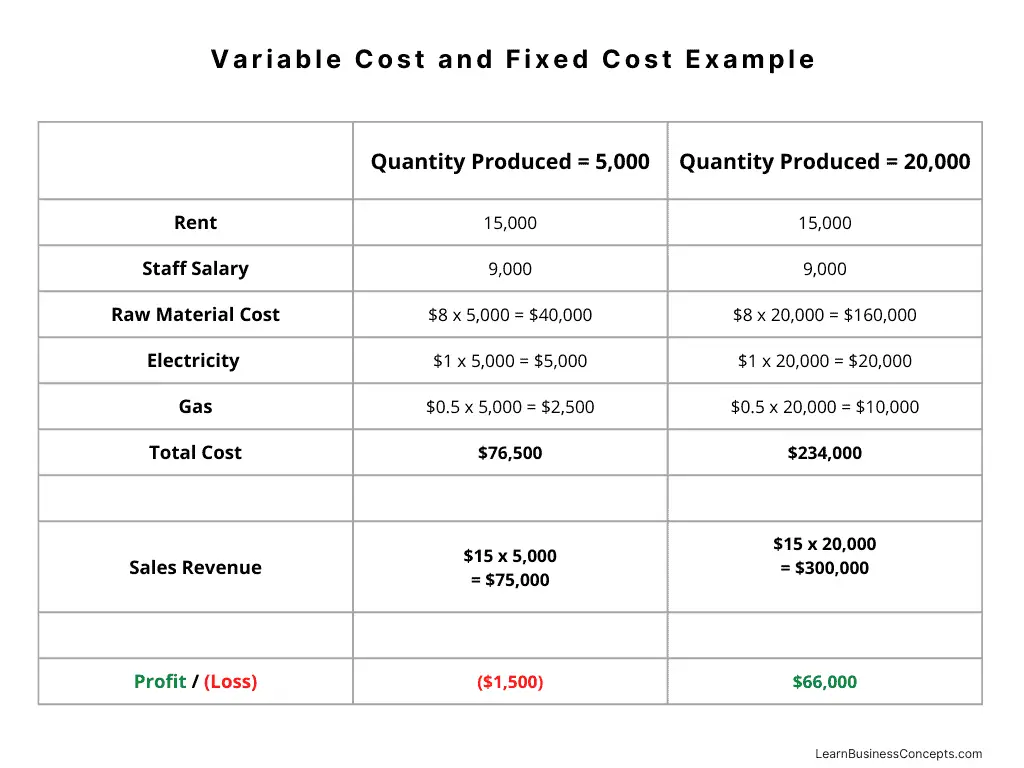
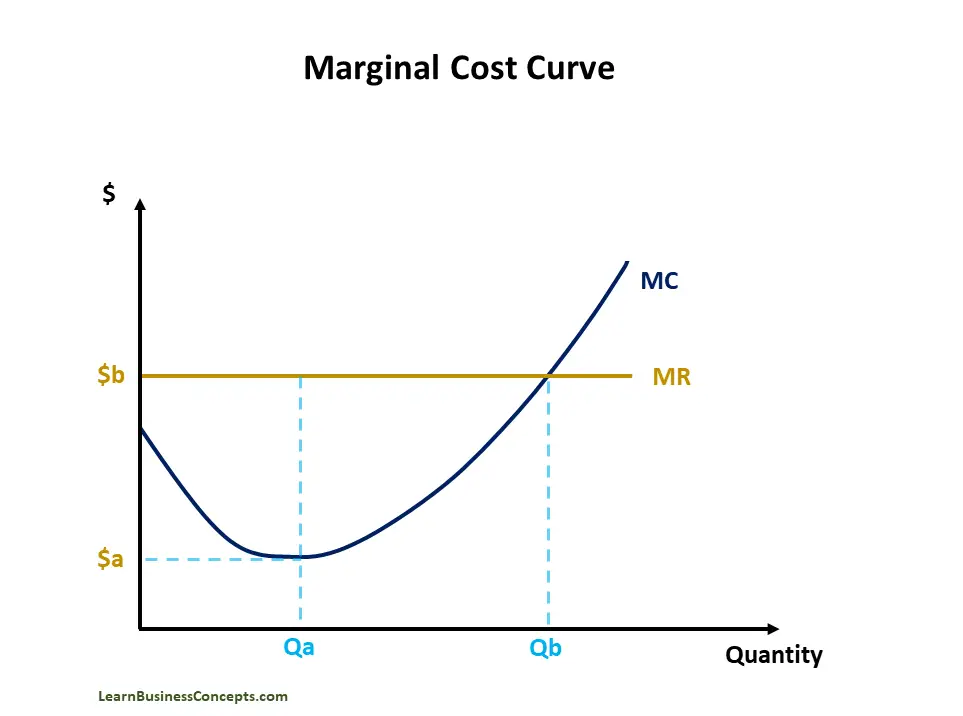
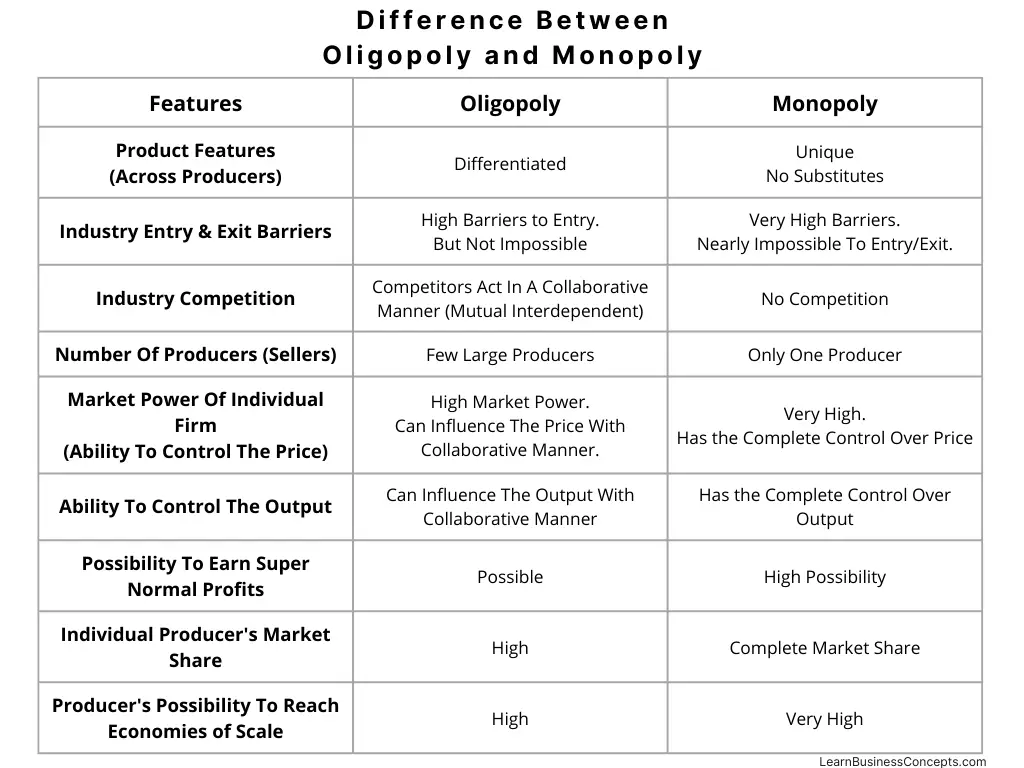
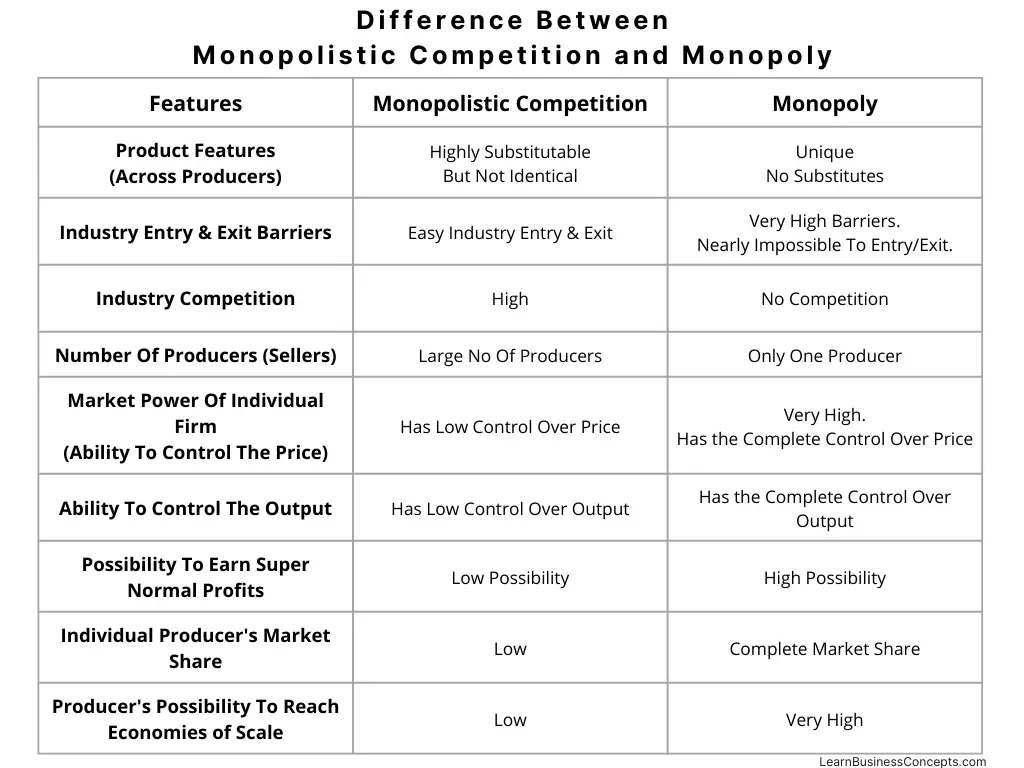
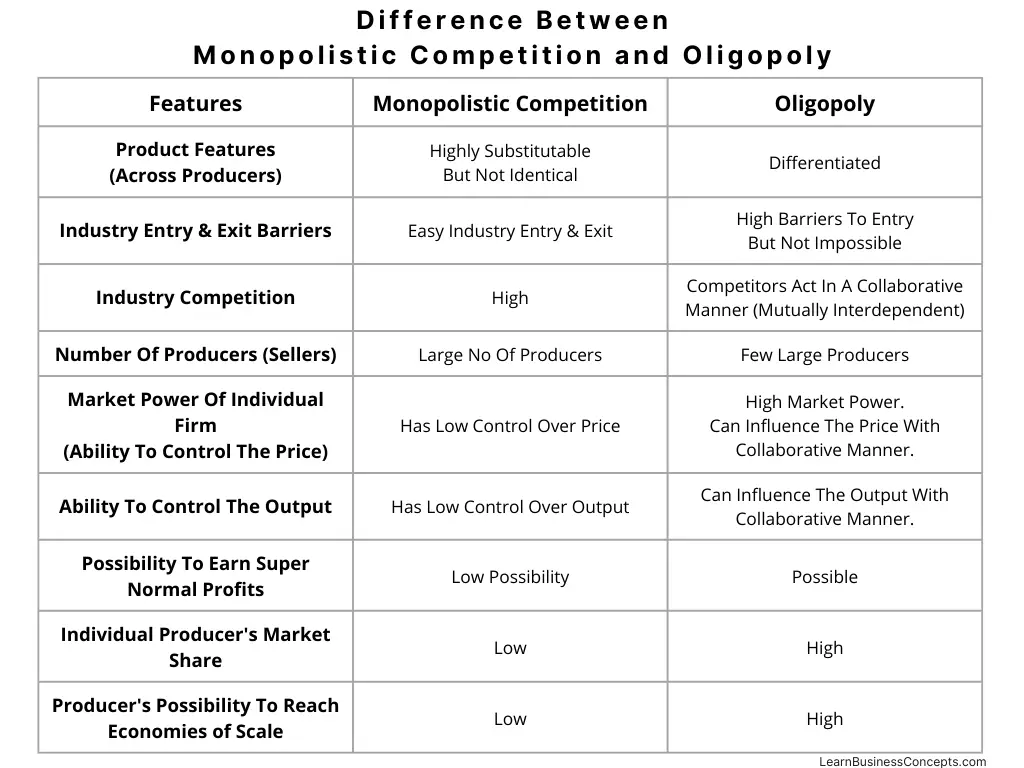
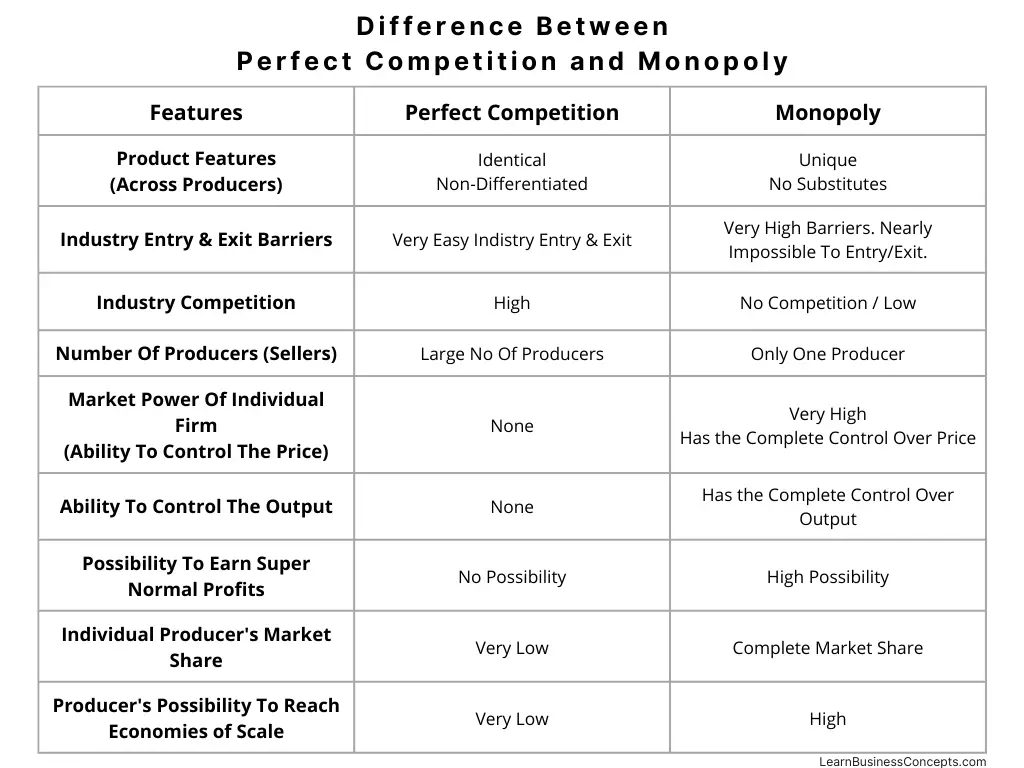
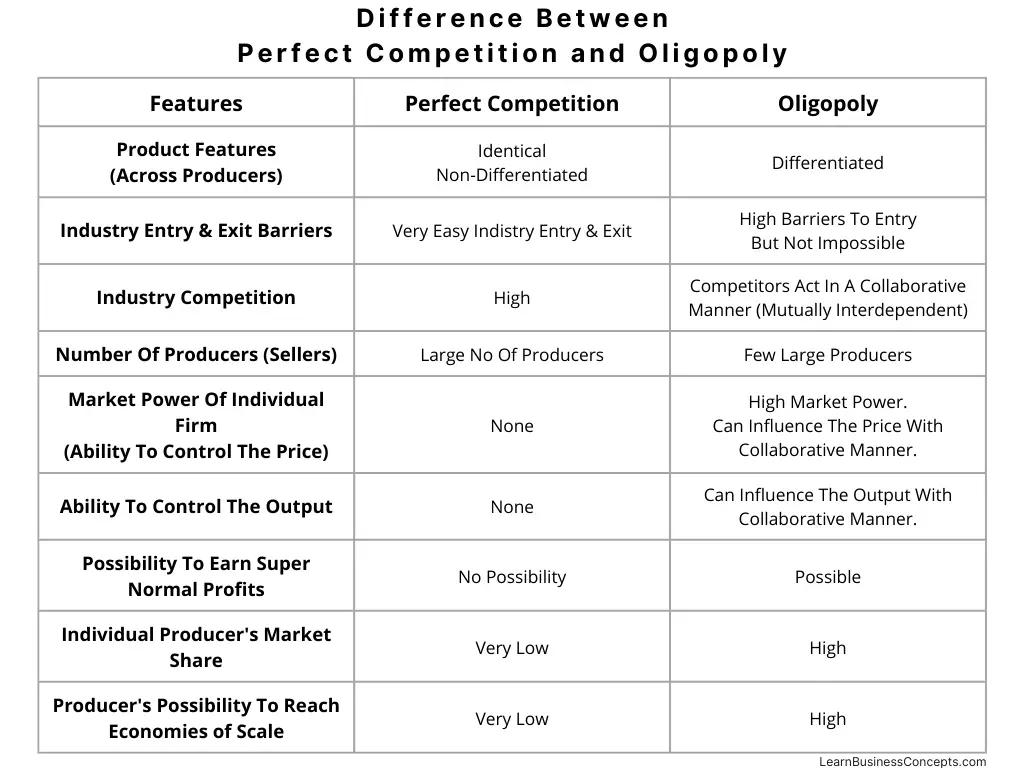
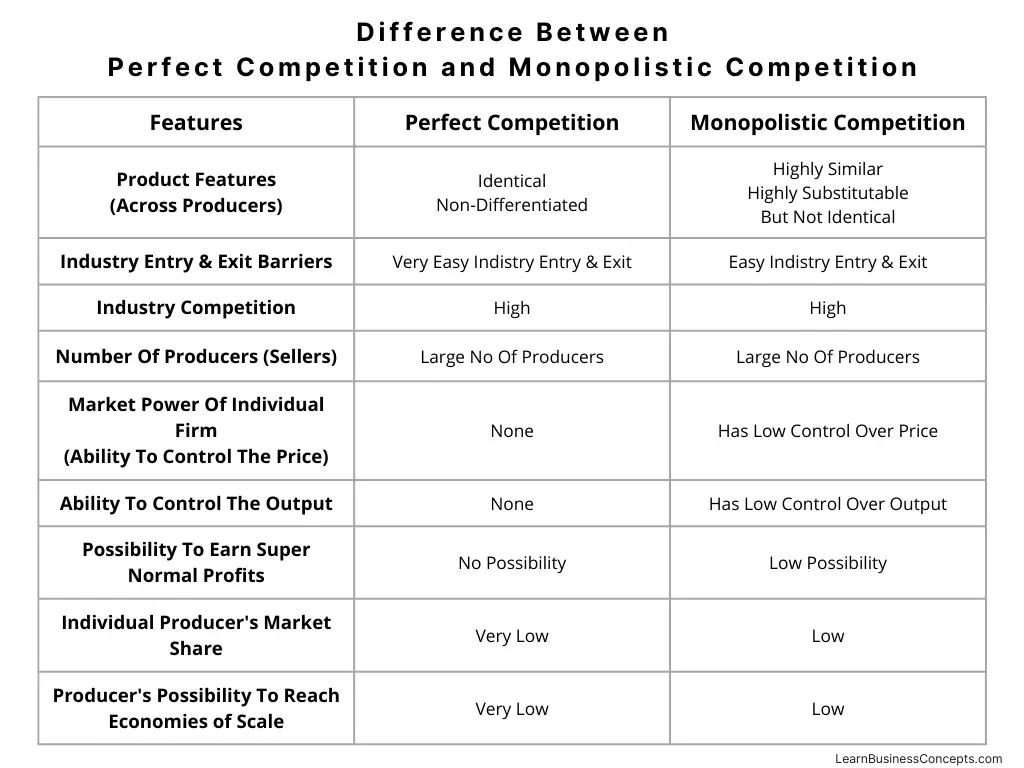
Variable Cost: Explanation, Formula, Calculation, Examples
Variable costs are expenses that the amount depending on the volume of goods or services produces. In simple terms, variable cost is changing based on the production/service output quantity/volume.