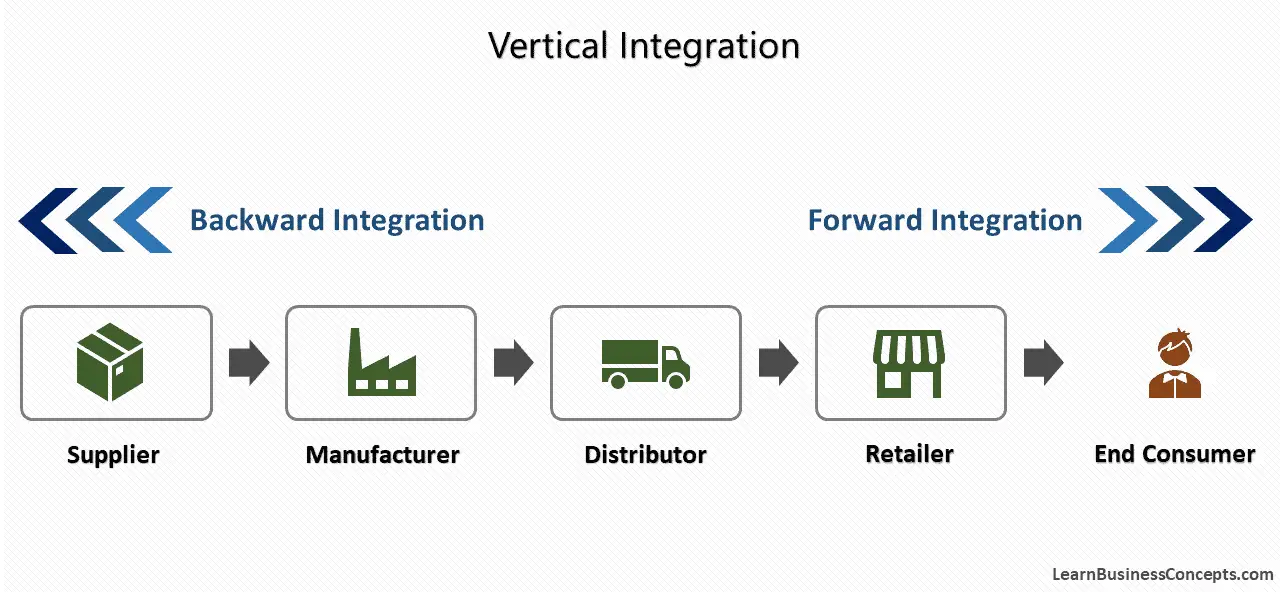
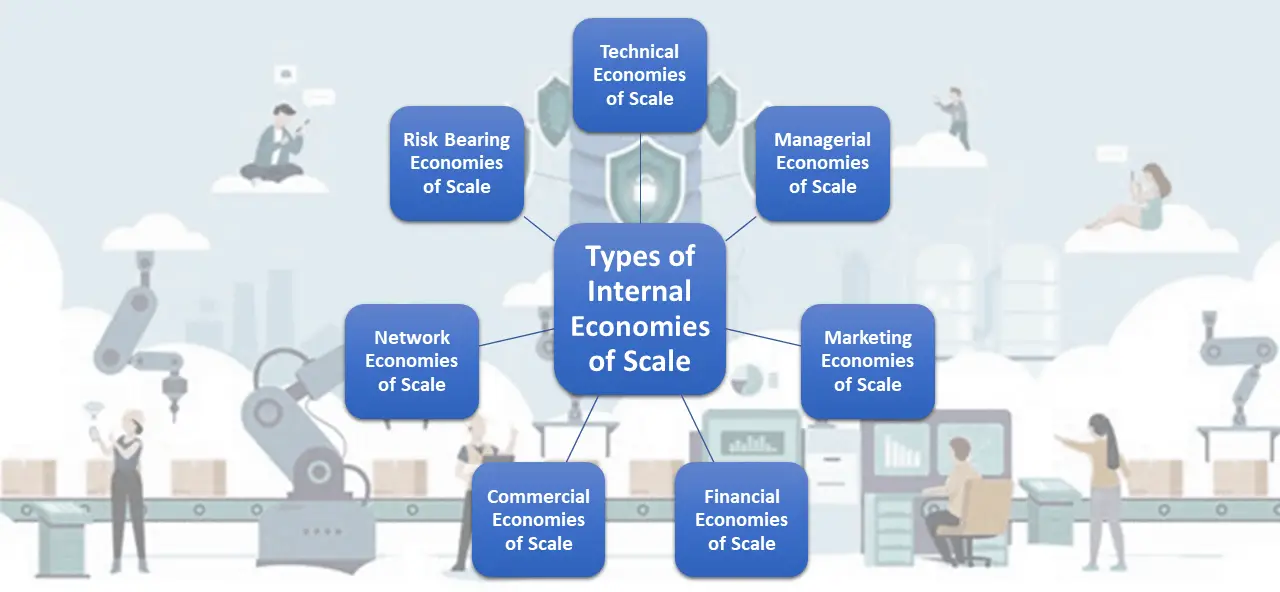
Economies of Scale: Definition, Types, Internal, and External
Economies of scale is an important concept in economics and business strategy, offering companies the opportunity to achieve significant cost advantages as they expand their output. This occurs due to the strong relationship between...