Year-Over-Year (YoY) Analysis: Advantages and Disadvantages
Table of Content:
- Definition of Year Over Year (YoY) Analysis
- Advantages (Pros / Positives / Benefits) of Year Over Year Analysis (YoY)
- Disadvantages (Cons / Negatives / Drawbacks) of Year Over Year Analysis (YoY)
- Why YoY Analysis is Famous in the World in Many Industries
- How to Calculate Year Over Year (YoY) using Formula – with Examples
- Excel Template for Calculate Year Over Year Analysis (YoY) – with Sample Calculation
- Real-World Examples of Companies that have Effectively Leveraged YoY Analysis
- Usage of the YoY Output to Grow the Business
- Common Business and Financial Metrics of YoY
- Alternative Methods for YoY Analysis
- What is a Good YoY Growth Rate
- Industry Specific Averages of YoY Growth Rate
- Importance and Usage of Year Over Year (YoY)
- Difference Between Year-Over-Year, Month-Over-Month, and Quarter-Over-Quarter
- FAQs
Definition of Year Over Year (YoY) Analysis
Year-Over-Year (YoY) is a type of financial analysis used to compare data between time series. It is a data comparison for a specific period with the same period from the previous year. Year-Over-Year (YoY) analysis is used in economic and investment analysis and helps to comprehend the growth pattern from year to year.
YoY analysis helps to calculate the percentage change between a certain metric in the current year and the same metric in the previous year. This helps to eliminate seasonal variations and provides a clearer understanding of the underlying trend.
As an example, an investor would be keen to compare the performance of investment returns on a year-over-year basis to decide whether to invest or not, understand the growth pattern, and also choose the best with multiple investment options.
Advantages (Pros / Positives / Benefits) of Year Over Year Analysis (YoY)
1. Helps to analyze the annual, quarterly as well as monthly growth trend based on financial need
YoY analysis helps in identifying long-term trends by comparing performance over the same period (ex: month) in different years. This can reveal whether the performance consistently improving, declining, or remaining stable over time.
As an example, Quarter 4 in any year (October, November, December) is a comparatively high performing quarter for most companies. Company management can do a YOY analysis to compare the current year’s Quarter 4 with the last year’s Quarter 4 to understand whether the company is growing (considering the seasonal factor), rather than comparing Quarter 4 with Quarters 3, 2, and 1 in the same year.
2. Calculates the growth trends by mitigating seasonality factors
YoY analysis helps in eliminating the effects of seasonal variations or one-time events that may distort monthly or quarterly comparisons. Also, YoY analysis allows for the detection of seasonal patterns or fluctuations that may occur within a year. Businesses can better understand the cyclicality of their operations and adjust strategies accordingly by comparing data from the same season in different years.
As an example: Most companies expected to improve sales in the December month of any year due to the Christmas season. Comparing the sales data of the December month between years will be more beneficial for the investors rather comparing the yearly total. Investors can easily figure out the revenue trend and growth while considering the seasonal factor.
3. The YoY analysis method is a simple calculation. This does not require complex calculation methods
Simply the YoY can be calculated using one of the below approaches,
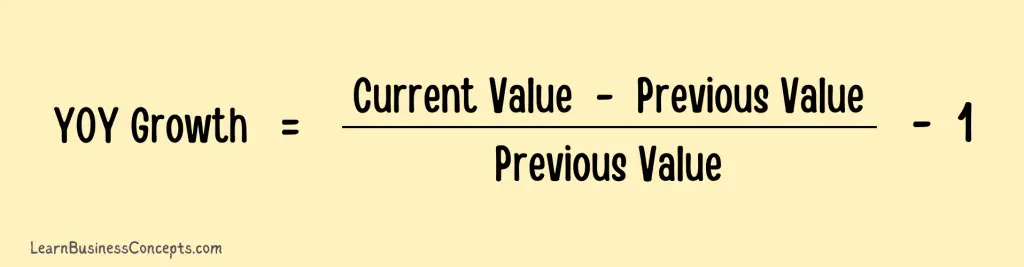
Approach 1: current year value divided by the previous year’s value, subtract the result from 1
Approach 2: current value minus the previous value and then divide the result by the previous value
Also YoY facilitates the simple evaluation of growth rates by comparing the percentage change in a metric from one year to the next. This helps in assessing the pace of growth or decline and determining whether it meets organizational objectives in a simplified manner.
4. YoY helps benchmark the performance of the company
Company will compare the performance on a year-over-year basis and will benchmark against past performance, industry standards, or competitors’ performance. This helps businesses assess their progress and competitiveness in the market.
5. YoY calculation results in a percentage value which easily comparable
As an example, if an investor does a YoY calculation of multiple investments, all the calculations return the percentages values, which the investor can easily compare and make decisions. Investors often rely on YoY analysis to gauge the financial health and growth prospects of a company. Consistent improvement in key metrics over multiple years can instill confidence and attract investment.
6. YoY is a popular and effective way to evaluate the financial statistics of a company and also evaluate the investment returns. Trend and growth are directly visible in the analysis
YoY analysis serves as a tool for performance evaluation by highlighting areas of strength and weakness over time. It enables businesses to identify areas that require improvement and allocate resources accordingly.
7. Provide direction to business strategy
YoY analysis provide the data of percentage change between a certain metric in the current year and the same metric in the previous year. This data will help the senior management to craft the business strategy correctly. As an example, if the YoY sales growth is high but the YoY Revenue growth is low, it will indicate an issue in the cost center which the senir
Disadvantages (Cons / Negatives / Drawbacks) of Year Over Year Analysis (YoY)
1. Does not provide information on how to improve performance
YoY analysis provides a historical comparison but may lack context from external factors such as changes in market conditions, economic trends, or regulatory environments. The analysis may not fully capture the reasons behind performance changes without considering these factors. YoY only provides the percentage value of the growth compared with the previous time-frame given.
2. Not practical for startup companies since no previous stats are available
Year-Over-Year (YoY) analysis is often impractical for startup companies due to the absence of historical data. Since startups typically operate for less than a year before requiring detailed performance reviews, they lack the previous year’s statistics necessary for YoY comparisons. This absence makes it impossible to measure growth, performance, or trends over a full year, which is essential for traditional YoY analysis.
Additionally, startups often undergo rapid changes in their early stages, including shifts in business models, target markets, and product offerings. These frequent changes can make YoY comparisons less meaningful, as the business context may differ significantly from one year to the next. Instead, startups tend to focus on shorter-term metrics like Month-Over-Month (MoM) growth, which provide more immediate insights and allow them to adapt quickly to market demands and operational challenges.
3. Does not consider inflation into the account
Inflation is the general increase in the prices of goods and services in an economy. Inflation will impact YoY comparisons of financial metrics such as revenue or profit. Apparent growth may be overstated, leading to a misinterpretation of financial performance without adjusting for inflation.
4. Could be difficult in identifying outliers
Outliers, such as one-time events or exceptional circumstances, can significantly impact YoY comparisons. Identifying and appropriately adjusting for these outliers is challenging and may distort the interpretation of performance trends.
5. The YoY method can compare only two measured events at a single calculation
YoY analysis can only compare two measured events at a given time. As example, it can only provide the percentage based outcome.
6. Could mask the seasonal variations
YoY analysis can mask short-term seasonal shifts or unusual variations within a single year. For instance, if a business experiences an unexpected surge or drop in sales due to a unique event, such as a one-time promotion or an economic downturn, YoY comparisons might overlook these anomalies because they focus on annualized trends. This can lead to an incomplete understanding of current performance dynamics, as the analysis smooths out short-term fluctuations, potentially masking important seasonal or temporary changes that could impact strategic decisions.
7. Challenges the accuracy of reporting if changes in accounting methods
Changes in accounting methods or reporting standards between years can affect YoY comparisons. These changes may artificially inflate or deflate YoY performance metrics and will challenge to accurately assess year-over-year changes.
8. Oversimplify the performance evaluation with cyclical nature of business
Some industries or businesses experience cyclical patterns that extend beyond a one-year period. YoY analysis may oversimplify performance evaluation by not accounting for longer-term cycles, leading to misinterpretation of trends.
9. Overemphasis on short-term results
YoY analysis focuses on comparing performance between two specific points in time, which may lead to an overemphasis on short-term results. Businesses may overlook important trends or developments that occur over longer time horizons.
Why YoY Analysis is Famous in the World in Many Industries
Year-over-Year (YoY) analysis is widely applicable across many industries due to its versatility and effectiveness in assessing performance trends over time. The key reason for its widespread use is its ability to provide a clear and straightforward comparison of metrics or indicators between two consecutive years. This simplicity makes YoY analysis accessible and applicable to businesses of all sizes and across various sectors, from retail and manufacturing to finance and healthcare.
YoY analysis helps businesses account for seasonal variations and short-term fluctuations that may occur within a year. YoY analysis enables organizations to identify underlying performance trends and patterns, separate from transient factors by comparing data from the same time period in different years. This is especially crucial in industries where demand or revenue fluctuates seasonally, such as retail during holiday seasons or agriculture during growing seasons.
Moreover, YoY analysis facilitates bench-marking against past performance, industry standards, or competitors’ performance, providing valuable insights into a company’s relative position and progress over time. This allows businesses to evaluate their performance trajectory, set realistic goals, and make informed strategic decisions. Additionally, investors often rely on YoY analysis to assess the financial health and growth potential of companies, making it a vital tool for maintaining investor confidence and attracting capital.
Furthermore, YoY analysis supports forecasting and planning by helping businesses anticipate future trends based on historical data. By understanding historical performance patterns, organizations can make more accurate predictions about future outcomes and allocate resources effectively. This enhances decision-making processes and enables proactive management of business operations, ultimately contributing to long-term success and sustainability.
How to Calculate Year Over Year (YoY) using Formula – with Examples
There are two approaches to calculating the Year-Over-Year (YoY),
Approach 1: Current year value divided by the previous year’s value, subtract the result from 1
Example (a): If a return on investment was $10,000 in Year 2 and $12,500 in Year 2, the YOY growth can be calculated as ($12,500 / 10,000) – 1, resulting in 25%.
Example (b): Clothing company Year 1 December month sales were $63,000 and Year 2 December month sales were $78,000. The YOY growth can be calculated as ($78,000 / $63,000) – 1 = 23.8%.
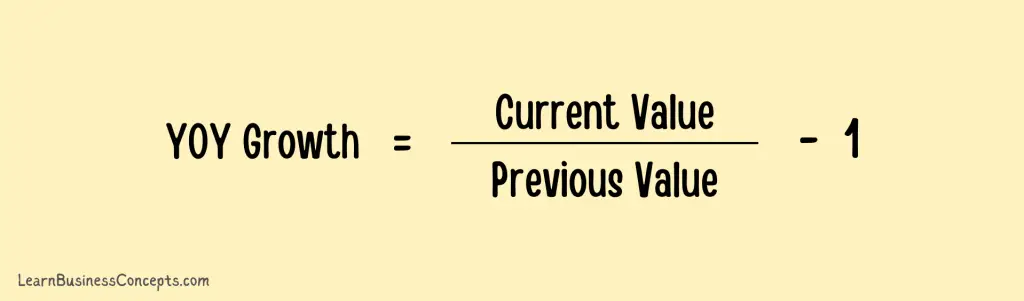
Approach 2: Current value minus the previous value and then divide the result by the previous value
Example (a): if a return on investment was $10,000 in Year 2 and $12,500 in Year 1, the YOY growth can be calculated as ($12,500 – $10,000) / 10,000, resulting in 25%.
Example (b): Clothing company Year 1 December month sales were $63,000 and Year 2 December month sales were $78,000. The YOY growth can be calculated as ($78,000 – $63,000) / $63,000 = 23.8%.
You can also refer to the sample Excel (spreadsheet) template which contains the monthly Year-Over-Year (YOY) calculation for three consecutive years. This is a fully editable file where you can download, comprehend, and amend this according to your preference.
Excel Template for Calculate Year Over Year Analysis (YoY) – with Sample Calculation
The below sample Excel (spreadsheet) template contains the monthly Year-Over-Year (YOY) calculation for three consecutive years as a sample. This is a fully editable file where you can download, comprehend, and amend this according to your preference.
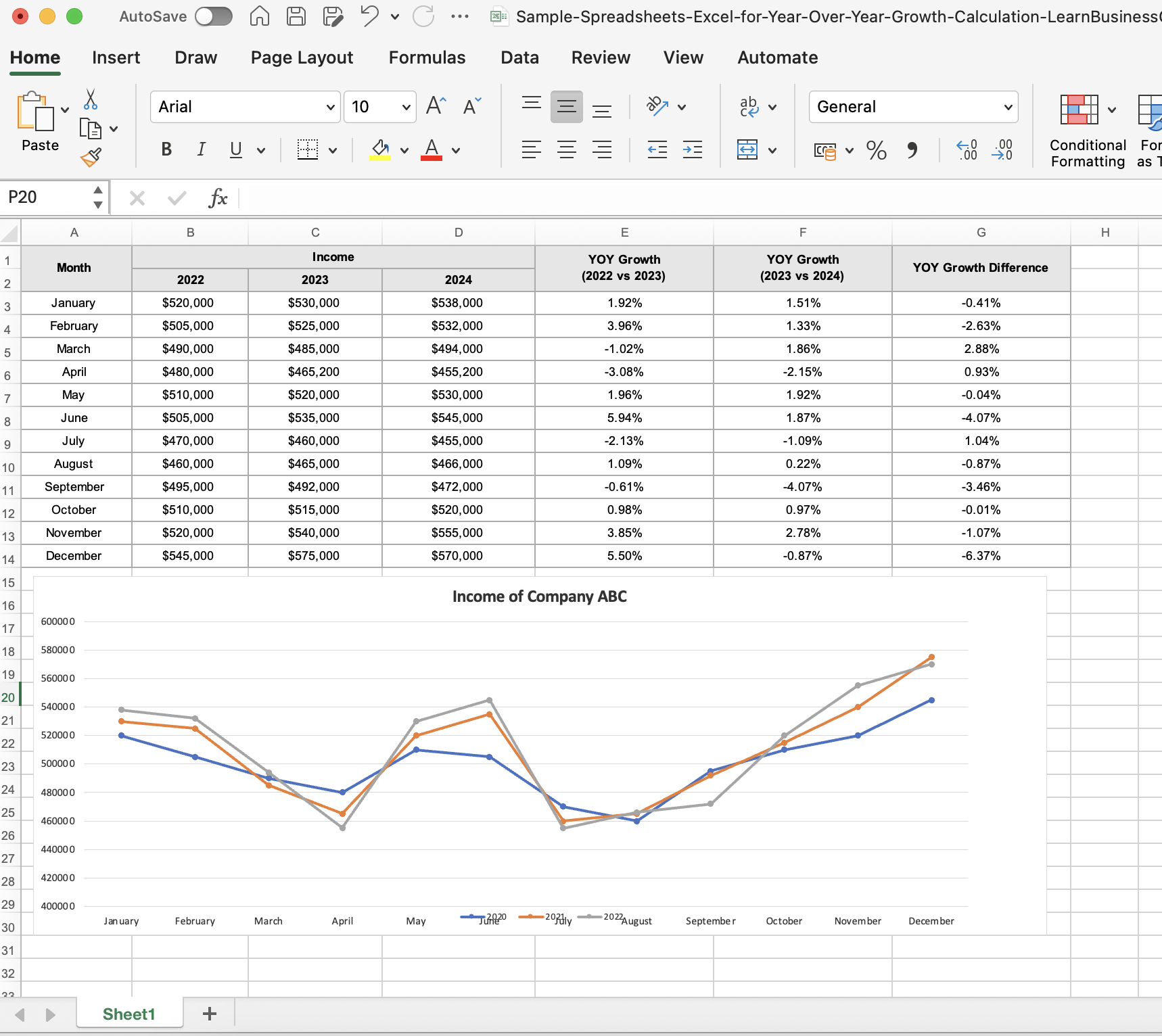
Real-World Examples of Companies that have Effectively Leveraged YoY Analysis
1. Amazon
- Example: Amazon is known for its data-driven approach to decision-making, and YoY analysis plays a significant role in its strategy. The company regularly analyzes YoY trends in sales, customer engagement, and operational metrics to identify growth opportunities, optimize pricing strategies, and enhance customer experience.
- Impact: By leveraging YoY analysis, Amazon has been able to make data-driven decisions that fuel its continuous growth and expansion into new markets. For example, it uses YoY data to refine its inventory management, improve product recommendations, and tailor its marketing efforts to specific customer segments.
- Reference: Amazon stated in their news release in aboutamazon.com that “AWS segment sales increased 13% year-over-year to $90.8 billion“.
2. Netflix
- Example: Netflix relies heavily on data analytics to drive content creation, user engagement, and subscriber growth. YoY analysis is integral to its strategy for evaluating the performance of original content, tracking subscriber churn rates, and identifying emerging trends in viewer preferences.
- Impact: By analyzing YoY trends in viewer engagement and subscription metrics, Netflix can make data-driven decisions about content investments, pricing strategies, and international expansion. For example, it uses YoY data to determine which original series or movies resonate most with viewers and prioritize investments accordingly.
- Reference: Netflix Research Analytics – research.netflix.com
3. Walmart
- Example: As one of the world’s largest retailers, Walmart utilizes YoY analysis extensively to optimize its operations and drive sales growth. The company analyzes YoY trends in sales, inventory turnover, and customer behavior to identify opportunities for improving efficiency, enhancing product assortment, and tailoring promotions.
- Impact: By leveraging YoY analysis, Walmart has been able to make strategic decisions that drive revenue growth and improve customer satisfaction. For instance, it uses YoY data to forecast demand for seasonal products, adjust pricing strategies based on competitor trends, and optimize its supply chain operations to reduce costs.
- Reference: Walmart 2023 Annual Report
4. Google
- Example: Google employs YoY analysis to evaluate the performance of its advertising platforms, measure user engagement across its various products and services, and track trends in online search behavior. By analyzing YoY data, Google can identify emerging market trends, refine its algorithms, and optimize ad targeting strategies.
- Impact: By leveraging YoY analysis, Google can make data-driven decisions that drive revenue growth and enhance user experience. For example, it uses YoY data to identify changes in user search behavior, adjust its algorithms to deliver more relevant search results, and optimize ad placements to maximize click-through rates.
Usage of the YoY Output to Grow the Business
Output of the YoY can be leveraged by gaining valuable insights into performance trends and areas for improvement. It is possible to adjust strategies to capitalize on successful initiatives or address challenges by identifying which metrics are experiencing growth or decline over time.
As an example, if YoY analysis reveals a consistent increase in revenue from a particular product or market segment, you can allocate resources towards expanding those areas further. Conversely, if there’s a decline in profitability, you can investigate the underlying causes and implement corrective actions. Also YoY analysis helps in setting realistic goals and benchmarks for future growth, which enables to make informed decisions and drive sustainable business expansion.
Common Business and Financial Metrics of YoY
Following is the list of common business and financial metrics analyzed on a year-over-year (YoY) basis. These metrics offer valuable insights into different aspects of a business’s performance and are essential for making informed decisions, setting targets, and tracking progress over time.
1. Revenue YoY Growth
This is the percentage change in total revenue from the current period compared to the same period in the previous year. This metric is useful to measure the growth or decline in a company’s top-line revenue. This indicates the company’s ability to generate more revenue over time and assesses the effectiveness of sales and marketing efforts
Revenue YoY Growth Calculation = (Current Year Revenue − Previous Year Revenue) / Previous Year Revenue x 100
2. Profit YoY Growth
This is the percentage change in net profit or earnings from the current period compared to the same period in the previous year. This helps to evaluate the efficiency of operations and management’s ability to generate profits. This metric provides insight into the company’s profitability trends and helps assess overall financial health.
Profit YoY Growth Calculation = (Current Year Profit – Previous Year Profit) / Previous Year Profit x 100
3. Customer Acquisition YoY Growth
This metric reflects the percentage change in the number of customers acquired during the current period compared to the same period in the previous year. This measures the effectiveness of marketing and sales strategies in attracting new customers. Also this metric indicates the company’s ability to expand its customer base, which is crucial for sustainable growth.
Customer Acquisition YoY Growth Calculation = (Current Year New Customers – Previous Year New Customers) / Previous Year New Customers x 100
4. Customer Retention Rate YoY
This reflects the percentage of customers retained from the previous year. This is useful to evaluate the effectiveness of customer service, product quality, and overall customer satisfaction. High retention rates indicate customer loyalty and can lead to increased lifetime value and reduced marketing costs.
Customer Retention Rate YoY Calculation = (Number of Customers at End of Year – Number of New Customers Acquired During Year) / Number of Customers at Start of Year x 100
5. Inventory Turnover YoY
This reflect the number of times inventory is sold or used in a given period, compared to the previous year. This metric helps you to measures how efficiently a company manages its inventory and cash flow. High inventory turnover indicates strong sales and efficient inventory management, while low turnover may suggest excess inventory or slow-moving products.
Inventory Turnover Calculation = Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) / Average Inventory
Inventory Turnover YoY Calculation = (Current Year Inventory Turnover – Previous Year Inventory Turnover) / Previous Year Inventory Turnover x 100
6. Return on Investment (ROI) YoY
This is the percentage change in the return on investment from the current period compared to the same period in the previous year. This is useful to assesses the profitability of investments made by the company. This metric helps to evaluate the effectiveness of investment decisions and capital allocation strategies.
Return on Investment (ROI) YoY Calculation = (Current Year ROI – Previous Year ROI) / Previous Year ROI x 100
7. Employee Productivity YoY
This metrics provides the percentage change in employee productivity, typically measured as revenue or output per employee, compared to the previous year. This is useful to evaluates workforce efficiency and effectiveness. This indicates whether the company is getting more output from its workforce and can help identify areas for improvement in human resource management.
Employee Productivity YoY Calculation = Current Year Revenue or Output per Employe / Previous Year Revenue or Output per Employee x 100
Alternative Methods for YoY Analysis
There are some alternative approaches for YoY Analysis that can be used depending on the specific requirements.
1. Quarter-over-Quarter (QoQ) Analysis
This compares data from one quarter to the previous quarter within the same year. QoQ analysis provides insights into shorter-term trends and fluctuations within the year, whereas YoY analysis offers a broader view of changes over a full year, smoothing out seasonal variations.
2. Month-over-Month (MoM) Analysis
This compares data from one month to the previous month within the same year. MoM analysis offers even shorter-term insights into trends and fluctuations, which can be useful for identifying more immediate changes. However, it may be more susceptible to noise and short-term variations compared to YoY analysis.
3. Trend Analysis
This provides the analysis of data over multiple periods to identify long-term trends and patterns. Trend analysis focuses on identifying and extrapolating patterns over time, regardless of specific year-over-year comparisons. It provides insights into the overall direction of the data but may not capture short-term fluctuations as effectively as YoY analysis.
4. Seasonally Adjusted Analysis
This metric adjusts data to remove the effects of seasonal variations, allowing for more accurate comparisons across different periods. Seasonally adjusted analysis aims to isolate underlying trends by removing seasonal fluctuations, which can be beneficial when comparing data across different seasons or months. YoY analysis, on the other hand, captures both seasonal and non-seasonal changes.
5. Rolling Average Analysis
Calculates the average of data over a rolling period, such as a moving average over the past 3, 6, or 12 months. Rolling average analysis smooths out short-term fluctuations and can provide a clearer picture of trends over time. However, it may not capture the specific year-over-year changes as directly as YoY analysis.
6. Index Analysis
Expresses data relative to a base period or index value, allowing for comparisons across different time periods. Index analysis provides a relative comparison of data over time, which can be useful for tracking relative changes and performance. However, it may not capture the absolute magnitude of changes as YoY analysis does.
YoY analysis provides a broad view of changes over a full year and helps smooth out seasonal variations, but these alternatives offer more granular or specialized perspectives that may be better suited to certain contexts.
What is a Good YoY Growth Rate
YoY growth rates provides the comparative analysis of the growth across several periods. The output of this formula is a percentage which reflects the growth compared with the previous period. Hence it is hard to provide a good YoY growth rate which common across industries and other factors. Generally an increase in YoY Growth Rate reflects positive outlook in growth. In comparison, a decrease in YoY Growth Rate reflects negative outlook in growth.
A good Year-over-Year (YoY) growth rate number depends on the industry, company size, and market conditions. There are certain benchmarks in the industry which we can consider as a good YoY growth rate,
- Startup and High-Growth Companies – A YoY growth rate of 20-50% or more is often considered excellent. In the Technology or SaaS sectors, growth rates as high as 100%+ can be common in the early stages.
- Small to Medium Businesses (SMBs) – A healthy growth rate typically ranges from 10-20%, reflecting steady expansion without overextending resources.
- Large Corporations – Mature companies often aim for 3-10% YoY growth. Sustaining even single-digit growth at this scale is impressive given market saturation and operational complexities.
Industry Specific Averages of YoY Growth Rate
- Technology and SaaS – 15–100%, higher for startups and early-stage companies.
- Healthcare – 5–20%, influenced by innovation and aging demographics.
- Retail – 3–30%, with e-commerce on the higher end.
- Manufacturing and Industrial – 2–8%, steady growth tied to demand and innovation.
- Finance and Banking – 3–50%, with fintech showing faster growth.
- Energy and Utilities – 2–30%, renewable energy leading the higher range.
- Travel and Hospitality – 5–20%, heavily influenced by economic cycles.
- Education – 2–25%, digital education platforms driving growth.
- Real Estate – 3–10%, dependent on economic and sector-specific trends.
- Media and Entertainment – 1–30%, streaming and gaming showing robust growth.
- E-commerce – 15-30% YoY growth is strong due to online shopping’s rapid adoption.
- Manufacturing – A modest 3-5% growth reflects stable performance.
- Retail – 5-10% is typical for established players.
Importance and Usage of Year Over Year (YoY)
1. Year Over Year (YoY) method is useful to compare any metric like investment return, revenue, profit, cost, sales quantity, sales returns, machine hours, waste, and employee hours worked.
2. Company management can view how the company operations have changed over the last year by comparing the company’s performance status at the same point in the previous year (ex: compare the current year’s January month with last year’s January month statistics).
3. Company financial metrics like sales and profits change during different periods of the year because most businesses have a high-demand season and a low-demand season. Month-to-month comparison helps to analyze performance in the same month in the year.
Example: December seasonal sales of this year versus last year, to understand whether the company has improved the sales compared with last year’s Christmas season.
4. The company board can baseline the company financials using the YOY analysis. By conducting the YOY analysis of the last couple of years in a row, the company’s board can establish the baseline revenue or other financial metric to provide a target to the management team.
5. Financial investors can use the YOY analysis to foresee the returns of their investment and decide whether to proceed with the investment or not.
Difference Between Year-Over-Year, Month-Over-Month, and Quarter-Over-Quarter
Year-Over-Year (YoY)
Year-Over-Year (YoY) comparison involves analyzing data from the same period in two consecutive years. For example, comparing sales or revenue figures from January 2025 to January 2024. This method helps highlight long-term trends by accounting for seasonality, which is especially useful in industries with significant seasonal fluctuations, such as retail, tourism, or agriculture.
YoY is commonly used to assess annual growth, performance stability, and market share. It provides insights into whether a business is growing, stagnating, or declining over time. By eliminating seasonal effects, YoY comparisons give a clearer view of a company’s true performance, making it valuable for strategic planning, annual reporting, and long-term forecasting.
Month-Over-Month (MoM)
Month-Over-Month (MoM) comparison looks at performance changes from one month to the next. For instance, comparing sales figures from December 2024 to January 2025. This type of analysis focuses on short-term variations, which can help businesses quickly identify immediate improvements or declines.
MoM is ideal for monitoring the impact of recent marketing campaigns, product launches, or operational changes. It allows businesses to respond swiftly to positive or negative trends, making it a valuable tool for agile decision-making. Companies often use MoM analysis to fine-tune their strategies and address short-term issues promptly, such as adjusting inventory levels, refining marketing tactics, or optimizing pricing strategies.
Quarter-Over-Quarter (QoQ)
Quarter-Over-Quarter (QoQ) comparison analyzes performance changes between consecutive quarters. For example, comparing Q1 2025 to Q4 2024. This method offers a balance between short-term and long-term analysis, providing insights into business performance over a three-month period.
QoQ is particularly useful for assessing the impact of strategic initiatives, such as entering new markets, launching significant products, or restructuring operations. It smooths out the monthly volatility seen in MoM comparisons while still offering timely insights, making it ideal for quarterly financial reporting, investor presentations, and evaluating short to medium-term business strategies.
As a conclusion – Year-Over-Year, Month-Over-Month, and Quarter-Over-Quarter serves unique purposes in business analysis. YoY is best for understanding long-term trends and seasonal impacts, MoM focuses on short-term changes and immediate action, while QoQ provides a balanced view that helps in tracking medium-term performance with reduced volatility. Together, these methods offer a comprehensive toolkit for businesses to monitor, analyze, and respond to various performance metrics effectively, ensuring informed decision-making at every level.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1 – What is Year-Over-Year (YoY) analysis?
Year-Over-Year (YoY) analysis is a method used to compare data from one period, such as a month or quarter, to the same period in the previous year. This approach helps in identifying long-term trends and understanding performance by accounting for seasonality.
Q2 – How can YoY analysis mask seasonal variations?
While YoY analysis is designed to account for seasonality by comparing the same period across years, it can sometimes mask short-term seasonal shifts or unique events within a year. This happens because YoY analysis focuses on annual trends, which can overlook temporary fluctuations or changes in seasonal patterns that may have significant short-term impacts.
Q3 – When is YoY analysis most useful?
YoY analysis is most useful in industries with strong seasonal trends, such as retail, agriculture, and tourism. It helps businesses in these sectors understand long-term growth and performance trends without being distorted by seasonal fluctuations. By focusing on the same period each year, companies can better assess their progress and make informed strategic decisions.
Q4 – Can YoY analysis be used for all business metrics?
Yes, YoY analysis can be applied to a variety of business metrics, including revenue, profit, customer growth, and expenses. However, its effectiveness depends on the specific nature of the business and the metric being analyzed. In some cases, other methods like MoM or QoQ analysis may provide more relevant insights.
Q4 – Why is YoY analysis not practical for startup companies?
YoY analysis is often impractical for startups because they typically lack the historical data needed for meaningful comparisons. Since startups are in their early stages, they focus more on short-term metrics like Month-Over-Month (MoM) growth to quickly adapt to market changes and measure their immediate progress.
Q5 – How does YoY analysis differ from MoM and QoQ analysis?
YoY analysis compares the same period across consecutive years, which is useful for understanding long-term trends. In contrast, Month-Over-Month (MoM) analysis compares one month to the previous month, providing short-term insights. Quarter-Over-Quarter (QoQ) analysis compares one quarter to the previous quarter, offering a balance between short-term and long-term performance analysis.
Q6 – What industries benefit the most from YoY analysis?
Industries with significant seasonal patterns, such as retail, agriculture, and tourism, benefit the most from YoY analysis. It helps these industries track long-term trends and performance without being skewed by seasonal fluctuations. By using YoY analysis, businesses in these sectors can better understand their growth and make informed decisions.
Q7 – Can YoY analysis be used alongside other analysis methods?
Yes, YoY analysis can be used alongside other methods like Month-Over-Month (MoM) and Quarter-Over-Quarter (QoQ) analysis to provide a comprehensive view of business performance. Combining these methods helps businesses capture both short-term and long-term insights, allowing for more effective decision-making.
Q8 – What are some common challenges with YoY analysis?
One common challenge with YoY analysis is dealing with data anomalies, such as one-time events or economic downturns, which can distort the comparison. Additionally, businesses undergoing rapid changes may find YoY analysis less relevant, as their current operations may differ significantly from the previous year. Ensuring data accuracy and consistency over time is also crucial for meaningful YoY comparisons.
Q9 – How can businesses improve the accuracy of YoY analysis?
To improve the accuracy of YoY analysis, businesses should ensure they have consistent and reliable data collection processes. It’s also important to account for any significant changes or events that could impact the data, such as new product launches, market expansions, or external economic factors. Regularly reviewing and updating the data used for YoY comparisons can help maintain accuracy and relevance.
Q10 – Is YoY analysis suitable for all business sizes?
While YoY analysis is valuable for many businesses, its suitability depends on the availability of historical data and the nature of the industry. Larger, established companies with stable operations and seasonal trends may find YoY analysis highly beneficial. However, smaller or rapidly changing businesses, such as startups, may need to rely more on short-term analysis methods until they accumulate sufficient historical data.
Read More:
1. Year Over Year (YoY) Analysis: Guide, Calculation & Template
2. Sample Spreadsheets (Excel) for Year-Over-Year Growth Calculation