Market Structures – Overview, Features, Types, Examples
Overview of Market Structures
Market structure refers to how markets/industries are differentiated based on the nature of competition, product uniqueness, the comfort of entry and exit, the degree of mutual interdependence, and other factors. There are four types of market structures include perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and monopoly.
The concept of market structure is applicable for both economics and marketing. Market structure has an important role in decision-making. The decisions made by industry actors such as buyers and sellers differ in each market.
Features / Characteristics of Market Structure Classification
There are certain features (characteristics) of the market, which classify the market structure as perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, or monopoly. Classification of each market structures type depends on the following features (characteristics),
- The number of producers in the market.
- Degree of product differentiation.
- Buyer’s behavior in the industry.
- Seller’s behavior in the industry.
- Market share of the largest player.
Market Structure Types
Market structures are grouped into four types/categories,
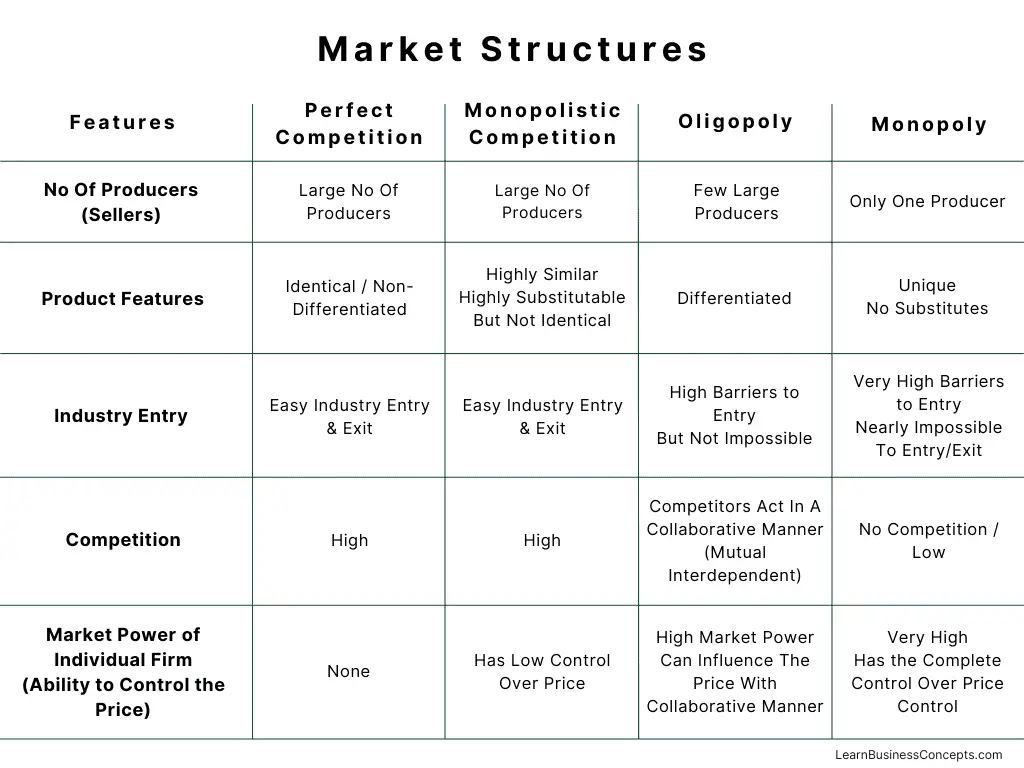
The following table presents an overview of the features/classification for each market structure,
| Features | Perfect Competition | Monopolistic Competition | Oligopoly | Monopoly |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Of Producers (Sellers) | Large No Of Producers | Large No Of Producers | Few Large Producers | Only One Producer |
| Product Features | Identical / Non-Differentiated | Highly Similar Highly Substitutable But Not Identical | Differentiated | Unique No Substitutes |
| Industry Entry | Easy Industry Entry & Exit | Easy Industry Entry & Exit | High Barriers to Entry But Not Impossible | Very High Barriers to Entry Nearly Impossible To Entry/Exit |
| Competition | High | High | Competitors Act In A Collaborative Manner (Mutual Interdependent) | No Competition / Low |
| Market Power of Individual Firm (Ability to Control the Price) | None | Has Low Control Over Price | High Market Power Can Influence The Price With Collaborative Manner | Very High Has the Complete Control Over Price Control |
1. Perfect Competition
Perfect competition is a market structure in which all companies sell identical products and any company cannot determine prices. Following are the features of perfect competition market structure,
- There is a large number of producers in the market.
- None of the firms can influence the market price of their products.
- Identical / non-differentiated products produced by every firm in the market.
- All firms are price takers.
- Product price is determined by the forces of demand and supply.
- Buyers have perfect information about the product being sold and the prices charged by each firm.
- Entry barriers for the market are very low/none.
- Seller competition is high.
- Any firm can not earn supernormal profits.
The wheat farmers’ market in the United States is a closely related real-life example of perfect competition. There is a large number of producers. Identical / non-differentiated products. The entry and exit of the market are quite easy.
Ideally, pure perfect competition is a theoretical situation that cannot possibly exist in a market. In real-world economics, perfect competition is used as a base to compare with other market structure types.
You may refer to the following articles on this website to read more about the perfect competition market structure,
Read More About Perfect Competition:
- Perfect Competition: Overview, Definition, & Features
- Perfect Competition: 8 Main Characteristics / Causes
- Perfect Competition: Advantages and Disadvantages
Crops in the United States, Pulp & Paper Manufacturing in Canada, Foreign Exchange Market in World, and Sugarcane Production in Australia are some real-world examples of Perfect Competition Market. You may refer to the below article on our website to refer to more examples and detailed information,
2. Monopolistic Competition
Monopolistic competition is a market structure in which many firms offer products that are similar substitutes. Following are the features of monopolistic competition market structure,
- There is a large number of producers in the market.
- Products are highly similar and highly substitutable. But not identical
- Entry barriers are low.
- Decisions of one firm do not directly affect competitors.
- All firms are price takers (firms have low control of the price).
- One firm’s decision does not require other companies to change their behavior.
In monopolistic competition, the firms must be able to differentiate their products from competitors to raise their prices. Firms typically attempt product differentiation to achieve supernormal profits.
Companies must continuously invest in product development and advertising. Also, they may increase the variety of their products to appeal to their target markets to achieve good profit.
You may refer to the following articles on this website to read more about monopolistic competition market structure,
Read More About Monopolistic Competition:
- Overview, Definition, & Features of Monopolistic Competition
- Main Characteristics / Causes of Monopolistic Competition
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Monopolistic Competition
Hairdresser Industry in the USA, Shoe Production Market in Canada, Fast Food Restaurants in Australia, and Bakery Shops in America are some real-world examples of Monopolistic Competition Market. You may refer to the below article on our website to refer to more examples and detailed information,
3. Oligopoly
An oligopoly is a market structure dominated by a small number of suppliers acting collaboratively. Following are the features of oligopoly market structure,
- There are a few large producers in the market.
- Firms can collaboratively influence the market price.
- Differentiated products are produced by every firm in the market.
- Firms are price setters (collaboratively).
- High entry barriers for the market.
- Firms can earn supernormal profits.
You may refer to the following articles on this website to read more about oligopoly market structure,
Read More About Oligopoly Market:
- Definition, Types, and Characteristics of Oligopoly Market
- Seven Important Characteristics of Oligopoly Market
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Oligopoly Market
In the USA, Mass Media Industry, Computer Operating Systems, and Mobile Network Operator Market are some examples of Oligopoly Markets. You may refer to the below article of our website to refer more examples and detailed information,
4. Monopoly
A monopoly is a market structure characterized by a single seller selling a unique product. Following are the features of the monopoly market structure,
- There is only one producer in the market.
- The monopoly firm has full control of the market price.
- Unique product produced by the firm. No substitutes are available.
- Very high entry barriers for the market. Nearly impossible to enter and exit.
- Competition is none.
- The firm can earn supernormal profits.
A monopoly market is contrary to a perfectly competitive market. One company owns all the market share and can control production output and prices.
Factors like license, patent, resources ownership, and very high starting cost influence the monopoly of the market. Monopoly firm has information that is not known to other sellers.
You may refer to the following articles on this website to read more about the monopoly market structure,
Read More About Monopoly:
- Definition, Examples, and Characteristics of Monopoly Market
- Important Characteristics / Causes of Monopoly Market
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Monopoly Market
Carnegie Steel, Canada Post, Standard Oil Company, and The American Tobacco Company are some examples of Monopoly Market. You may refer to the below article on our website to refer to more examples and detailed information,
Read More:
How and Why Companies Become Monopolies – Article Published By Investopedia.com
Additional Reading:
As a high school or college student, you generally have significant free time to spend. There’s no better way to spend your free time than becoming a student entrepreneur. Here are the best 24 easy-to-start business ideas for you.