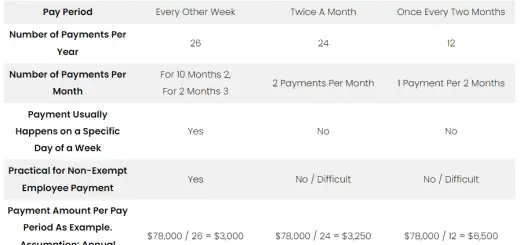
Different Ways For Banks To Make Money
Banks provide various services to the general public as well as for business enterprises. There are four different ways for banks to generate profit to make money.
1. Profit from Loan Interest
Customers make cash deposits to the Bank. Borrowers request money from the Bank as loans. Both deposits and loans are tied up with an interest component. Banks compensate the depositors with certain interest rates and banks charge borrowers with certain interest rates. Banks gain profit by lending cash to the borrowers for a higher interest rate than the deposit interest rate.
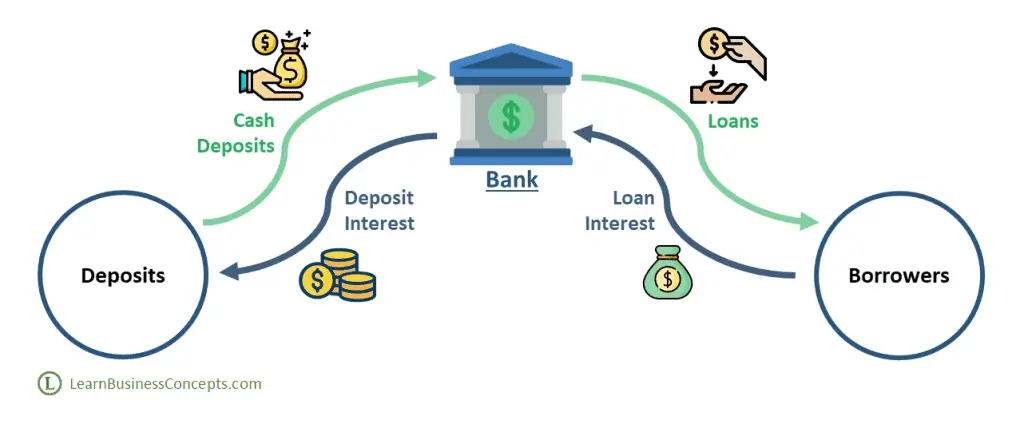
Interest related profit of the bank depends on various factors such as,
| Interest Received from Borrowers (Loan Interest) | XX,XXX.XX |
| ( – ) Interest Paid to the Depositors (Deposit Interest) | (XX,XXX.XX) |
| ( – ) Administration and Operation Cost of Loan Processing | (X,XXX.XX) |
| ( – ) Cost of Some Borrower’s Default | (X,XXX.XX) |
| Profit from Interest Income | X,XXX.XX |
Some percentage of borrowers could default even though Bank has assessed the creditworthiness of the borrowers. This will be a loss for the Bank. Banks do the risk analysis accordingly to determine the minimum interest rate which covers up the potential losses that could occur with the adequate profit.
Interest income is the primary way for most banks to earn profit. Depositors gain certain interest over their deposit and also security for their funds. Bank lends those cash at a higher interest rate. Country-wise interest rate is regulated by the central bank to promote a strong economy to control inflation. Supply and demand will also affect the interest rate.
2. Profit from Interchange
Banks gain interchange profit from processing credit and debit card transactions. Merchant has to pay an interchange charge when the cardholder uses the card in-store purchase or for online purchase. Bank charge this to provide the point of sale (POS) payment facility or online eCommerce (internet payment gateway) payment facility for their Merchants.
This interchange charge will be a profit for the Cardholder’s bank and Merchant’s bank, as per the profit-sharing agreements with the payment schemes. Cardholder’s bank will get the majority of this interchange profit from a transaction. Merchant’s bank will get a comparatively lower interchange profit from a transaction.
Imagine that you are visiting your favorite coffee shop to taste a Mocha and a Wrap. You have placed the order to the Barista and gave them your credit card for the payment of $10. Barista swipes the card in the POS (Point of Sale) device. You have left the coffee shop after spending some good time in the coffee shop.
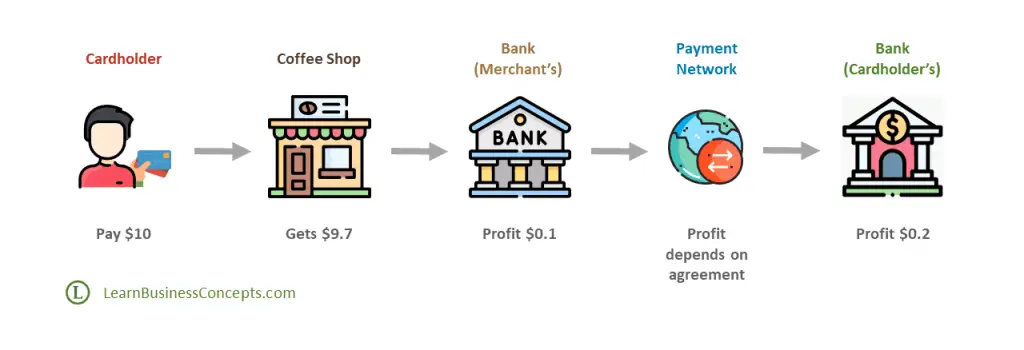
The coffee shop will not get the exact $10 settled from their Bank for this transaction. They will get around $9.7 (97% of the transaction). The bank that provides the payment services for the Merchant (the Bank to which the Merchant’s POS device is connected) will get around $0.1 profit from this transaction. The cardholder’s bank will get around $0.2 profit from this transaction. Profit-sharing percentage values depend on the agreements between Bank and the Payment Networks.
Banks gain significant profit when thousands or millions of cards based transactions are processed on daily basis.
3. Profit from Fees
Banks charge fees from the consumers for the services that are offering. A fee is charged from various services offered to the general public as well as to the business entities. Fee will be a profit for the Bank.
Following are some fees that Banks are chagrining,
Examples of Fees Charged by Banks to Cardholders
| Card Fee Name | Card Fee Description |
|---|---|
| Annual Credit Card Fee | Banks charge the annual fee for the credit card service offered to the customer |
| Finance Charge (Credit Card Interest Rate) | Banks charge interest rate if the credit card balance is carried forward beyond the grace period |
| Late Payment Fee | Banks charge a late payment fee if the credit card balance is not settled by the grace period |
| Balance Transfer Fee | Banks charge a balance transfer fee if a credit card balance is transferred to another credit card |
| Card Issuance Fees | Bank charge fees when a debit or credit card is issued to the customer |
| Card Replacement Fees | Bank charge fee to reissue a card if the customer lost their credit or debit card |
| Cash Advance Fee | Bank charge cash advance fee if a customer uses the credit card to withdraw cash |
Examples of Fees Charged by Banks to Customers in General
| Fee Name | Fee Description |
|---|---|
| Account Maintenance Fee | Banks charge fees from the account holder for maintaining the accounts |
| ATM Fees | Banks charge a fee from cardholder when using the ATM for cash withdrawal/balance check services |
| Overdraft Fees | Bank’s let the account holder process the payment for credit if adequate funds are not available. A fee will be charged by the bank for using this service |
| Minimum Balance Fees | Banks charge a fee if the account balance is lower than the minimum balance agreed |
| Insufficient Funds Fee | Banks charge a fee if a transaction initiated more than the balance available in the account |
| Excess Transactions Fee | Many banks have the maximum monthly free withdrawals the consumers can make. Banks charge fees if this is exceeded |
| Account Closing Fee | Bank charge fee on account closure |
| Penalty Charges | Banks charge a late payment penalty fee for credit cards |
| Monthly or Annual Service Fees | Banks charged monthly or annual fees for the services offered such as online banking, SMS alerts, etc. |
4. Profit from Capital Market Services
Investment banks provide capital market-related services to enterprises and investors. A capital market is a market where buyers and sellers engage in the trade of financial instruments such as bonds, stocks, etc. Following are some capital market services provided by Banks,
Mergers and Acquisition Advisory
Leading investment banks in the world do advisory services for corporate enterprises for Mergers and Acquisition activities. This is the process of assisting the enterprises to find, strategize, analyze, negotiate, finance, and complete the entire process of merger or acquisition activities of their business.
A merger is where two enterprises combined to join and move forward as one entity. An acquisition is where one enterprise buys another enterprise to expand its business. Banks charge fees for the enterprises to act as advisors on mergers and acquisitions for both buyers and sellers of businesses. This fee will be a profit for the bank.
JPMorgan Chase & Co. is an American multinational investment bank that provides Mergers and Acquisition Advisory Services for their Consumers.
https://www.jpmorgan.com/solutions/cib/investment-banking/corporate-finance-advisory
Underwriting Services
Investment banks offer underwriting services to enterprises who want to raise capital for their business or want to list their company on the stock exchange. This service helps enterprises to mitigate their risk in exchange for a premium. There are three types of most common underwriting contracts,
- Firm commitment contract: Underwriting bank guarantees the sale of the issued stock at the offering price. Underwriting banks will buy securities from the issuer company if in case of failure to sell.
- Best effort contract: Underwriting bank agrees to sell many shares at the offering price. Underwiring bank returns any unsold shares to the company.
- All-or-none: Underwriting bank agrees either to sell the entire offering or to cancel the deal
Sales and Trading Services
Many investment banks provide services for investors with ideas and opportunities to enter and exit from investments. Banks communicate information about large-scale securities to their investors, analyze investment news, develop relationships with investors, etc. Banks get a certain percentage of the total amount of money invested by clients.
PR Newswire UK Reports that Investment Banking & Trading Services Market to Reach $520.02 Bn, Globally, by 2027
https://www.prnewswire.co.uk/news-releases/investment-banking-amp-trading-services-market-to-reach-520-02-bn-globally-by-2027-at-5-8-cagr-allied-market-research-846531153.html