Porter’s Five Forces: Advantages and Disadvantages
Table of Contents
- Purpose of Porter’s Five Forces
- Advantages (Pros / Benefits) of Porter’s Five Forces
- Disadvantages (Cons / Drawbacks) of Porter’s Five Forces
- Explanation of Porter’s Five Forces
- How to use Porter’s Five Forces to Enter a New Market
- Impact of the Digital Disruption on Porter’s Five Forces
- Making Strategic Decisions with Porter’s Five Forces
Porter’s Five Forces is a simple framework to analyze the competitive position of the company. This will demonstrate how industry-related forces affect your company’s performance.
Purpose of Porter’s Five Forces
Porter’s Five Forces is a competitive position analysis tool. Primary purpose of this model is to analyze the competitive dynamics of an industry and assess its attractiveness for profitability. There are five forces of competition which examines with this model – threat of new entrants, bargaining power of suppliers, bargaining power of buyers, threat of substitute products or services, and rivalry among existing competitors.
This analysis provides information to companies to identify strategic opportunities, anticipate competitive threats, and formulate effective strategies to enhance the competitive advantage within the industry. Simply, porter’s five forces analysis business concept demonstrates how industry-related forces affect your company’s performance. If the competitive forces are strong then it is unlikely for an industry to be profitable.
Advantages (Pros / Benefits) of Porter’s Five Forces
1) Helps to Estimate the Competition in the Industry
Porter’s five forces help to measure the threat of new entrants, the threat of substitution, supplier bargaining power, and buyer bargaining power. All of these will sum up to provide the competitive rivalry of the industry. This will support the company to understand the current competition of the industry to adjust the corporate strategy accordingly.
2) Showcase where the Strengths and Threats Exist
Porter’s five forces provide the output of understanding the supplier and buyer forces with risk of new entrants and substitute products. This will enable the senior management to find out where does the company’s strengths place in and where does the threat exist. Management will be able to take precautionary actions for the threats while enhancing the strengths more.
3) Identify which Entities Holding the Power
There are three entities to which Porter’s Five Forces are related. Those are suppliers, buyers (consumers), and competitors. This analysis will provide insights into which are entities hold more power and less power. This will enable the companies to make decisions on the best strategies to handle these entities.
4) Display Opportunities to Expand the Business
Porter’s five forces provide the power of suppliers and buyers in the industry. This will help the company to make decisions on whether to proceed with verticle integration to acquire suppliers and buyers to reduce their power and expand the business. Simply the business can conduct the forward integration to acquire their consumer side of the value chain, and/or backward integration to acquire their supplier side of the value chain, according to the information provided from the five forces.
Also, this will help the company on having insights into the competitive rivalry, where the company can seek the possibility of conducting horizontal integration to acquire a competitor, to reduce the risk of competition.
5) Assist to Understand the Corporate Risk
Porter’s five forces will provide valuable insights into the power of suppliers, power of consumers, and power of competitors. All of this information will help the company to understand the corporate risk of the business, and make responses to those risks.
6) Helpful in Making Corporate Strategy and Vision
The corporate strategy helps the company to make strategic decisions by looking across all aspects of the business to determine how best possible to create the most value. Porter’s five forces will provide valuable information for this to make the corporate strategy more accurate by considering the impact of the external forces.
Disadvantages (Cons / Drawbacks) of Porter’s Five Forces
1) Limitation on the Composition
Porter’s five forces only concentrate on the power of suppliers, power of consumers, substitution, and new competition. But other technological factors and business strategies that impact the company are not considered. As an example, technological evolvement is one of the biggest threats for all companies across all industries. Also, external forces such as government policies, taxation policies, cross-border business risk, environmental impact, etc are not considered. This can be a major aspect of the growth or else the downfall of the company.
2) Unavailability of Quantitative Dimensions
There is no built-in method to conduct the quantitative analysis of the external factors. This tool does not provide a quantitative idea of the depth and impact of the five forces described. Also, there is no quantitative idea of which forces out of the five are most important and least important.
3) Impractical to use on Large Companies
Practically it is difficult to use this analytical framework for a company that has a large product portfolio and operates in different market segments. This framework is meant to analyze a company in a single industry.
4) Can Be Used as Starting Point for the Analysis
Porter’s five forces is a simple tool that contains five external factors which can be beneficial or else drawback for a company. This can be used only as a tool for the starting point of a deep investigation. This framework provides the initial understanding of the company’s competitive position in an industry. This framework can not alone provide an in-detail investigation of the company.
5) Not Applicable for All Industries Universally
Porter’s five forces practically can not be used for some industries. As an example, not-for-profit companies can not use this method for the analysis. Also, companies conducting activities like R&D will not have much benefit from this.
6) Not Consider Business Risk Factors
External business risk factors like foreign exchange instabilities, natural catastrophes, methods of financing, legal constraints, fast technological evolutions, fluctuations in interest rates, etc not considered for this framework. These are major factors in determining the business risk of the company.
Explanation of Porter’s Five Forces
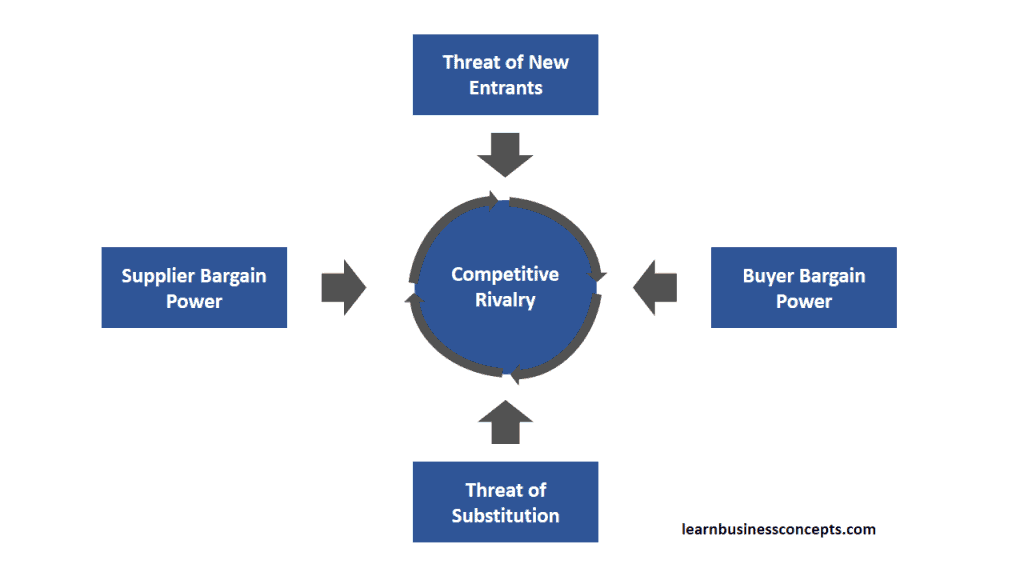
1. Threat of New Entrants
This force determines the relative easiness to enter a particular industry. The company’s risk of market share dilution depends on this force. The power of this force depends on the difficulty of a new company to offer the same product and enter the industry. This is also called as barriers of entering into the industry,
Typical example for this is the airline industry which has high barriers to entry. These are typically the high capital requirements for aircraft, strict regulatory requirements, and established brand loyalty among customers.
Read more about Porter’s Five Forces Model Applied To Airline Industry with Real World Example. This article contains real world examples of major airlines in the world like American, Emirates, British Airlines, Easy Jet, Delta, Southwest, and United.
2. Buyer Bargain Power
This force evaluates the influence customers have on prices, product choices, and terms of sale. Buyers can demand lower prices or higher quality products when buyers have substantial power.
Typical example is in the retail industry, large retailers like Walmart wield significant bargaining power over suppliers due to their size and purchasing volume, allowing them to negotiate favorable terms and lower prices.
Buyer bargain power depends on easiness for the buyer (customer) to drive the prices down. There are four drives of this power,
- Cost of Switching Suppliers – Customer’s power of bargain will be more if switching cost is less.
- Number of Sellers versus Number of Customers – Customer’s power of bargain will be more if the relative number of customers is less than the suppliers.
- Product Differentiation – Customer’s power of bargain will be more if products are less differentiated.
- The Threat of Forward Integration – Customer’s power of bargain will be more there is less threat of forwarding value chain integration.
3. Threat of Substitution
This force determines the likelihood of the product being replaced. Simply, this depends on how much is it easy for the customer to find a similar product in the market. The threat of substitutes arises when customers can easily switch to alternatives, putting pressure on prices and profitability.
Most common example is the beverage industry. In this industry, consumers have various options such as soft drinks, juices, tea, and coffee, leading to intense competition and price sensitivity.\
Also clothing industry faces a moderate threat from substitute products. Substitutes include alternative clothing options such as second-hand apparel, rental services, and online marketplaces for pre-owned clothing. These alternatives cater to price-conscious consumers, sustainable fashion enthusiasts, and those seeking unique pieces.
You can read more about Porter’s Five Forces: Applied To Clothing / Fashion Industry with Real World Examples. This article contains the detail application of Porter’s Five Forces to Clothing / Fashion Industry with good explanation through examples.
4. Supplier Bargain Power
Bargain power of suppliers related to how much influence the supplier has to demand the price, quality, and delivery timelines. When suppliers have significant leverage, they can dictate terms to the industry players.
One of the classic example is with the automobile manufacturing industry. Specialized component suppliers may have high bargaining power if they provide unique or critical parts, giving them leverage over automakers. Another example is Starbucks, which has established strong relationships with coffee bean suppliers worldwide, often working directly with farmers through its ethical sourcing programs.
You can read more about Porter’s Five Forces Applied To Starbucks with Examples. This article contains detailed description of each force applied to Starbucks Corporation with some good real world examples.
5. Competitive Rivalries
The competitive rivalry of Porter’s Five Forces Analysis is related to how intense the competition of the industry as a whole. This force depends on all four previous forces. Factors such as market concentration, differentiation, and exit barriers influence the level of rivalry. Market attractiveness reduces when competitors offer undifferentiated products/services. The company should be aware of its competitors to ensure its market share.
A good example is the smartphone industry. It is characterized by fierce rivalry among major players like Apple, Samsung, and Huawei, leading to continuous innovation, aggressive marketing, and price competition to gain market share.
Also the banking industry is facing intense competition. Competitive factors include interest rates, fees, range of products and services, customer service, and technological innovation. Banks compete for customers and market share through aggressive marketing strategies and differentiation in terms of offerings and customer experience.
You can read more about Porter’s Five Forces: Applied To Banking Industry with Real World Examples to understand how this analysis can be applied to the banking industry.
How to use Porter’s Five Forces to Enter a New Market
When entering to a new market involves conducting a comprehensive analysis to assess the attractiveness and competitiveness of the industry. Below is a step-by-step guide on how to apply Porter’s Five Forces framework for market entry,
1. Identify the Market
Define the market you intend to enter, including its scope, size, and characteristics. Understand the industry dynamics and key players operating within the market.
2. Evaluate the Threat of New Entrants
You should assess barriers to entry such as capital requirements, economies of scale, brand loyalty, and regulatory restrictions. Likelihood of new competitors should be determined when entering the market. Also should consider the potential impact on industry profitability.
3. Analyze the Bargaining Power of Suppliers
Suppliers should be identified within the industry and should be evaluated their bargaining power based on factors such as the availability of alternative suppliers, the importance of their inputs, and the concentration of suppliers. Also need to assess the potential impact of supplier bargaining power on your ability to enter the market and maintain profitability.
4. Assess the Bargaining Power of Buyers
You have to analyze the bargaining power of buyers, including their ability to negotiate prices, demand quality improvements, or switch to alternative products or services. You should consider factors such as buyer concentration, switching costs, and the availability of substitutes that may influence buyer power.
5. Evaluate the Threat of Substitute Products or Services
In this step, you have to identify substitute products or services that fulfill similar needs or offer comparable benefits to customers. Also need to assess the availability, quality, and pricing of substitutes, as well as the ease with which customers can switch to alternatives.
6. Assess Rivalry Among Existing Competitors
You should analyze the competitive intensity within the industry, considering factors such as the number and size of competitors, differentiation strategies, and market concentration. It is needed to evaluate the level of rivalry and its potential impact on your market entry strategy, including pricing, marketing, and positioning strategies.
7. Develop Entry Strategies
Based on the insights gained from Porter’s Five Forces analysis, identify strategic opportunities and potential risks associated with entering the market. It is essential to develop entry strategies that leverage your strengths, mitigate competitive threats, and capitalize on industry dynamics. You have to consider factors such as market positioning, pricing strategy, distribution channels, and marketing tactics to differentiate your offering and gain a competitive advantage.
8. Monitor and Adapt
It is needed to continuously monitor changes in industry dynamics, competitive forces, and market trends to adapt your market entry strategy accordingly. You have to stay vigilant for new threats and opportunities that may arise over time, and be prepared to adjust your approach to remain competitive in the market.
Impact of the Digital Disruption on Porter’s Five Forces
Digital disruption has significantly impacted the application of Porter’s Five Forces framework by altering industry dynamics, reshaping competitive landscapes, and introducing new sources of competitive advantage. Here’s how digital disruption has influenced each of the five forces:
1. Threat of New Entrants
Digital technologies have lowered barriers to entry in many industries by reducing the need for physical infrastructure, enabling startups to enter markets with innovative business models and disruptive technologies. Platforms like e-commerce marketplaces, app stores, and digital content platforms have democratized access to markets. This allows the new entrants to reach customers globally with minimal upfront investment.
The classic example is the rise of digital platforms like Airbnb and Uber has transformed industries traditionally dominated by established players, challenging incumbents and reshaping market dynamics.
3. Bargaining Power of Buyers
Digital channels have shifted power to buyers by increasing price transparency, expanding product choices, and enabling comparison shopping across multiple vendors. Online reviews, social media, and peer recommendations have given power to the buyers with information and insights. This makes them more discerning and demanding in their purchasing decisions.
As an example online marketplaces like Amazon and Alibaba give buyers access to a vast array of products from multiple sellers, allowing them to compare prices, read reviews, and make informed purchasing decisions, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
4. Threat of Substitute Products or Services
Digital disruption has accelerated the emergence of digital substitutes and alternatives, posing a significant threat to traditional products and services. Disruptive technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and augmented reality have enabled the creation of innovative solutions that compete directly with existing offerings.
As an example, streaming services like Netflix and Spotify have disrupted traditional media and entertainment industries by offering convenient, on-demand access to content, posing a threat to traditional cable TV and physical media formats.
2. Bargaining Power of Suppliers
Digital technologies have empowered suppliers by providing them with new channels to reach customers directly. This has reduced their dependence on traditional distribution channels and intermediaries. Suppliers with unique digital capabilities or proprietary technology may have increased bargaining power. They can offer differentiated products or services that are difficult for buyers to replicate or substitute.
As an example software-as-a-Service (SaaS) providers like Netflix, Canva, Shopify, Zoom, can leverage subscription-based models to establish recurring revenue streams and negotiate favorable terms with customers, enhancing their bargaining power.
5. Rivalry Among Existing Competitors
Digital disruption has intensified competition by lowering barriers to entry, enabling agile startups to challenge incumbents and disrupt established markets. Digital natives and tech giants leverage data analytics, machine learning, and digital platforms to rapidly innovate, iterate, and scale, driving incumbents to respond with their own digital initiatives.
As an example, fierce competition among technology companies like Apple, Google, and Microsoft fuels continuous innovation in smartphones, software, and cloud services, resulting in rapid product development cycles and pricing pressures.
Making Strategic Decisions with Porter’s Five Forces
You can utilize the Porter’s Five Forces framework to make strategic decisions to identify competitive forces and their implications. By assessing the threat of new entrants, businesses can anticipate potential disruptions and invest in barriers to entry to protect market share. For example, established pharmaceutical companies invest in R&D and regulatory compliance to deter new entrants.
Analyzing the bargaining power of suppliers enables companies to negotiate favorable terms and secure reliable supply chains. For instance, automobile companies may establish long-term partnerships with key suppliers to ensure access to critical components.
Understanding the bargaining power of buyers helps businesses tailor pricing strategies and enhance customer value propositions. Retailers use loyalty programs and personalized offerings to retain customers and mitigate price sensitivity. Also the evaluation of the threat of substitutes allows companies to differentiate their products and services to minimize substitution risks. Beverage companies invest in branding and product innovation to create unique value propositions and reduce the appeal of substitutes.
Lastly, assessing rivalry among existing competitors informs strategic positioning and resource allocation. Smartphone manufacturers like Apple, Samsung, Nokia, Oppo, differentiate through product features and marketing strategies to gain market share amidst intense competition.
Businesses can make informed strategic decisions that mitigate risks, capitalize on opportunities, and enhance long-term competitiveness in their industries by leveraging insights from Porter’s Five Forces analysis.
Read More About Porter’s Five Forces,
- Porter’s Five Forces: Explanation with Industry Examples
- Porter’s Value Chain: Primary & Support/Secondary Activities
- How to Apply Porter’s Five Forces to Industry / Business: Step-By-Step Simple Detail Guide with Examples
- Porter’s Five Forces Model: Applied To Airline Industry with Real World Examples
- Porter’s Five Forces: Applied To Fast Food Restaurants Industry with Real World Examples
- Porter’s Five Forces: Applied To Starbucks with Examples
- Porter’s Five Forces: Applied To Banking Industry with Real World Examples
- Porter’s Five Forces: Applied To Clothing / Fashion Industry with Real World Examples